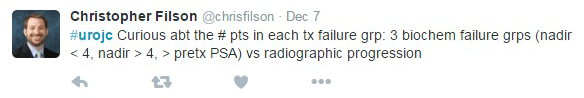The 6th BJUI Social Media Awards (2018)
It’s hard to believe that we have been doing the BJUI Social Media Awards for six years now! I recall vividly our inaugural BJUi Social Media Awards in 2013, as the burgeoning social media community in urology gathered in the back of an Irish Bar in San Diego to celebrate all things social. At that time, many of us had only got to know each other through Twitter, and it was certainly fun going around the room putting faces with twitter handles for the first time. That spirit continues today as the “uro-twitterati” continues to grow, and the BJUi Awards, remain a fun annual focus for the social-active urology community to meet up in person.
We continue to alternate the Awards between the annual congresses of the American Urological Association (AUA) and of the European Association of Urology (EAU). Last year we descended on Boston, MA, to join the 15,000 or so other delegates attending the AUA Annual Meeting and to enjoy beautiful Boston. This year, we set sail for the #EAU18 Annual Meeting in the wonderful (but very cold) city of Copenhagen, along with over 13,000 delegates from 100 different countries.
On therefore to the Awards. These took place on Sunday 18th March 2018 in the Crowne Plaza Hotel, Copenhagen. Over 50 of the most prominent uro-twitterati from all over the world turned up to enjoy the hospitality of the BJUI and to hear who would be recognised in the 2018 BJUI Social Media Awards. Individuals and organisations were recognised across 12 categories including the top gong, The BJUI Social Media Award 2018, awarded to an individual, organization, innovation or initiative who has made an outstanding contribution to social media in urology in the preceding year. The 2013 Award was won by the outstanding Urology Match portal, followed in 2014 by Dr Stacy Loeb for her outstanding individual contributions, and in 2015 by the #UroJC twitter-based journal club. In 2017 we recognised the #ilooklikeaurologist social media campaign which we continue to promote. This year our Awards Committee consisted of members of the BJUI Editorial Board – Declan Murphy, Prokar Dasgupta, Matt Bultitude, Stacy Loeb, John Davis, as well as BJUI Managing Editor Scott Millar whose team in London drive the content across our social platforms. The Committee reviewed a huge range of materials and activity before reaching their final conclusions.
The full list of winners is as follows:
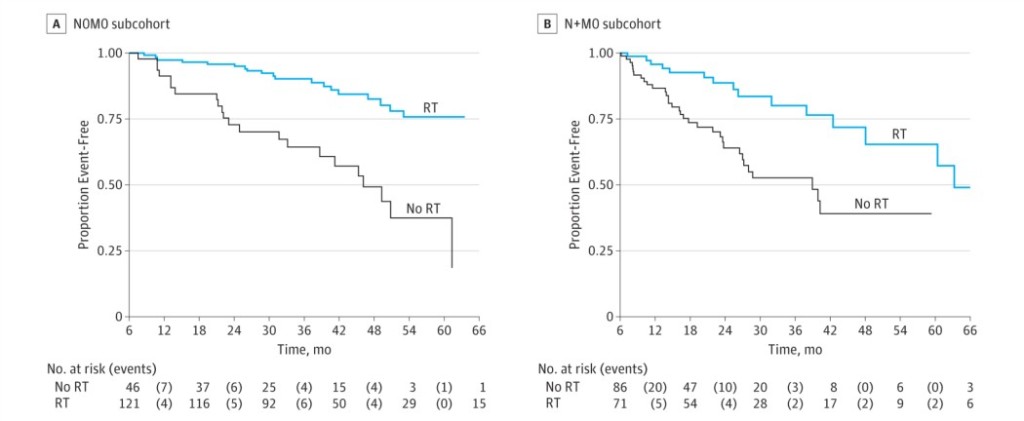
- Most Read Blog@BJUI – “Changing the LATITUDE of Treatment for High-Risk Hormone-Naïve Prostate Cancer: STAMPEDE-ing Towards Androgen Biosynthesis Inhibition”. Dr Zach Klaassen, Toronto, Canada
- Most Commented Blog@BJUI – “The Urology Foundation – Cycle to Vietnam” – Prof Roger Kirby, London, UK.
