Posts
Article of the week: RS‐RARP vs standard RARP: it’s time for critical appraisal
Every week, the Editor-in-Chief selects an Article of the Week from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
In addition to the article itself, there are two accompanying editorials written by prominent members of the urological community. These are intended to provoke comment and discussion and we invite you to use the comment tools at the bottom of each post to join the conversation. There is also a podcast by one of our Resident Podcasters describing the article.
If you only have time to read one article this week, it should be this one.
Retzius‐sparing robot‐assisted radical prostatectomy (RS‐RARP) vs standard RARP: it’s time for critical appraisal
Thomas Stonier*, Nick Simson*, John Davis† and Ben Challacombe‡
*Department of Urology, Princess Alexandra Hospital, Harlow, ‡Urology Centre, Guy ’s Hospital, London, UK and †Department of Urology, MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX, USA
Since robot‐assisted radical prostatectomy (RARP) started to be regularly performed in 2001, the procedure has typically followed the original retropubic approach, with incremental technical improvements in an attempt to improve outcomes. These include the running Van‐Velthoven anastomosis, posterior reconstruction or ‘Rocco stitch’, and cold ligation of the Santorini plexus/dorsal vein to maximise urethral length. In 2010, Bocciardi’s team in Milan proposed a novel posterior or ‘Retzius‐sparing’ RARP (RS‐RARP), mirroring the classic open perineal approach. This allows avoidance of supporting structures, such as the puboprostatic ligaments, endopelvic fascia, and Santorini plexus, preserving the normal anatomy as much as possible and limiting damage that may contribute to improved postoperative continence and erectile function. There has been much heralding of the excellent functional outcomes in both the medical and the lay press, but as yet no focus or real mention of any potential downsides of this new technique.
Editorial: Retzius‐sparing robot‐assisted radical prostatectomy
In their commentary in the current issue of BJUI, Stonier et al. [1] examine the potential technical pitfalls and published results of the Retzius‐sparing technique of robotic radical prostatectomy. The authors reviewed three studies from three different groups [2,3], including a study by our group [4], and raised three specific concerns: the oncological efficacy of the procedure; the long learning curve; and the generalizability of the technique to challenging surgical scenarios. We offer a few clarifications and comments.
The first study on Retzius‐sparing robot‐assisted radical prostatectomy came from the Bocciardi group [2]. This was a prospective, single‐arm study of 200 patients. The authors reported a 14‐day continence rate of 90–92%, a 1‐year potency rate of 71–81% (in preoperatively potent patients undergoing bilateral intrafascial nerve‐sparing) and a positive surgical margin rate of 25.5%. The positive surgical margin rate improved in patients with pT2 disease, from 22% to 9% (P = 0.04) over the course of the study (initial 100 vs subsequent 100 patients), while in patients with pT3 disease, it remained stable at ~45%. Lim et al. [3] also noted an improvement in their overall positive surgical margin rate from 20% to 8% when comparing the initial 25 patients with the subsequent 25 patients. In that study, a standard robot‐assisted radical prostatectomy comparator arm was included and there were no differences in overall positive surgical margin rates (14% in both arms), while continence was better with the Retzius‐sparing approach.
Recognizing the potentially technically challenging nature of the Bocciardi approach, we performed a randomized controlled trial to objectively evaluate the technique. Randomized controlled trials are typically designed to answer a single question. Our trial was designed to determine whether there were differences in the rate of return of urinary continence, the primary benefit that previous non‐controlled studies had reported. This our study clearly showed [4].
Once the trial was completed, post hoc analysis of secondary outcomes was performed [5]. One of these outcomes was the positive surgical margin rate. In our trial, we noted an overall positive surgical margin rate of 25% in the Retzius‐sparing arm vs 13% in the control arm, a difference that did not achieve statistical significance (P = 0.11). Stonier et al. [1] suggested that if the sample size of our trial were doubled, then the positive surgical margin rate in each group would be doubled as well, leading to significance. This conclusion is problematic. The likelihood that doubling the sample size would result in the exact doubling of numbers in all four cells of a 2 × 2 contingency table is estimated at <5% using Fisher’s exact test (this calculation is different from the P value). Furthermore, the surgical margins depend as much on the pathological stage as on surgical approach. In our trial, patients were matched preoperatively for risk in the best manner possible for a pragmatic randomized trial. However, it is impossible to predict and control for the final pathological characteristics. Pathological analysis showed that patients undergoing Retzius‐sparing surgery did have significantly more aggressive disease: ≥pT3 disease in 45% vs 23.3% of patients (P = 0.04) [4, 5]. This, by itself, could account for a substantial difference in surgical margin rates.
