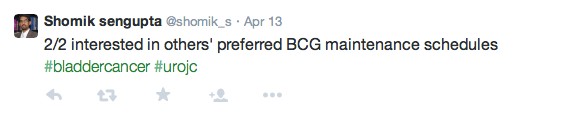The Surgical Safety Check List – May #urojc
Ever since the World Health Organisation launched the Safe Surgery Saves Lives campaign in 2007, surgical safety has been drawn to the forefront of the daily surgical routine. The introduction of the 19-point Surgical Safety Checklist, aimed at reducing preventable complications, has become key, with shouts of ‘time-out’ or ‘checklist’ becoming the norm at the start of each case. Equally whether known as the ‘huddle’ or ‘team brief’, the meeting of all team members at the beginning of the list not only helps plan for any changes from the normal routine, but gives a good chance to get to know any new members of staff and helps to promote the team-based atmosphere that encompasses a productive operating list. In the 2009 study evaluating the benefits of the Surgical Safety Checklist, a reduction in both the mortality rate and rate of inpatient complications were found to be significantly reduced1. Implementation of these safety protocols however requires effort and engagement from all members of the theatre team.
In the May, the International Urology Journal Club (@iurojc) #urojc debated a study by Haynes et al in which the reduction of 30-day mortality following the implementation of a voluntary, checklist-based surgical quality improvement program2. The study identified that hospitals completing the program had a significantly lower rate of 30-day mortality following inpatient surgery.
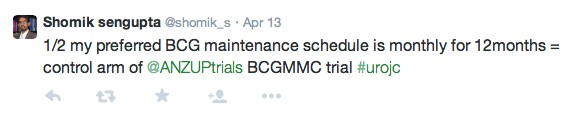
One of the first topics brought up in the debate is the variability in the implementation of safety checklists.
@StorkBrian raised the possibility that due to the addition of more items at the surgical time out, effectiveness decreases. Whether there is a lack of ability to concentrate on too much paper work was discussed
Speaking only for myself, and after signing numerous pre operative forms, think we do…@iurojc #urojc
— Dr. Brian Stork (@StorkBrian) May 7, 2017
Surgical checklists seem intuitively useful. But conflicting evidence – https://t.co/l8e53xfgNp. Why the disconnect? Ceiling effect? #urojc
— Christopher Wallis (@WallisCJD) May 7, 2017
The different outcomes from the two studies may however be attributed to the difference in follow up period and study design.
Another aspect of study design discussed was the inclusion criteria – which excluded day case procedures. Whether the outcome in 30-day mortality would be different if these are included, as they are more likely to be lower-risk surgery, is unclear.
Inclusion criteria were 'inpatient' surgical cases. Potential bias by removal of high volume rapid turnover day only procedures?#urojc
— Henry Woo (@DrHWoo) May 7, 2017
Equally whether 30-day mortality is the most appropriate endpoint for the study was questioned – although clearly very important, it would be interesting to know if other factors, such as significant morbidity, altered following the quality improvement program.
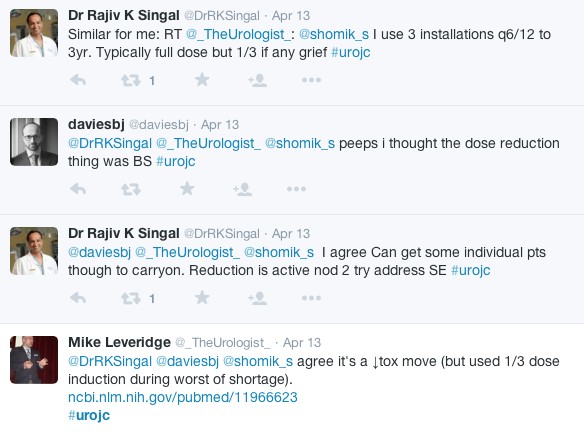
Although the surgical checklist has become part of our daily life, the question as to why they are important was raised by @CanesDavid, with a variety of responses.
Why do you all believe (or not) in time-outs? I do it for reasons other than mortality. #urojc
— 𝙳𝚊𝚟𝚒𝚍 𝙲𝚊𝚗𝚎𝚜 (@CanesDavid) May 8, 2017
For many, it seemed that alongside the safety promotion, it helps to promote cohesive teamwork and communication, which may give all team members the confidence to voice any concerns.
Giving all team members the ability to speak up with confidence if they identify any concerns will only benefit patients and staff.
Attended a CRM lecture yesterday: in wrong site surgery 80% time at least 1 person sees error but fails to change course of action #urojc
— Dag Gullan (@Dukendude) May 9, 2017
Equally, the culture of safety promoted in teams who engage with the surgical checklist process may not be limited to the checklist itself, but to the surgical environment in general
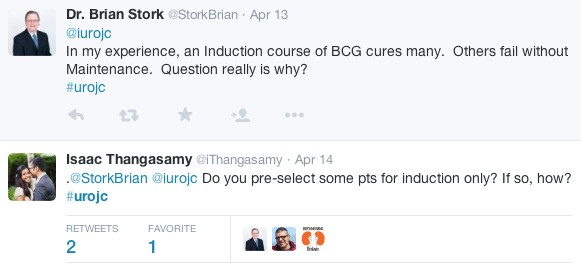
One clear concern some have with the mandating of the surgical checklist is ensuring it does not just become a ‘tick-box’ exercise
Regardless of whether you find the checklist another form to fill, or a key part of your operating list, the goal of the process is clear: to protect our patients from preventable mistakes.
Also, if it saves me from wrong side surgery even once, participation a million times will have been worth the effort #urojc
— 𝙳𝚊𝚟𝚒𝚍 𝙲𝚊𝚗𝚎𝚜 (@CanesDavid) May 8, 2017
This study, confirming the original findings from the 2009 study that surgical safety checklists improve operative mortality, adds to the argument that this must become an inherent part of our practice. Key in this study however was the entire program promoting engagement in the concept of surgical safety, and supporting the team as a unit in this. The debate around this paper has highlighted that although the process of completing the mandatory checklists is important, perhaps the more important aspect is creating a culture of safety, openness and honest communication in which all team members can work together to promote safe surgery.
Sophia Cashman is a urology trainee working in the East of England region, UK. Her main areas of interest are female and functional urology. @soph_cash
References
1. Haynes AB, Weiser TG, Berry WR, et al. A Surgical Safety Checklist to Reduce Morbidity and Mortality in a Global Population. New England Journal of Medicine 2009;360(5):491-9
2. Haynes AB, Edmondson LBA, Lipsitz SR, et al. Mortality Trends After a Voluntary Checklist-based Surgical Safety Collaborative. Annals of Surgery 2017. Published Ahead-of-Print
3. Urbach DR, Govindarajan A, Saskin R, et al. Introduction of Surgical Safety Checklists in Ontario, Canada. New England Journal of Medicine 2014;370(11):1029-1038