- Most Social Paper – “Unprofessional content on Facebook accounts of US urology residency graduates”. Accepted by Dr Matt Bultitude on behalf of Dr Ann Gormley and colleagues
- Best BJUI Tube Video – “The value of In-111 PSMA radioguided surgery for salvage lymphadenectomy in recurrent prostate cancer”. Dr Tobias Maurer, Munich, Germany.
- Best Urology Conference for Social Media – awarded to the EAU for #EAU17 and #EAU18. Accepted by Prof Jim Catto on behalf of the EAU Communications Department.
- Innovation Award – EAU Communications Department, for their excellent Twitter strategy. Accepted by Prof Jim Catto onbehalf of Marc van Gurp and EAU colleagues
- #UroJC Award – Dr David Penson, Vanderbilt, USA. Accepted by Matt Bultitude
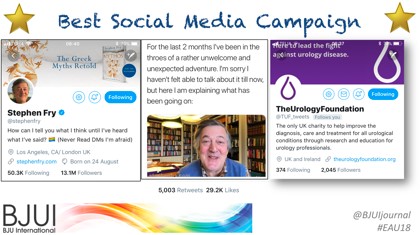
- Best Social Media Campaign – awarded to The Urology Foundation, London, UK. In recognition of their use of social media to promote their advocacy, awareness and fundraising efforts in urology. Also an acknowledgement of twitter super-user Stephen Fry as a supporter of TUF, and his use of twitter to share his recent personal prostate cancer journey.
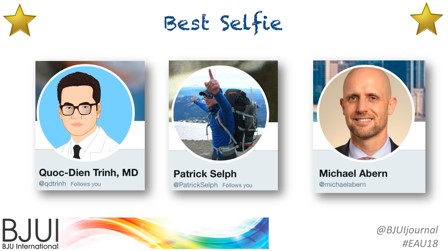
- Best #Selfie – awarded to wandering AUA/EAU Scholarship trio Quoc Trinh, Patrick Selph, and Michael Abern
- Most Social Trainee – Awarded to the “Bellclapper Podcasts”, featuring Jesse Ory, Kyle Lehman, Jeff Himmelman, from Dalhousie University, Canada.
- The BJUI Social Media Award 2018 – awarded to @BURSTurology, in recognition of their use of social media to engage with other urology trainee and research groups around the world to drive collaborative research, including the #identify project. Collected by BURST Chair Veeru Kasi.
A number of the BJUI senior editorial team were also present to join the fun!
A special thanks to our outstanding BJUI team at BJUI in London, Scott Millar, Max Cobb and team, who manage our social media and website activity as well as the day-to-day running of our busy journal.
See you all in Chicago for #AUA19 where we will present the 7th BJUI Social Media Awards ceremony!