In writing our paper, we made no judgements as to whether the Bocciardi or posterior technique is fundamentally superior to an anterior or Menon approach, whether it is easier to perform, how generalizable it is [6], or what the learning curve may be. That is best left to the individual surgeon’s training and judgement. We do suggest, however, that surgical margins be interpreted as a function of pathological variables, and not in isolation, and that it is simplistic to assume that identical results will be obtained by doubling sample size. We suggest that such conclusions are hypothesis‐generating, and should best be explored through a separate, purpose‐designed randomized trial.
Authors: Akshay Sood, Firas Abdollah and Mani Menon
References
- Stonier T, Simson N, Davis J, Challacombe B. Retzius‐sparing robot‐assisted radical prostatectomy (RS‐RARP) vs standard RARP: it’s time for critical appraisal. BJU Int 2019; 123: 5–10
- Galfano A, Di Trapani D, Sozzi F et al. Beyond the learning curve of the Retzius‐sparing approach for robot‐assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: oncologic and functional results of the first 200 patients with >/= 1 year of follow‐up. Eur Urol 2013; 64: 974–80
- Lim SK, Kim KH, Shin TY et al. Retzius‐sparing robot‐assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: combining the best of retropubic and perineal approaches. BJU Int 2014; 114: 236–44
- Dalela D, Jeong W, Prasad MA et al. A pragmatic randomized controlled trial examining the impact of the Retzius‐sparing approach on early urinary continence recovery after robot‐assisted radical prostatectomy. Eur Urol 2017; 72: 677–85
- Menon M, Dalela D, Jamil M et al. Functional recovery, oncologic outcomes and postoperative complications after robot‐assisted radical prostatectomy: an evidence‐based analysis comparing the Retzius sparing and standard approaches. J Urol 2018; 199: 1210–7
- Galfano A, Secco S, Bocciardi AM. Will Retzius‐sparing prostatectomy be the future of prostate cancer surgery? Eur Urol 2017; 72: 686–8
Editorial: Reply: RS-RARP vs standard RARP
Since the introduction of robotic surgery in the treatment of patients with prostate cancer (PCa), different surgical innovations have been implemented in order to preserve postoperative functional outcomes while maintaining oncological safety. Sparing the Retzius space during robot‐assisted radical prostatectomy (RARP) was introduced early this decade by Galfano et al [1]. Interestingly, 90% and 96% of patients treated with Retzius‐sparing RARP (RS‐RARP) were continent (no pad/safety pad) at 1 week and 1 year, respectively. Similarly, our group reported a 70% continence rate (no pad) at 1 month after RS‐RARP [2].
The fast urinary continence recovery after RS‐RARP is related to several anatomical factors: the anterior Retzius space is kept intact; the urinary bladder is not dropped; the endopelvic fascia and puboprostatic ligaments are preserved; and there is minimal distortion of the supporting urethral tissues. A recent study reported [3] that less bladder neck descent was observed during postoperative cystogram in patients treated with RS‐RARP than in those treated with standard RARP.
