Posts
Article of the week: A transcriptomic signature of tertiary Gleason 5 predicts worse clinicopathological outcome
Every week, the Editor-in-Chief selects an Article of the Week from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
In addition to the article itself, there is an editorial written by a prominent member of the urological community, and a video produced by the authors. These are intended to provoke comment and discussion and we invite you to use the comment tools at the bottom of each post to join the conversation.
If you only have time to read one article this week, it should be this one.
A transcriptomic signature of tertiary Gleason 5 predicts worse clinicopathological outcome
Alberto Martini*, Joanna Wang*, Nicholas M. Brown*, Shivaram Cumarasamy*, John P. Sfakianos*, Ardeshir R. Rastinehad*, Kenneth G. Haines III†, Nils Peter Wiklund*, Sujit S. Nair* and Ashutosh K. Tewari*
Departments of *Urology and †Pathology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai Hospital, New York, NY, USA
Abstract
Objective
To investigate the genomic features of tertiary pattern 5 (TP5) on radical prostatectomy specimens in an effort to explain the poor clinical outcomes associated with this disease subtype.
Patients and methods
Data from 159 men with Gleason Grade Group (GGG) 3 or 4 were considered. All patients had Decipher diagnostic testing with transcript profiles and single‐channel array normalisation (SCAN)‐normalised expression of coding genes.
The relationship between Decipher and TP5 was investigated by linear and binary logistic regressions. A differential transcriptomic analysis between patients with and without TP5 was performed. The prognostic role of these genes on progression‐free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) was evaluated using The Cancer Genome Atlas.
Results
In all, 52/159 (33%) patients had GGG 3–4 with TP5 disease. TP5 was associated with a higher Decipher score (β 0.07, 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.02–0.13; P = 0.04) and higher likelihood of falling within the intermediate‐ or high‐risk categories (odds ratio 3.34, 95% CI 1.34–8.35; P = 0.01). Analysis of microarray data revealed an 18‐gene signature that was differentially expressed in patients with TP5; 13 genes were over‐ and five under‐expressed in the TP5 cohort.
The overexpression of cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor 2B (CDKN2B), polo‐like kinase 1 (PLK1), or cell division cycle 20 (CDC20) was associated with worse PFS. The group harbouring overexpression of at least one gene had a 5‐year PFS rate of 50% vs 74% in the group without overexpression (P < 0.001).
Conclusions
Our studies have elucidated unique genomic features of TP5, whilst confirming previous clinical findings that patients harbouring TP5 tend to have worse prognosis. This is the first RNA‐based study to investigate the molecular diversity of TP5 and the first correlating CDKN2B to poorer prognosis in patients with prostate cancer.
Editorial: Transcriptomic signatures for tertiary pattern 5 in prostate cancer
Significant evidence is now emerging and publications have shown that the molecular characterization of tumours represents an important approach to stratifying patients with prostate cancer into appropriate treatments and their responses, helping to inform the next steps in the care pathway of these patients [1]. Understanding the functional role of the genes included in these signatures also gives an insight into the biology of the disease and how it develops and progresses.
BJUI has published papers in the past describing gene signatures that are associated with pathological Gleason score as pathological markers of aggressiveness and their potential role in predicting outcome [2].
The paper by Martini et al. [3] in the current issue of BJUI adds to this important literature. In a cohort of 159 patients, of whom 52 had tertiary pattern 5 (TP5) prostate cancer, Martini et al. showed that TP5 was associated with higher risk categories in the Decipher genomic score. Their study supports the literature showing that patients with TP5 have an elevated likelihood of developing disease after radical prostatectomy and have a poor prognosis [4]. It should be noted, however, that this is a small cohort with few patients defined as having TP5 disease. As prostate cancer is highly heterogeneous and gene expression can also be affected by the patient’s background, additional validation of this finding will be required in independent cohorts.
Additional analysis of the 698 gene by Martini et al. [3] identified a unique RNA signature of 18 genes for the TP5 cohort. A limitation of using the 698 gene previously demonstrated to be related to prostate cancer is that those with TP5 disease may be a unique subset of patients that may be associated with unfamiliar pathological pathways and new genes. An examination of novel genes whose expression pattern is unique to patients with TP5 disease may reveal additional genes.
