Article of the week: mpMRI and follow‐up to avoid prostate biopsy in 4259 men
Every week, the Editor-in-Chief selects an Article of the Week from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
In addition to the article itself, there is an editorial written by a prominent member of the urological community and a video prepared by the authors. These are intended to provoke comment and discussion and we invite you to use the comment tools at the bottom of each post to join the conversation.
If you only have time to read one article this week, it should be this one.
Multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging and follow‐up to avoid prostate biopsy in 4259 men
Wulphert Venderink*, Annemarijke van Luijtelaar*, Marloes van der Leest*, Jelle O. Barentsz*, Sjoerd F.M. Jenniskens*, Michiel J.P. Sedelaar†,Christina Hulsbergen-van de Kaa‡, Christiaan G. Overduin* and Jurgen J. Fütterer*
*Department of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine, †Department of Urology, and ‡Department of Pathology, Radboud University Medical Center, Nijmegen, the Netherlands
Abstract
Objective
To determine the proportion of men avoiding biopsy because of negative multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging (mpMRI) findings in a prostate MRI expert centre, and to assess the number of clinically significant prostate cancers (csPCa) detected during follow‐up.
Patients and method
Retrospective study of 4259 consecutive men having mpMRI of the prostate between January 2012 and December 2017, with either a history of previous negative transrectal ultrasonography‐guided biopsy or biopsy naïve. Patients underwent mpMRI in a referral centre. Lesions were classified according to Prostate Imaging Reporting And Data System (PI‐RADS) versions 1 and 2. Negative mpMRI was defined as an index lesion PI‐RADS ≤2. Follow‐up until 13 October 2018 was collected by searching the Dutch Pathology Registry (PALGA). Gleason score ≥3 + 4 was considered csPCa. Kaplan–Meier analysis and univariable logistic regression models were used in the cohort of patients with negative mpMRI and follow‐up.
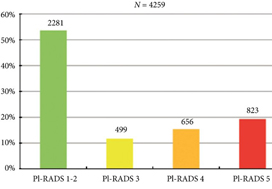
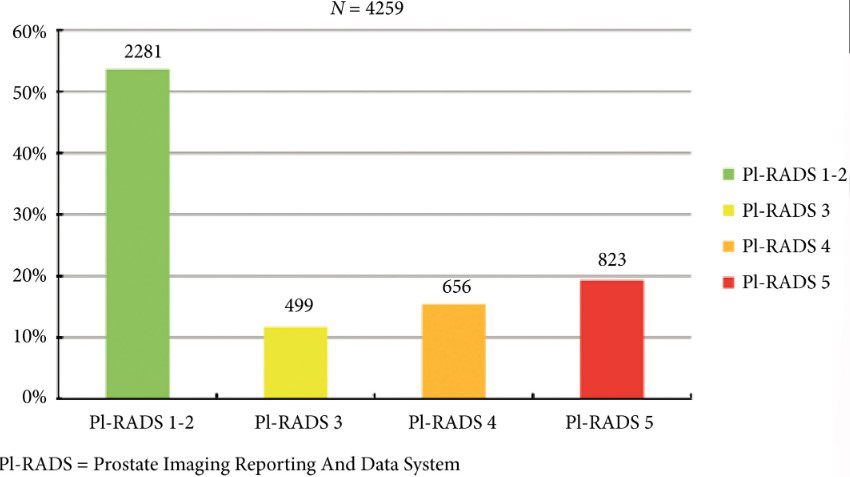
Fig. 2. Distribution of PI‐RADS scored in the entire cohort.
Results
Overall, in 53.6% (2281/4259) of patients had a lesion classified as PI‐RADS ≤2. In 320 patients with PI‐RADS 1 or 2, follow‐up mpMRI was obtained after a median (interquartile range) of 57 (41–63) months. In those patients, csPCa diagnosis‐free survival (DFS) was 99.6% after 3 years. Univariable logistic regression analysis revealed age as a predictor for csPCa during follow‐up (P < 0.05). In biopsied patients, csPCa was detected in 15.8% (19/120), 43.2% (228/528) and 74.5% (483/648) with PI‐RADS 3, 4 and 5, respectively.
Conclusion
More than half of patients having mpMRI of the prostate avoided biopsy. In those patients, csPCa DFS was 99.6% after 3 years.