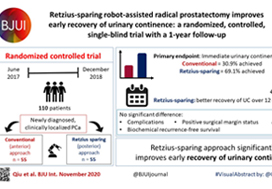
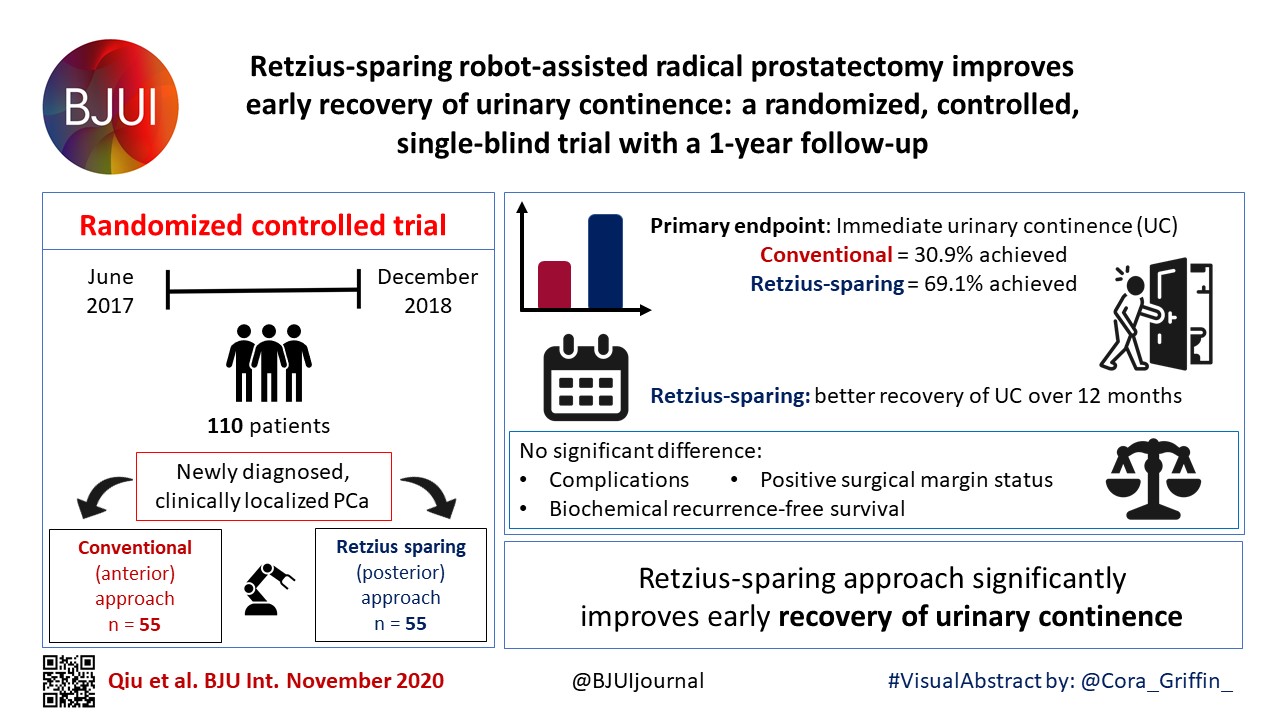
In a recent randomized controlled study, the postoperative continence rate at 1 week was 48% in standard RARP compared with 71% in RS‐RARP (P = 0.01), and this difference was maintained at 3 months (86% standard RARP vs 95% RS‐RARP; P = 0.02). At 1 year, however, the effect on urinary continence difference was muted (93.3% standard RARP vs 98.3% RS‐RARP; P = 0.09) [4]. Similarly, Chang et al. [3] found that the higher continence rate at 1 week (73.3% RS‐RARP vs 26.7% standard RARP; P = 0.000) had vanished at 1 year (100% vs 93.3%; P = 0.15). By contrast, a large recent prospective series showed that the superiority of RS‐RARP in terms of higher early urinary continence was maintained at 1 year (97.5% RS‐RARP vs 68.5% standard RARP) [5].
In addition to a higher early continence rate, RS‐RARP has a lower incidence of postoperative inguinal hernia occurrence compared with standard RARP [6]. Theoretically, RS‐RARP may provide several other potential advantages. It may be advantageous if patients require future surgery necessitating access to the Retzius space and dropping of the bladder, such as an artificial urinary sphincter implantation, an inflatable penile prosthesis insertion, or kidney transplantation. In addition, in patients with previous inguinal hernia repair using mesh, it enables the avoidance of anterior adhesions by accessing the prostate directly from the Douglas pouch. Notably, large‐size glands and/or middle‐lobe, advanced/high‐risk PCa, and patients with previous prostatic surgeries can be managed safely with RS‐RARP in experienced hands.
Undoubtedly, oncological safety is our main concern in treating cancer. To determine the effectiveness of new treatment methods, long‐term follow‐up is warranted. Biochemical recurrence (BCR) is widely used as a primary oncological outcome to assess PCa treatment success. To our knowledge, after radical prostatectomy, ~35% of patients are at risk of developing BCR in the next 10 years. Currently, there are insufficient data regarding the oncological outcomes of RS‐RARP. Only four articles have compared early oncological outcomes between RS‐RARP and standard RARP, and there was no significant difference (Table 1).
