Article of the Week: NSS Across a Nation
Every Week the Editor-in-Chief selects an Article of the Week from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
In addition to the article itself, there is an accompanying editorial written by a prominent member of the urological community. This blog is intended to provoke comment and discussion and we invite you to use the comment tools at the bottom of each post to join the conversation.
Finally, the third post under the Article of the Week heading on the homepage will consist of additional material or media. This week we feature a video from Archie Fernando and Tim O’Brien, discussing their paper.
If you only have time to read one article this week, it should be this one.
Nephron-sparing surgery across a nation – outcomes from the British Association of Urological Surgeons 2012 national partial nephrectomy audit
Objective
To determine the scope and outcomes of nephron-sparing surgery (NSS), i.e. partial nephrectomy, across the UK and in so doing set a realistic benchmark and identify fresh contemporary challenges in NSS.
Patients and Methods
In 2012 reporting of outcomes of all types of nephrectomy became mandatory in the UK. In all, 148 surgeons in 86 centres prospectively entered data on 6 042 nephrectomies undertaken in 2012. This study is a retrospective analysis of the NSS procedures in the dataset.
Results
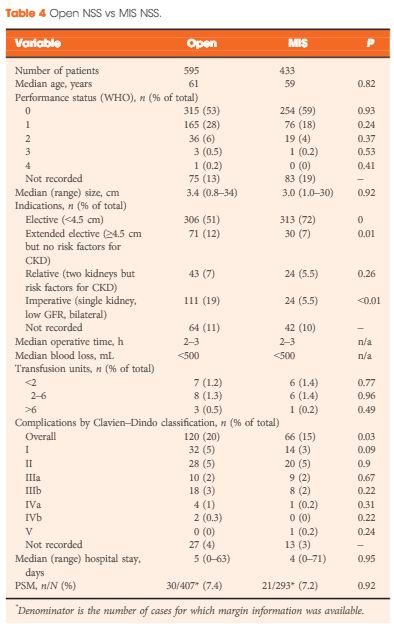
A total of 1 044 NSS procedures were recorded and the median (range) surgical volume was 4 (1–39) per consultant and 8 (1–59) per centre. In all, 36 surgeons and 10 centres reported on only one NSS. The indications for NSS were: elective with a tumour of ≤4.5 cm in 59%, elective with a tumour of >4.5 cm in 10%, relative in 7%, imperative in 12%, Von Hippel–Lindau in 1%, and unknown in 11%. The median (range) tumour size was 3.4 (0.8–30) cm. The technique used was minimally invasive surgery in 42%, open in 58%, with conversions in 4%. The histology results were: malignant in 80%, benign in 18%, and unknown in 2%. In patients aged <40 years 36% (36/101) had benign histology vs 17% (151/874) of those aged ≥40 years (P < 0.01). In patients with tumours of <2.5 cm 29% (69/238) had benign histology vs 14% (57/410) with tumours of 2.5–4 cm vs 8% (16/194) with tumours of ≥4 cm (P = 0.02). In patients aged <40 years with of tumours of <2.5 cm 44% (15/34) were benign. The 30-day mortality was 0.1% (1/1 044). There were major complications (Clavien–Dindo grade of ≥IIIa) in 5% (53/1 044). There was an increased risk of complications after extended elective NSS of 19% (19/101) vs elective at 12% (76/621) (relative risk [RR] 1.54; P < 0.01). Margins were recorded in 68% (709/1 044) of the patients, with positive margins identified in 7% (51/709). Positive surgical margins after NSS for pathological T3 (pT3) tumours were found in 47.8% (11/23) vs 6.1% (32/523) for pT1a, tumours (RR 5.61; P < 0.01). In all, 14% (894/6 042) of the patients underwent surgery for T1a tumours: 55% (488/894) by NSS, 42% (377/894) by radical nephrectomy (RN), and in 3% (29/894) the procedure used was unknown. Major complications after occurred in 4.9% (24/488) of NSS vs 1.3% (5/377) of RN (P < 0.01). Limitations included poor reporting of renal function data and no data on tumour complexity.
Conclusions
In its first year, mandatory national reporting has provided several challenging contemporary insights into NSS.