Article of the Week: Predicting complications in partial nephrectomy for T1a tumours: does approach matter?
Every Week the Editor-in-Chief selects an Article of the Week from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
In addition to the article itself, there is an accompanying editorial written by a prominent member of the urological community. This blog is intended to provoke comment and discussion and we invite you to use the comment tools at the bottom of each post to join the conversation.
If you only have time to read one article this week, it should be this one.
Predicting complications in partial nephrectomy for T1a tumours: does approach matter?
Objectives
To assess differences in complications after robot-assisted (RAPN) and open partial nephrectomy (OPN) among experienced surgeons.
Patients and Methods
We identified patients in our institutional review board-approved, prospectively maintained database who underwent OPN or RAPN for management of unifocal, T1a renal tumours at our institution between January 2011 and August 2015. The primary outcome measure was the rate of 30-day overall postoperative complications. Baseline patient factors, tumour characteristics and peri-operative factors, including approach, were evaluated to assess the risk of complications.
Results
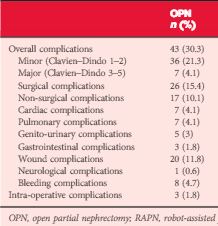
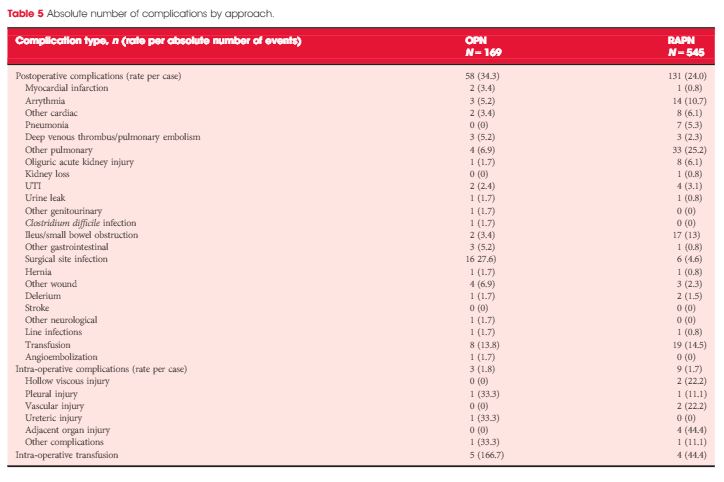
Patients who underwent OPN were found to have a higher rate of overall complications (30.3% vs 18.2%; P = 0.038), with wound complications accounting for the majority of these events (11.8% vs 1.8%; P < 0.001). Multivariable logistic regression analysis showed the open approach to be an independent predictor of overall complications (odds ratio 1.58, 95% confidence interval 1.03–2.43; P = 0.035). Major limitations of the study include its retrospective design and potential lack of generalizability.
Conclusions
The open surgical approach predicts a higher rate of overall complications after partial nephrectomy for unifocal, T1a renal tumours. For experienced surgeons, the morbidity associated with nephron-sparing surgery may be incrementally improved using the robot-assisted approach.