More recently, we reported on the mid‐term oncological outcomes of 359 patients who underwent RS‐RARP. The median follow‐up was 26 months. Although this period is not long enough to reach a meaningful conclusion on the oncological safety of RS‐RARP, it is the longest follow‐up period reported in literature. Overall, the positive surgical margin (PSM) rate was 30.6% (14.6% in pT2 and 40.8% in pT3a disease) and the BCR rate was 14.8%. In terms of functional outcomes, the urinary continence rate at 1 year was 93.9% [7]. Interestingly, 164 patients (45.7%) of our cohort had high‐risk PCa. In these patients, the PSM rate was 41.2%, the BCR rate was 22%, and the 3‐year BCR‐free survival (BCRFS) rate was 72%. We compared our results with those in patients with high‐risk PCa treated with standard RARP in the literature. In studies that used the D’Amico criteria the median follow‐up ranged from 12.5 to 37.3 months, the PSM rates were 20.5% to 53.3%, the BCR rates were 17.4% to 31% and the 3‐year BCRFS rates were 41.4% to 86%. In studies that used the National Comprehensive Cancer Network criteria, the median follow‐up ranged from 23.6 to 27 months, the PSM rates were 29% to 38%, the BCR rates were 9.4% to 33%, and the 3‐year BCRFS rates were 55% to 66% [7].
In summary, RS‐RARP is a novel surgical approach which is associated with better urinary continence recovery in the first few months compared with standard RARP [2,3,4,5]. This superiority might be maintained [5] or equalized at 1 year [3,4]. A few studies have compared the early oncological results between RS‐RARP and standard RARP and no significant difference was found [2,3,4,5]. Recently, our group reported the mid‐term oncological outcomes of patients with high‐risk PCa treated with RS‐RARP and these were similar to those of large studies of conventional RARP. This confirms effective and safe mid‐term BCR control after RS‐RARP, while the long‐term oncological results are awaited [7]. Currently, >4 000 cases of RS‐RARP are performed worldwide and more centres are beginning to use and converting to Retzius‐sparing surgery. All centres are experiencing faster recovery of continence. Thanks are due to Drs Galfano and Bocciardi for exploring and sharing this surgical frontier.
References
- Galfano A, Di Trapani D, Sozzi F, et al. Beyond the learning curve of the Retzius‐sparing approach for robotassisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: oncologic and functional results of the first 200 patients with ? 1 year of follow‐up. Eur Urol 2013; 64: 974‐80
- Lim SK, Kim KH, Shin TY et al. Retzius‐sparing robot‐assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: combining the best of retropubic and perineal approaches. BJU Int 2014; 114: 236–44
- Chang LW, Hung SC, Hu JC et al. Retzius‐sparing robotic‐assisted radical prostatectomy associated with less bladder neck descent and better early continence outcome. Anticancer Res 2018; 38: 345–51
- Menon M, Dalela D, Jamil M et al. Functional recovery, oncologic outcomes and postoperative complications after robot‐assisted radical prostatectomy: an evidence‐based analysis comparing the Retzius sparing and standard approaches. J Urol 2018; 199: 1210–7
- Sayyid RK, Simpson WG, Lu C et al. Retzius sparing robotic assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: a safe surgical technique with superior continence outcomes. J Endourol 2017; 31: 1244–50
- Chang KD, Abdel Raheem A, Santok GDR et al. Anatomical Retzius‐space preservation is associated with lower incidence of postoperative inguinal hernia development after robot‐assisted radical prostatectomy. Hernia 2017; 21: 555–61
- Abdel Raheem A, Kidon C, Alenzi M et al. Predictors of biochemical recurrence after retzius‐sparing robot‐assisted radical prostatectomy: analysis of 359 cases with a median follow‐up of 26 months. Int J Urol 2018; 25: 1006–14
Resident’s podcast: Retzius‐sparing robot‐assisted radical prostatectomy
Maria Uloko is a Urology Resident at the University of Minnesota Hospital. In this podcast she discusses the following BJUI Article of the Week:
Retzius‐sparing robot‐assisted radical prostatectomy (RS‐RARP) vs standard RARP: it’s time for critical appraisal
Thomas Stonier*, Nick Simson*, John Davis† and Ben Challacombe‡
*Department of Urology, Princess Alexandra Hospital, Harlow, ‡Urology Centre, Guy ’s Hospital, London, UK and †Department of Urology, MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX, USA
Abstract
Since robot‐assisted radical prostatectomy (RARP) started to be regularly performed in 2001, the procedure has typically followed the original retropubic approach, with incremental technical improvements in an attempt to improve outcomes. These include the running Van‐Velthoven anastomosis, posterior reconstruction or ‘Rocco stitch’, and cold ligation of the Santorini plexus/dorsal vein to maximise urethral length. In 2010, Bocciardi’s team in Milan proposed a novel posterior or ‘Retzius‐sparing’ RARP (RS‐RARP), mirroring the classic open perineal approach. This allows avoidance of supporting structures, such as the puboprostatic ligaments, endopelvic fascia, and Santorini plexus, preserving the normal anatomy as much as possible and limiting damage that may contribute to improved postoperative continence and erectile function. There has been much heralding of the excellent functional outcomes in both the medical and the lay press, but as yet no focus or real mention of any potential downsides of this new technique.