Martini et al. then used the independent TCGA provisional database to link the expression of these 18 genes with clinical features. Patients harbouring any of the three genes CDKN2B, PLK1 and CDC20 mRNA were found to have worse progression‐free survival. The authors go on to undertake analysis of the 18 genes using the ingenuity network analysis tool identifying pathways involved in the cell cycle, DNA replication and repair, cellular assembly, cell death and survival and gene expression, which would fit with the biology of progressive disease. They also revealed a role in the dedifferentiation process and progression of cells towards anaplasia. They specifically identified CDKN2B, which has previously been associated with tumour suppression but might actually be linked to tumour progression, and identified it for further investigation.
Finally the researchers found that 13 genes out of the 18‐gene TP5 signature are upregulated in tumour lesions with TP5. Following these results they performed a sensitivity analysis in which the expression values of the genes in the cohort with GGG3‐4 and TP5 were compared with those of patients with GGG5 and discovered that these genes were similarly overexpressed in both groups. This finding strengthens the hypothesis that these genes are implicated in the dedifferentiation process of tumour cells, but it also raises the question of whether the pattern of expression of these genes is unique to patients with TP5 only, or whether it is associated with every tumour (primary, secondary or tertiary) that is classified as GGG5. Further research is needed to understand what the clinical significance of this genetic signature is and what pathological process it describes in practice.
This investigation into the functional role of the genes has given an insight into the biology of prostate cancer progression and TP5 disease which might inform a future area of research for novel biomarker panels and therapeutic interventions.
by R. William Watson and Omri Taltsh
References
- , , , , , , Genomic markers in prostate cancer decision making. Euro Urol 2018; 73: 572– 82
- , , , , , , , ,, , , , Evaluation of a 24‐Gene signature for prognosis of metastatic events and prostate cancer‐specific mortality. BJU Int 2017; 119: 961– 7
- , , , , , , ,, , A transcriptomic signature of tertiary Gleason 5 predicts worse clinicopathological outcome. BJU Int 2019; 124: 155– 62
- , , , , , Significance of tertiary Gleason pattern 5 in Gleason score 7 radical prostatectomy specimens. J Urol 2008; 179:516– 22
Video: A transcriptomic signature of tertiary Gleason 5 predicts worse clinicopathological outcome
A transcriptomic signature of tertiary Gleason 5 predicts worse clinicopathological outcome
by Alberto Martini
Abstract
Objective
To investigate the genomic features of tertiary pattern 5 (TP5) on radical prostatectomy specimens in an effort to explain the poor clinical outcomes associated with this disease subtype.
Patients and methods
Data from 159 men with Gleason Grade Group (GGG) 3 or 4 were considered. All patients had Decipher diagnostic testing with transcript profiles and single‐channel array normalisation (SCAN)‐normalised expression of coding genes.
The relationship between Decipher and TP5 was investigated by linear and binary logistic regressions. A differential transcriptomic analysis between patients with and without TP5 was performed. The prognostic role of these genes on progression‐free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) was evaluated using The Cancer Genome Atlas.
Results
In all, 52/159 (33%) patients had GGG 3–4 with TP5 disease. TP5 was associated with a higher Decipher score (β 0.07, 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.02–0.13; P = 0.04) and higher likelihood of falling within the intermediate‐ or high‐risk categories (odds ratio 3.34, 95% CI 1.34–8.35; P = 0.01). Analysis of microarray data revealed an 18‐gene signature that was differentially expressed in patients with TP5; 13 genes were over‐ and five under‐expressed in the TP5 cohort.
The overexpression of cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor 2B (CDKN2B), polo‐like kinase 1 (PLK1), or cell division cycle 20 (CDC20) was associated with worse PFS. The group harbouring overexpression of at least one gene had a 5‐year PFS rate of 50% vs 74% in the group without overexpression (P < 0.001).
