Residents’ podcast: Urinary, bowel and sexual health in older men from Northern Ireland
Maria Uloko is a Urology Resident at the University of Minnesota Hospital and Giulia Lane is a Female Pelvic Medicine and Reconstructive Surgery Fellow at the University of Michigan.
In this podcast they discuss the following BJUI Article of the Week:
Urinary, bowel and sexual health in older men from Northern Ireland
David W. Donnelly*, Conan Donnelly†, Therese Kearney*, David Weller‡, Linda Sharp§, Amy Downing¶, Sarah Wilding¶, PennyWright¶, Paul Kind**, James W.F. Catto††, William R. Cross‡‡, Malcolm D. Mason§§, Eilis McCaughan¶¶, Richard Wagland***, Eila Watson†††, Rebecca Mottram¶, Majorie Allen¶, Hugh Butcher‡‡‡, Luke Hounsome§§§, Peter Selby¶, Dyfed Huws¶¶¶, David H. Brewster****, EmmaMcNair****, Carol Rivas††††, Johana Nayoan***, Mike Horton‡‡‡‡, Lauren Matheson†††, Adam W. Glaser¶ and Anna Gavin*
*Northern Ireland Cancer Registry, Centre for Public Health, Queen’s University Belfast, Belfast, UK, †National Cancer Registry Ireland, Cork, Ireland, ‡Centre for Population Health Sciences, University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, UK, §Institute of Health and Society, Newcastle University, Newcastle upon Tyne, UK, ¶Leeds Institute of Cancer and Pathology/Leeds Institute of Data Analytics, University of Leeds, Leeds, UK, **Institute of Health Sciences, University of Leeds, Leeds, UK, ††Academic Urology Unit, University of Sheffield, Sheffield, UK, ‡‡Department of Urology, St James’s University Hospital, Leeds, UK, §§Division of Cancer and Genetics, School of Medicine, Velindre Hospital, Cardiff University, Cardiff, UK, ¶¶Institute of Nursing and Health Research, Ulster University, Coleraine, UK, ***Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Southampton, Southampton, UK, †††Faculty of Health and Life Sciences, Oxford Brookes University, Oxford, UK, ‡‡‡Yorkshire Cancer Patient Forum, c/o Strategic Clinical Network and Senate, Yorkshire and The Humber, Harrogate, UK, §§§National Cancer Registration and Analysis Service, Public Health England, Bristol, UK, ¶¶¶Welsh Cancer Intelligence and Surveillance Unit, Cardiff, UK, ****Information Services Division, NHS National Services Scotland, Edinburgh, UK, ††††Department of Social Science, UCL Institute of Education, University College London, London, UK, and ‡‡‡‡Psychometric Laboratory for Health Sciences, Academic Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, University of Leeds, Leeds, UK
Abstract
Objectives
To provide data on the prevalence of urinary, bowel and sexual dysfunction in Northern Ireland (NI), to act as a baseline for studies of prostate cancer outcomes and to aid service provision within the general population.
Subjects and Methods
A cross‐sectional postal survey of 10 000 men aged ≥40 years in NI was conducted and age‐matched to the distribution of men living with prostate cancer. The EuroQoL five Dimensions five Levels (EQ‐5D‐5L) and 26‐item Expanded Prostate Cancer Composite (EPIC‐26) instruments were used to enable comparisons with prostate cancer outcome studies. Whilst representative of the prostate cancer survivor population, the age‐distribution of the sample differs from the general population, thus data were generalised to the NI population by excluding those aged 40–59 years and applying survey weights. Results are presented as proportions reporting problems along with mean composite scores, with differences by respondent characteristics assessed using chi‐squared tests, analysis of variance, and multivariable log‐linear regression.
Results
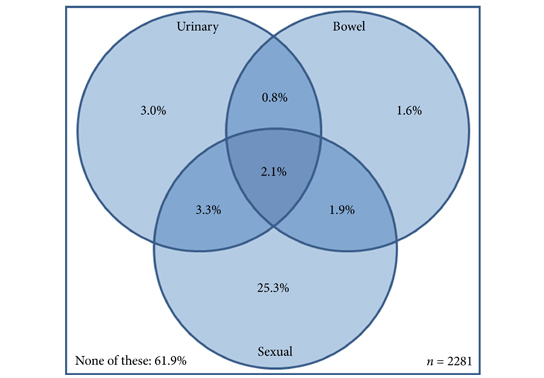
Amongst men aged ≥60 years, 32.8% reported sexual dysfunction, 9.3% urinary dysfunction, and 6.5% bowel dysfunction. In all, 38.1% reported at least one problem and 2.1% all three. Worse outcome was associated with increasing number of long‐term conditions, low physical activity, and higher body mass index (BMI). Urinary incontinence, urinary irritation/obstruction, and sexual dysfunction increased with age; whilst urinary incontinence, bowel, and sexual dysfunction were more common among the unemployed.
Conclusion
These data provide an insight into sensitive issues seldom reported by elderly men, which result in poor general health, but could be addressed given adequate service provision. The relationship between these problems, raised BMI and low physical activity offers the prospect of additional health gain by addressing public health issues such as obesity. The results provide essential contemporary population data against which outcomes for those living with prostate cancer can be compared. They will facilitate greater understanding of the true impact of specific treatments such as surgical interventions, pelvic radiation or androgen‐deprivation therapy.