Article of the week: A national study of artificial urinary sphincter and male sling implantation after radical prostatectomy in England
Every week, the Editor-in-Chief selects an Article of the Week from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
In addition to this post, there is an editorial written by a prominent member of the urological community. Please use the comment buttons below to join the conversation.
If you only have time to read one article this week, we recommend this one.
A national study of artificial urinary sphincter and male sling implantation after radical prostatectomy in England
Amandeep Dosanjh*†, Simon Baldwin*, Jemma Mytton*†, Dominic King†, Nigel Trudgill†, Mohammed Belal‡ and Prashant Patel†
*Department of Health Informatics, University Hospitals Birmingham NHS Foundation Trust, Birmingham, UK , †Institute of Cancer and Genomic Sciences, University of Birmingham, Birmingham, UK and ‡Department of Urology, University Hospitals Birmingham NHS Foundation Trust, Birmingham, UK
Abstract
Objectives
To consider the provision of post‐radical prostatectomy (RP) continence surgery in England.
Materials and Methods
Patients with an Office of Population Census and Surveys Classification of Interventions and Procedures, version 4 code for an artificial urinary sphincter (AUS) or male sling between 1 January 2010 and 31 March 2018 were searched for within the Hospital Episode Statistics (HES) dataset. Those without previous RP were excluded. Multivariable logistic regressions for repeat AUS and sling procedures were built in stata. Further descriptive analysis of provision of procedures was performed.
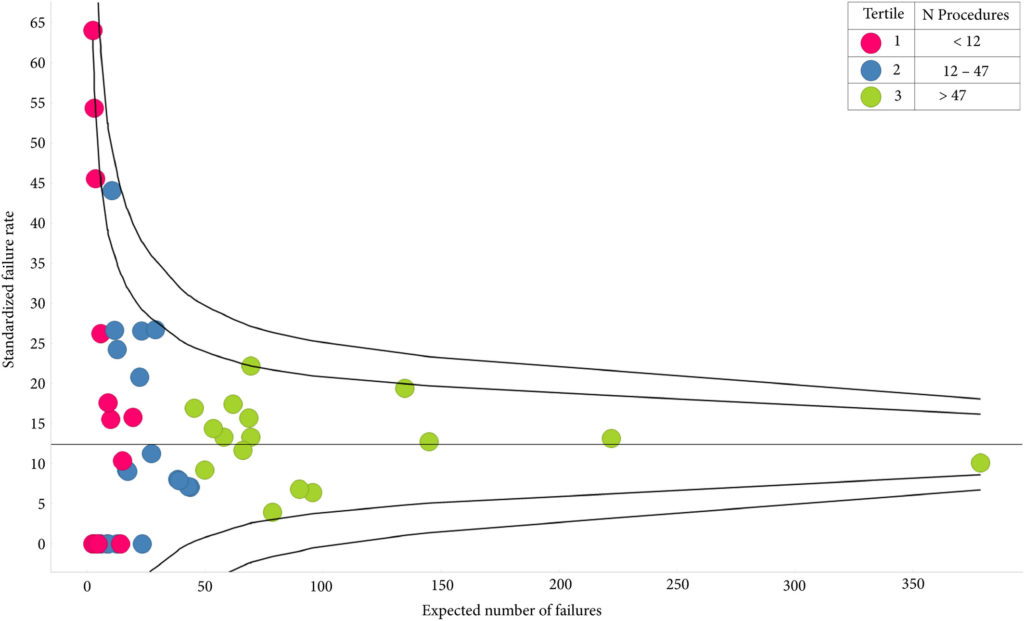
Results
A total of 1414 patients had received index AUS, 10.3% of whom had undergone prior radiotherapy; their median follow‐up was 3.55 years. The sling cohort contained 816 patients; 6.7% of these had received prior radiotherapy and the median follow‐up was 3.23 years. Whilst the number of AUS devices implanted had increased each year, male slings peaked in 2014/2015. AUS redo/removal was performed in 11.2% of patients. Patients in low‐volume centres were more likely to require redo/removal (odds ratio [OR] 2.23 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.02–4.86; P = 0.045). A total of 12.0% patients with a sling progressed to AUS implantation and 1.3% had a second sling. Patients with previous radiotherapy were more likely to require a second operation (OR 2.03 95% CI 1.01–4.06; P = 0.046). Emergency re‐admissions within 30 days of index operation were 3.9% and 3.6% fewer in high‐volume centres, for AUS and slings respectively. The median time to initial continence surgery from RP was 2.8 years. Increased time from RP conferred no reduced risk of redo surgery for either procedure.
Conclusion
There is a volume effect for outcomes of AUS procedures, suggesting that they should only be performed in high‐volume centres. Given the known impact of incontinence on quality of life, patients should be referred sooner for post‐prostatectomy continence surgery.