Conclusions
Our studies have elucidated unique genomic features of TP5, whilst confirming previous clinical findings that patients harbouring TP5 tend to have worse prognosis. This is the first RNA‐based study to investigate the molecular diversity of TP5 and the first correlating CDKN2B to poorer prognosis in patients with prostate cancer.
Article of the week: 68Ga‐PSMA PET/CT predicts complete biochemical response from RP and lymph node dissection in intermediate‐ and high‐risk PCa
Every week, the Editor-in-Chief selects an Article of the Week from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
In addition to the article itself, there is an editorial written by a prominent member of the urological community. These are intended to provoke comment and discussion and we invite you to use the comment tools at the bottom of each post to join the conversation.
If you only have time to read one article this month, it should be this one.
Gallium‐68‐prostate‐specific membrane antigen (68Ga‐PSMA) positron emission tomography (PET)/computed tomography (CT) predicts complete biochemical response from radical prostatectomy and lymph node dissection in intermediate‐ and high‐risk prostate cancer
Pim J. van Leeuwen*, Maarten Donswijk†, Rohan Nandurkar‡, Phillip Stricker§¶, Bao Ho**, Stijn Heijmink††, Esther M.K. Wit*, Corinne Tillier*, Erik van Muilenkom*, Quoc Nguyen§, Henk G. van der Poel* and Louise Emmett‡§**
*Department of Urology, †Department of Nuclear Medicine, The Netherlands Cancer Institute, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, ‡Faculty of Medicine, University of New South Wales Sydney, §The Australian Prostate Cancer Research Centre-NSW, The Garvan Institute of Medical Research, ¶St Vincent’s Clinic, **Department of Theranostics and Nuclear Medicine, St Vincent’s Hospital Sydney, Sydney, New South Wales, Australia and ††Department of Radiology, The Netherlands Cancer Institute, Amsterdam, The Netherlands
Abstract
Objective
To determine the value of gallium‐68‐prostate‐specific membrane antigen (68Ga‐PSMA)‐11 positron emission tomography (PET) /computed tomography (CT) in men with newly diagnosed prostate cancer.
Patients and methods
We analysed results of 140 men with intermediate‐ and high‐risk prostate cancer. All men underwent 68Ga‐PSMA‐11 PET/CT and multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging (mpMRI) before radical prostatectomy (RP) with extended pelvic lymph node (LN) dissection. For each patient, the clinical and pathological features were recorded. Prostate‐specific antigen (PSA) was documented at staging scan, and after RP, at a median (interquartile range) of 110 (49–132) days. A PSA level of ≥0.03 ng/mL was classified as biochemical persistence (BCP). Logistic regression was performed for association of clinical variables and BCP.
Results
In these 140 patients with intermediate‐ and high‐risk prostate cancer, 27.1% had PSMA PET/CT‐positive findings in the pelvic LNs. Sensitivity and specificity for detection of LN metastases were 53% and 88% (PSMA PET/CT) and 14% and 99% (mpMRI), respectively. The overall BCP rate was 25.7%. The BCP rate was 16.7% in men who were PSMA PET/CT LN‐negative compared to 50% in men who were PSMA PET/CT LN‐positive (P < 0.05). The presence of PSMA‐positive pelvic LNs was more predictive of BCP after RP than cT‐stage, PSA level, and the Gleason score, adjusted for surgical margins status.
Conclusions
68Ga‐PSMA‐11 PET/CT is highly predictive of BCP after RP, and should play an important role informing men with intermediate‐ or high‐risk prostate cancer.
Editorial: Preoperative PSMA‐targeted PET imaging: more than just a tool for prostate cancer staging?
The presence of lymph node metastases at the time of prostate cancer diagnosis has significant implications for treatment. According to current guidelines from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network, men with positive lymph nodes on initial staging imaging should be offered treatment with androgen deprivation (± abiraterone) along with consideration for external beam radiation therapy [1]. In contrast, men with clinically localised high‐ or very‐high‐risk prostate cancer have the option of undergoing radical prostatectomy. Unfortunately, currently available diagnostic imaging modalities (i.e. contrast‐enhanced CT and MRI) fall short in their ability to accurately identify lymph node metastases, which are often small and difficult to discern from other structures within the pelvis. Thus, there exists a conundrum: if we cannot accurately detect lymph node involvement, how can we appropriately manage it?