BJUI Podcasts now available on iTunes, subscribe here https://itunes.apple.com/gb/podcast/bju-international/id1309570262
Article of the Week: Retzius-sparing RALP: combining the best of retropubic and perineal approaches
Every week the Editor-in-Chief selects the Article of the Week from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
In addition to the article itself, there is an accompanying editorial written by a prominent member of the urological community. This blog is intended to provoke comment and discussion and we invite you to use the comment tools at the bottom of each post to join the conversation.
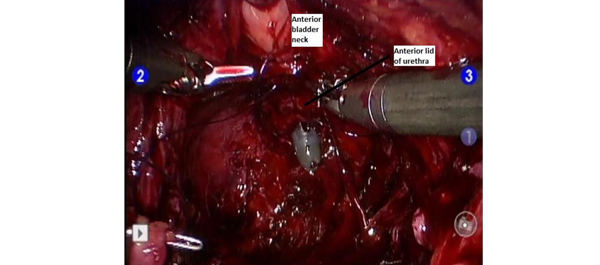
Finally, the third post under the Article of the Week heading on the homepage will consist of additional material or media. This week we feature a video demonstrating the Retzius-sparing approach to robot-assisted prostatectomy.
If you only have time to read one article this week, it should be this one.
Retzius-sparing robot-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: combining the best of retropubic and perineal approaches
Sey Kiat Lim*†, Kwang Hyun Kim*, Tae-Young Shin*, Woong Kyu Han*, Byung Ha Chung*, Sung Joon Hong*, Young Deuk Choi* and Koon Ho Rha*
*Department of Urology, Urological Science Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, South Korea and †Department of Urology, Changi General Hospital, Singapore
OBJECTIVE
To compare the early peri-operative, oncological and continence outcomes of Retzius-sparing robot-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy (RALP) with those of conventional RALP.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
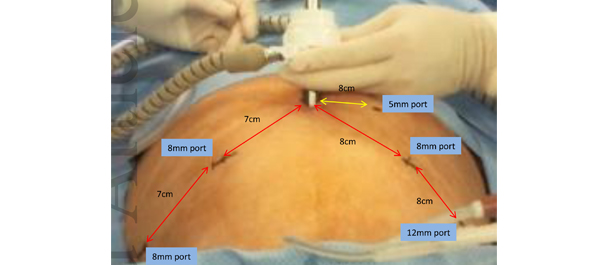
Data from 50 patients who underwent Retzius-sparing RALP and who had at least 6 months of follow-up were prospectively collected and compared with a database of patients who underwent conventional RALP. Propensity-score matching was performed using seven preoperative variables, and postoperative variables were compared between the groups.
RESULTS
A total of 581 patients who had undergone RALP were evaluated in the present study. Although preoperative characteristics were different before propensity-score matching, these differences were resolved after matching. There were no significant differences in mean length of hospital stay, estimated blood loss, intra- and postoperative complication rates, pathological stage of disease, Gleason scores, tumour volumes and positive surgical margins between the conventional RALP and Retzius-sparing RALP groups. Console time was shorter for Retzius-sparing RALP. Recovery of early continence (defined as 0 pads used) at 4 weeks after RALP was significantly better in the Retzius-sparing RALP group than in the conventional RALP group.
CONCLUSIONS
The present results suggest that Retzius-sparing RALP, although technically more demanding, was as feasible and effective as conventional RALP, and also led to a shorter operating time and faster recovery of early continence. Retzius-sparing RALP was also reproducible and achievable in all cases.
Editorial: Pushing the robot-assisted prostatectomy envelope – to the safety limits? Better outcomes
The present article by Lim et al. [1] describing the new technique for robot-assisted radical prostatectomy is provocative. It really does highlight the dramatic improvement in outcomes of prostate cancer surgery for men over the last 25 years. What used to be a 3-week hospital stay with a 50% incontinence rate and a 100% impotence rate [2, 3] now becomes a day case with a high likelihood of excellent urinary control early after surgery and a fair potential for potency preservation. Twenty-five years ago men who underwent radical prostatectomy were truly brave patients.