Declan Murphy
Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre, Melbourne, Australia
Associate Editor, BJUI
@declangmurphy
































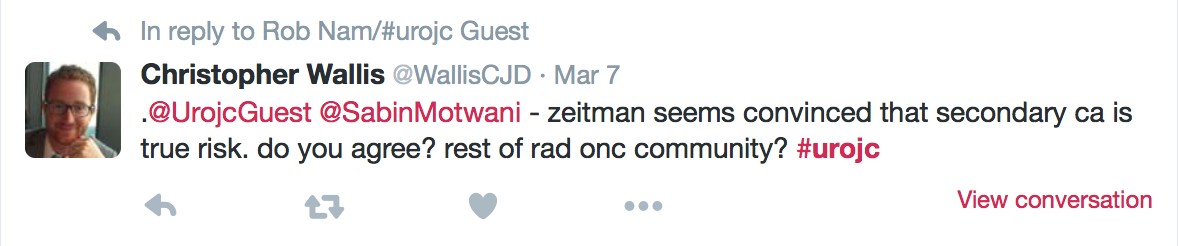
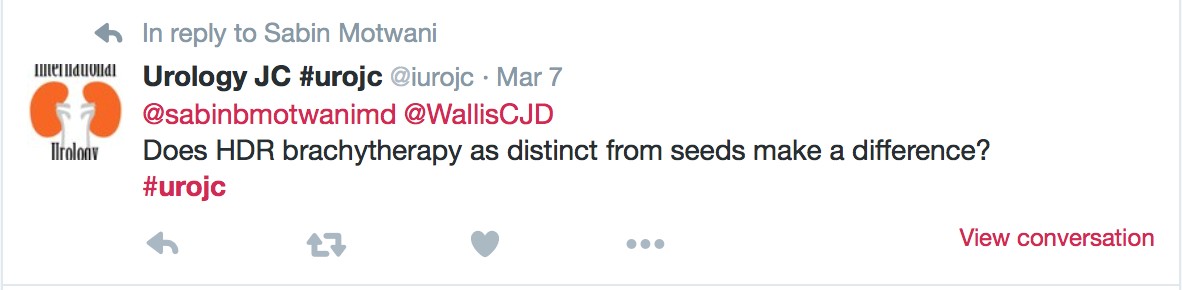
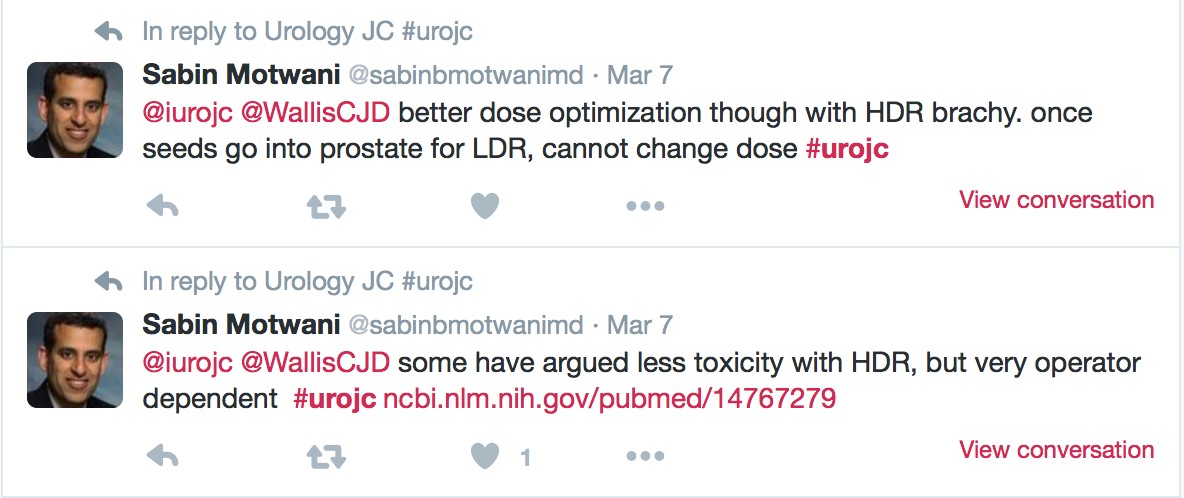
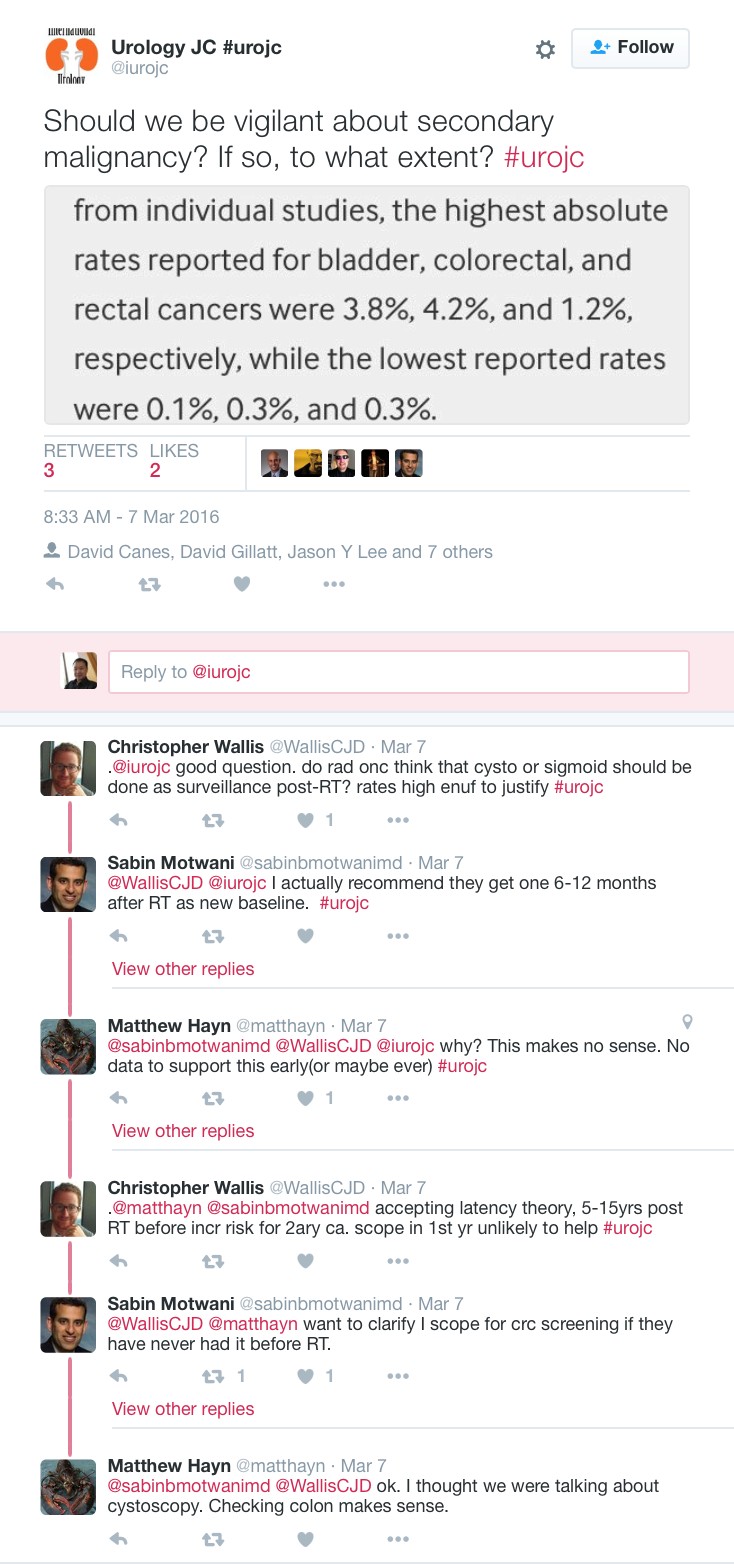
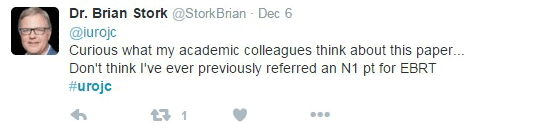
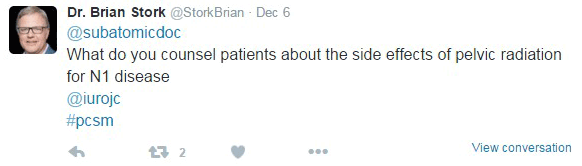
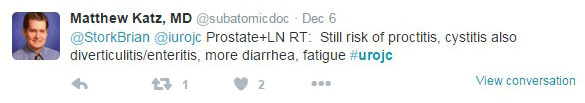
 JH population was "unique". Therapeutic benefit depends on the cohort being studied.
JH population was "unique". Therapeutic benefit depends on the cohort being studied. ) therapeutic benefit for standard PLND versus ePLND?
) therapeutic benefit for standard PLND versus ePLND?