In this edition of the BJUI, Leeuwen et al. [2] report on the utility of molecular imaging with 68Ga‐PSMA‐11 positron emission tomography (PET)/CT in the preoperative staging of men with prostate cancer. To date, the greatest clinical utility of PSMA‐targeted PET has been in the management of men with biochemically recurrent prostate cancer [3]. In the present study by Leeuwen et al. [2], 140 patients with newly diagnosed intermediate‐ or high‐ risk prostate cancer underwent 68Ga‐PSMA‐11 PET/CT before radical prostatectomy with extended pelvic lymph node dissection. Surgical pathology served as the reference standard to which findings on 68Ga‐PSMA‐11 PET/CT were compared. In total, 27.1% of men were found to have radiotracer uptake in their pelvic lymph nodes, resulting in a sensitivity of 53% and a specificity of 88%. In contrast, multiparametric MRI had a sensitivity of only 14%, albeit with a higher specificity of 99%. These findings are in line with prior studies evaluating the diagnostic performance of PSMA‐targeted PET imaging for preoperative prostate cancer staging [4]. Of greater interest, however, is the authors’ observation that positivity on 68Ga‐PSMA‐11 PET/CT was strongly associated with postoperative PSA persistence (i.e. failure to cure). More specifically, after controlling for Gleason score, surgical margin status, and preoperative PSA level, positivity on PET/CT had an odds ratio of 5.87 (95% CI 1.30–26.59) for biochemical persistence. Furthermore, men with pN1 disease and a positive preoperative PET/CT (i.e. true positives) were over three times more likely to experience biochemical persistence than patients with pN1 disease and negative imaging (71.4% vs 21.4%). Thus, PSMA‐targeted PET not only stands to inform clinical staging, but also has the potential to offer independent prognostic information.
A future line of investigation is to explore the biological basis of the authors’ observation regarding PSMA as a prognostic marker. One explanation is that PET/CT identified men with higher volume lymph node metastases (a known prognostic factor), whilst patients with smaller more curable nodes were negative on imaging. After all, the authors state that the imaging test did not detect any pathologically positive lymph nodes <2 mm. Furthermore, only 27% of positive lymph nodes between 2 and 4 mm showed radiotracer uptake. Unfortunately, the authors did not account for differences in the volume of nodal metastases in their analysis. A second possible explanation for the authors’ observation is that PSMA is upregulated through the same signaling pathways that drive an aggressive prostate cancer phenotype, allowing for PSMA expression to provide prognostic information independent of tumour volume. Indeed, others have previously shown that PSMA expression, as measured by immunohistochemistry, corresponds with increasing tumour grade, stage and risk of biochemical failure [5]. Of course, these concepts are not mutually exclusive and further investigation is needed in order for PSMA‐targeted imaging to be rationally applied as a prognostic test.
References
- NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology: Prostate Cancer (Version 4.2018). 2018. Accessed November 2018. Available at: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/prostate.pdf.
- , , et al. Gallium‐68‐prostate‐specific membrane antigen (68Ga‐PSMA) positron emission tomography (PET)/computed tomography (CT) predicts complete biochemical response from radical prostatectomy and lymph node dissection in intermediate‐ and high‐risk prostate cancer. BJU Int 2019; 124: 62– 8
- , , , . Impact of 68Ga‐PSMA PET on the management of patients with prostate cancer: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Eur Urol 2018; 74: 179– 90
- , , et al. Prostate specific membrane antigen targeted 18F‐DCFPyL positron emission tomography/computerized tomography for the preoperative staging of high risk prostate cancer: results of a prospective, phase II, single center study. J Urol 2018; 199: 126– 32
- , , et al. High level PSMA expression is associated with early PSA recurrence in surgically treated prostate cancer. Prostate 2011; 71: 281– 8
Article of the week: The impact on oncological outcomes after RP for PCa of converting soft tissue margins at the apex and bladder neck from tumour‐positive to ‐negative
Every week, the Editor-in-Chief selects an Article of the Week from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
In addition to the article itself, there is an editorial written by a prominent member of the urological community and the authors have also kindly produced a video describing their work. These are intended to provoke comment and discussion and we invite you to use the comment tools at the bottom of each post to join the conversation.