Lim et al. report a single series by the senior author of 50 cases performed using the so-called Retzius preservation technique. Their cohort of 50 patients treated this way was compared with a retrospective cohort of the surgeon’s patients. The patients had lower-risk disease and patients who had seminal vesicle invasion or extracapsular extension noted preoperatively, presumably on MRI, were excluded from the series. The authors report a shorter operating time and an earlier return to urinary continence in the first 6 months after surgery.
I guess where surgeons are now taking us is to an attempt to remove the prostate from the hammock of neurovascular, muscular and fascial tissue surrounding it, without disturbing the anatomy [4]. If this can be achieved then radical prostatectomy with minimal morbidity is a very compelling choice for the primary treatment of prostate cancer.
The authors’ hypothesis is that preservation of the levator fascia, puboprostatic ligaments and detrusor apron will fix the bladder somewhat like a sling would, with support at the bladder neck during increased intra-abdominal pressure.
It should be noted, however, that the present paper represents a single series of patients selected after a long learning curve by a very experienced surgeon. These excellent outcomes may simply reflect the fact that the surgeon is now extremely technically capable. It is contentious to assume that a propensity score matching of a retrospective cohort would represent a true comparator to contemporary outcomes. These excellent outcomes probably reflect technical improvements achievable with more risky and innovative surgery – after many cases. The authors should be congratulated on pushing the envelope to achieve even better outcomes for patients undergoing this operation, but the exclusion of patients with high-risk disease is probably the major negative aspect of their report. It has become increasingly obvious that patients with high-risk disease are those who benefit most from radical prostatectomy surgery. Surgery for patients with very-low-risk disease (Gleason 6) is probably unnecessary. Nevertheless, with continued insights such as those provided by these surgeons, we may be able to increase the range of patients to whom Retzius-sparing surgery in higher risk cohorts can be offered.
Anthony J. Costello
Department of Urology, Royal Melbourne Hospital, Parkville, Victoria, Australia
References
- Lim SK, Kim KH, Shin T-Y et al. Retzius-sparing Robot-assisted Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy – combining the best of retropubic and perineal approaches. BJU Int 2014; 114: 236–244
-
Wein AJ, Kavousi LR, Novick AC, Partin AW, Peters CA. Campbell-Walsh Urology, 10th edn. Saint Louis, MO: Saunders, 2011: 5688
-
Catalona WJ, Carvalhal GF, Mager DE, Smith DS. Potency, continence and complication rates in 1,870 consecutive radical retropubic prostatectomies. J Urol 1999; 162: 433–438
- Costello AJ, Brooks M, Cole OJ. Anatomical studies of the neurovascular bundle and cavernosal nerves. BJU Int 2004; 94: 1071–1076
Video: Retzius-sparing approach to RALP
Retzius-sparing robot-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: combining the best of retropubic and perineal approaches
Sey Kiat Lim*†, Kwang Hyun Kim*, Tae-Young Shin*, Woong Kyu Han*, Byung Ha Chung*, Sung Joon Hong*, Young Deuk Choi* and Koon Ho Rha*
*Department of Urology, Urological Science Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, South Korea and †Department of Urology, Changi General Hospital, Singapore
OBJECTIVE
To compare the early peri-operative, oncological and continence outcomes of Retzius-sparing robot-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy (RALP) with those of conventional RALP.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Data from 50 patients who underwent Retzius-sparing RALP and who had at least 6 months of follow-up were prospectively collected and compared with a database of patients who underwent conventional RALP. Propensity-score matching was performed using seven preoperative variables, and postoperative variables were compared between the groups.
RESULTS
A total of 581 patients who had undergone RALP were evaluated in the present study. Although preoperative characteristics were different before propensity-score matching, these differences were resolved after matching. There were no significant differences in mean length of hospital stay, estimated blood loss, intra- and postoperative complication rates, pathological stage of disease, Gleason scores, tumour volumes and positive surgical margins between the conventional RALP and Retzius-sparing RALP groups. Console time was shorter for Retzius-sparing RALP. Recovery of early continence (defined as 0 pads used) at 4 weeks after RALP was significantly better in the Retzius-sparing RALP group than in the conventional RALP group.
CONCLUSIONS
The present results suggest that Retzius-sparing RALP, although technically more demanding, was as feasible and effective as conventional RALP, and also led to a shorter operating time and faster recovery of early continence. Retzius-sparing RALP was also reproducible and achievable in all cases.