Article of the Week: Functional role of the TRPM8 ion channel in the bladder
Every Week the Editor-in-Chief selects an Article of the Week from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
In addition to the article itself, there is an accompanying editorial written by a prominent member of the urological community. This blog is intended to provoke comment and discussion and we invite you to use the comment tools at the bottom of each post to join the conversation.
If you only have time to read one article this week, it should be this one.
Functional role of the transient receptor potential melastatin 8 (TRPM8) ion channel in the urinary bladder assessed by conscious cystometry and ex vivo measurements of single-unit mechanosensitive bladder afferent activities in the rat
Objective
To evaluate the role of the transient receptor potential melastatin 8 (TRPM8) channel on bladder mechanosensory function by using L-menthol, a TRPM8 agonist, and RQ-00203078 (RQ), a selective TRPM8 antagonist.
Materials and methods
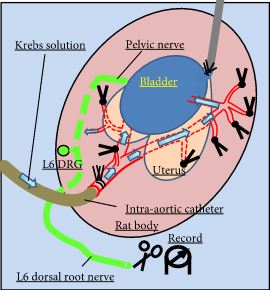
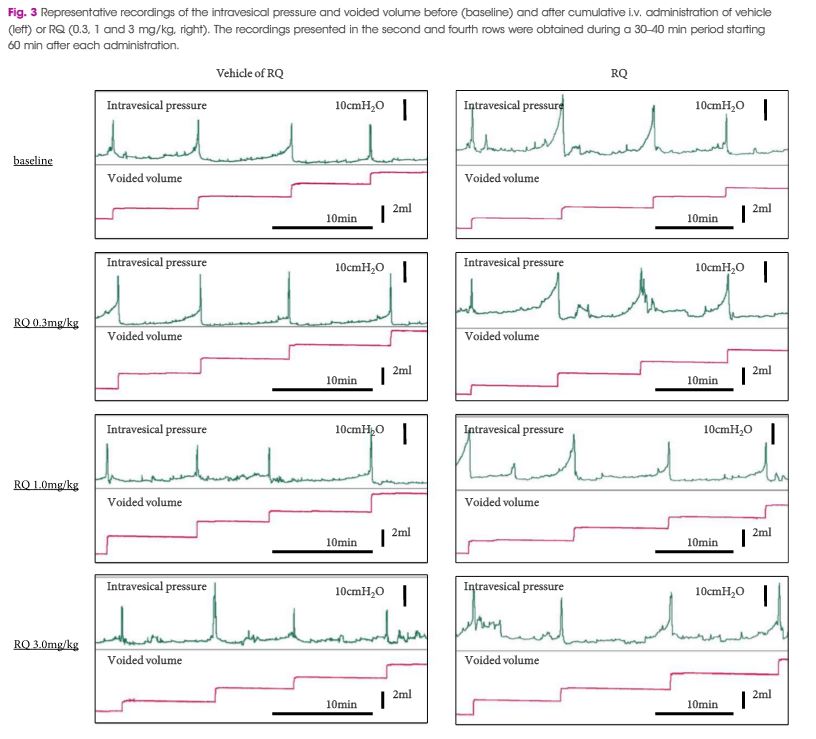
Female Sprague–Dawley rats were used. In conscious cystometry (CMG), the effects of intravesical instillation of L-menthol (3 mm) were recorded after intravenous (i.v.) pretreatment with RQ (3 mg/kg) or vehicle. The direct effects of RQ on conscious CMG and deep body temperature were evaluated with cumulative i.v. administrations of RQ at 0.3, 1, and 3 mg/kg. Single-unit mechanosensitive bladder afferent activities (SAAs) were monitored in a newly established ex vivo rat bladder model to avoid systemic influences of the drugs. Recordings were performed after cumulative intra-aortic administration of RQ (0.3 and 3 mg/kg) with or without intra-vesical L-menthol instillation (3 mm).
Results
Intravesical L-menthol decreased bladder capacity and voided volume, which was counteracted by RQ-pretreatment. RQ itself increased bladder capacity and voided volume, and lowered deep body temperature in a dose-dependent manner. RQ decreased mechanosensitive SAAs of C-fibres, and inhibited the activation of SAAs induced by intravesical L-menthol.
Conclusion
Our results suggest that TRPM8 channels have a role in activation of bladder afferent pathways during filling of the bladder in the normal rat. This effect seems, at least partly, to be mediated via mechanosensitive C-fibres.