If you only have time to read one article this week, it should be this one.
The impact on oncological outcomes after radical prostatectomy for prostate cancer of converting soft tissue margins at the apex and bladder neck from tumour‐positive to ‐negative
Sahyun Pak*, Sejun Park†, Myong Kim*, Heounjeong Go‡, Yong Mee Cho‡ and Hanjong Ahn*
*Department of Urology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, †Department of Urology, Ulsan University Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Ulsan and ‡Department of Pathology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
Abstract
Objectives
To assess the impact of conversion from histologically positive to negative soft tissue margins at the apex and bladder neck on biochemical recurrence‐free survival (BCRFS) and distant metastasis‐free survival (DMFS) after radical prostatectomy (RP) for prostate cancer.
Materials and Methods
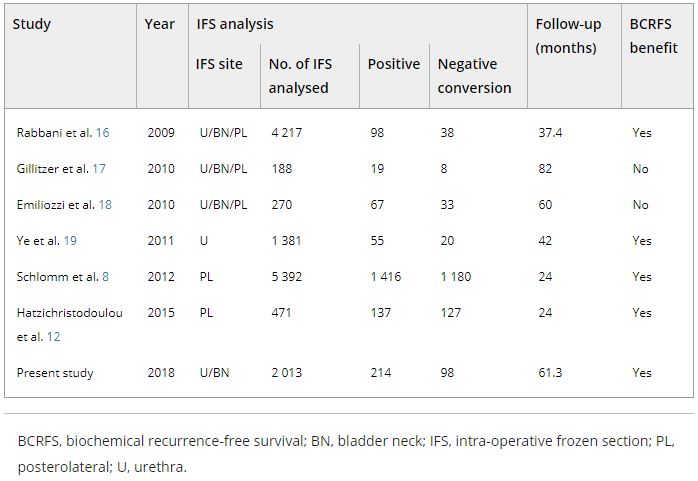
The records of 2 013 patients who underwent RP and intra‐operative frozen section (IFS) analysis between July 2007 and June 2016 were reviewed. IFS analysis of the urethra and bladder neck was performed, and if malignant or atypical cells remained, further resection with the aim of achieving histological negativity was carried out. Patients were divided into three groups according to the findings: those with a negative surgical margin (NSM), a positive surgical margin converted to negative (NCSM) and a persistent positive surgical margin (PSM).
Table 4. Impact of converting margins from tumour‐positive to ‐negative on biochemical recurrence
Results
Among the 2 013 patients, rates of NSMs, NCSMs and PSMs were 75.1%, 4.9%, and 20.0%, respectively. The 5‐year BCRFS rates of patients with NSMs, NCSMs and PSMs were 89.6%, 85.1% and 57.1%, respectively (P < 0.001). In both pathological (p)T2 and pT3 cancers, the 5‐year BCRFS rate for patients with NCSMs was similar to that for patients with NSMs, and higher than for patients with PSMs. The 7‐year DMFS rates of patients with NSMs, NCSMs and PSMs were 97.8%, 99.1% and 89.4%, respectively (P < 0.001). Among patients with pT3 cancers, the 7‐year DMFS rate was significantly higher in the NCSM group than in the PSM group (98.0% vs 86.7%; P = 0.023), but not among those with pT2 cancers (100% vs 96.9%; P = 0.616). The 5‐year BCRFS rate for the NCSM group was not significantly different from that of the NSM group among the patients with low‐ (96.3% vs 95.8%) and intermediate‐risk disease (91.1% vs 82.8%), but was lower than that of the NSM group among patients in the high‐risk group (73.2% vs 54.7%).
Conclusions
Conversion of the soft tissue margin at the prostate apex and bladder neck from histologically positive to negative improved the BCRFS and DMFS after RP for prostate cancer; however, the benefit of conversion was not apparent in patients in the high‐risk group.