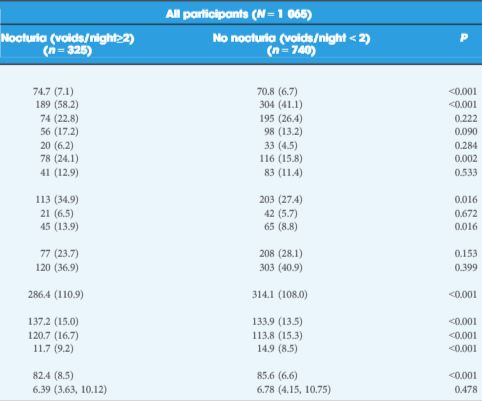
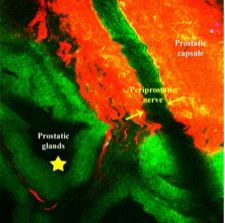
 Intraoperative in vivo tracking of a periprostatic nerve with multiphoton microscopy in rat model.
Intraoperative in vivo tracking of a periprostatic nerve with multiphoton microscopy in rat model.
In the last 6 months, the BJUI editorial team has evaluated an average of 59 urological oncology papers per month with an average acceptance rate of 16%. We receive additional papers for our ‘Translational Science’ section. Studies with high-quality methods are given the highest priority. Other papers compete well if they are highly applicable to clinical practice (i.e. comparative, multicentre, multi-surgeon design) and/or show us new ideas in surgical technique, re-designed study endpoints, or explore new sources of data. For translational science, the best candidates are studies that look at new diagnostic tests in humans and beyond simple immunostaining techniques. We want to evaluate biomarkers likely to be validated and translated into a clinical test. Clinical impact will be even higher if a biomarker is linked to a therapy outcome rather than just a risk estimate. We want our papers to guide us to better outcomes for our patients, hopefully control healthcare costs, and, yes, be well-cited in the literature.
Our review process is tough but fair, and we congratulate and highlight three authorship groups for acceptance into this month’s issue of BJUI. The theme of ‘clever surgeons and challenging study endpoints’ is well illustrated by all three groups. Zargar et al. [1] report on an exclusive database of high-volume minimally invasive surgeons who have tackled the partial nephrectomy option for small renal masses. The comparison is simple in concept and retrospective in design, but what they have done is to significantly increase the outcome measures into a ‘trifecta’ concept in perioperative outcomes (previously reported) with an even more stringent ‘optimal outcome’ endpoint that includes renal function preservation. With a database of 1185 robotic and 646 laparoscopic cases, the robotic procedures showed superior trifecta results (70% vs 33%), complication rates (14.8% vs 20.9%), positive surgical margin rates (3.2% vs 9.7%), and warm ischaemia time (18 vs 26 min). The optimal outcome endpoint included a minimum 90% estimated GFR (eGFR) preservation and no chronic kidney disease upstaging. Only the robotic cohort had sufficient data available and the rate was 38.5%. The latter figure is an interesting challenge, as defining such a high threshold for success challenges surgical technique and allows more room to identify incremental advancement. This may be the largest study of its kind, but non-randomised and with limitations discussed in peer review such as the learning curve influence, use of eGFR as an endpoint with two kidneys, and incomplete data. The definitions used are of interest and the field could use some uniformity moving forward in measuring perioperative and long-term benchmarks of quality.
Durand et al. [2] give us a glimpse into the future of surgery, a science fiction world of prostate surgery where nerves and prostatic glands can be colour coded and seen at a microscopic level in real time. The pictures stand for themselves, especially Fig. 1. If such imaging can be integrated into technique decisions, and perhaps future instrument designs, then perhaps we will have a whole new wave of studies possible on linking surgical technique to improved functional and oncological outcomes after radical prostatectomy. The paper has a nice depth in detail, methods, results, as well as narratives in solving technical problems with novel technology.
This issue’s ‘Article of the Month’ by Gavin et al. [3] is a different look at the question of morbidity after localised prostate cancer treatments, specific to long-term care at >2 years from treatment. The database is from a cancer registry and they have an impressive 54% response rate from a population that is 2–18 years from diagnosis. Rather than Likert-like scales of symptom severity, they simply look at ‘current’ vs ‘ever had’ symptoms and look at the total burden including multiple/overlapping symptoms. Although this may not be as robust and validated as the Expanded Prostate Cancer Index Composite (EPIC) instrument, the simple phrasing of ‘current’ vs ‘ever had’ is probably capturing a very high proportion of symptoms rather than dismissing them if minor or in the past. Again, we see more erectile dysfunction after radical prostatectomy and radiation with hormonal therapy, and more bowel symptoms after radiation therapy. Hormone therapy patients have hot flashes and fatigue, and watchful-waiting patients have some advantages but are certainly not free of symptoms. The burden of symptoms is interesting, nine of 10 reported at least one of seven key symptoms at some point and three of four are current. Therefore, as the authors indicate, ≈75% of prostate cancer survivors will have ongoing symptoms needing follow-up care. This is a significant database resource adding to our understanding of long-term outcomes of patients with prostate cancer and supporting the significance of the Durand et al. [2] study that may show the way forward towards reducing such burdens of disease treatment.
References
John W. Davis, MD
Associate Editor, BJUI