Melbourne played host to the Prostate Cancer World Congress last week. With over 1,000 delegates and a stellar International faculty comprising of 21 global leaders, it was no surprise that tweeters worldwide battled off sleep to keep up with the action.
Melbourne played host to the Prostate Cancer World Congress last week. With over 1,000 delegates and a stellar International faculty comprising of 21 global leaders, it was no surprise that tweeters worldwide battled off sleep to keep up with the action.

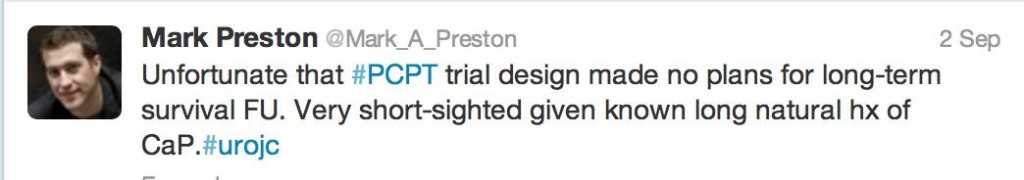
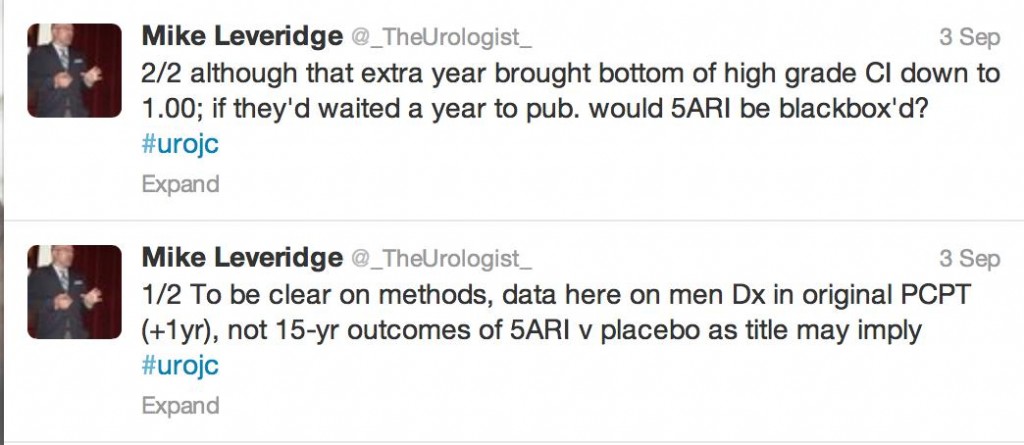
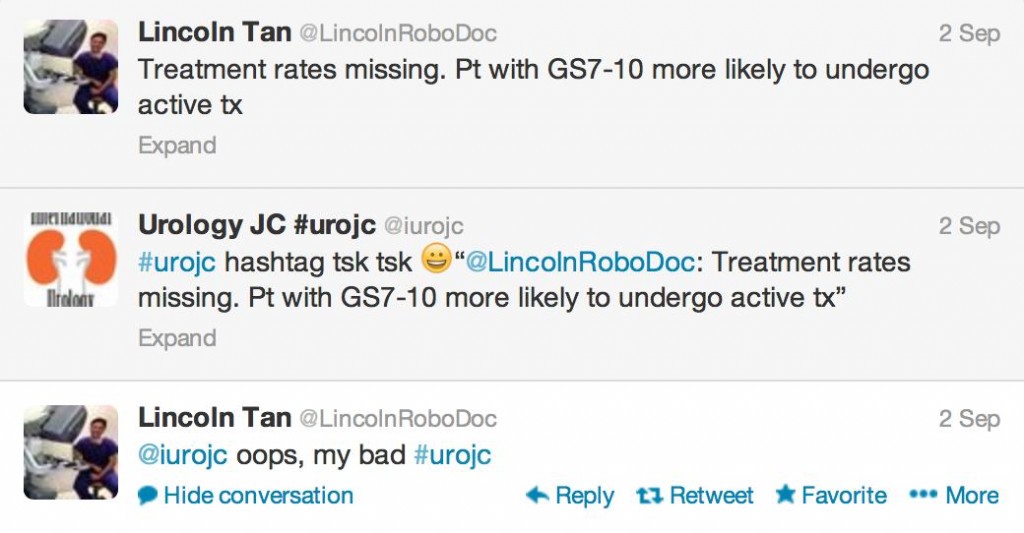
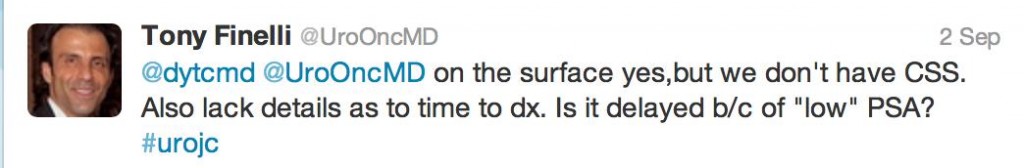
Amidst a buzzing crowd, overlooking the iconic @MCG #pcwc13 President Tony Costello reminisced about the very first conference; 2 speakers, 27 delegates made up largely of residents only fourteen years ago. Undoubtedly the highlight of the conference was the release of ‘The Melbourne Consensus Statement on Prostate Cancer Testing’. This gathering of worldwide experts allowed for the ideal opportunity to generate a set of consensus statements with the goal of finally ending the confusion that exists with current guidelines and allow for early detection of prostate cancer.
https://www.bjuinternational.com/bjui-blog/the-melbourne-consensus-statement-on-prostate-cancer-testing/
As well as major media coverage following the statements release #PCWC13 caused a stir virally around the globe. With tweeters from New Zealand, United Kingdom, Ireland, United States, Canada and all states and territories of Australia the success of #SoMe was a hot topic of discussion around the Convention Centre. Novel and newbie #SoMe users could not resist joining the frenzy of twitter traffic which grew in strength over the five days.

Dr Stacy Loeb kickstarts #PCWC live on @abc
The conference featured three main streams; Clinical Urology #CU, Translational Science #TS and Nurses & Allied Health #NAH, a programme which ensured the multidisciplinary team and all practitioners involved in prostate cancer care could learn and share expertise. Day 1 the tone was set at the moderated poster presentations by @DrHWoo who outlined some conference housekeeping rules ‘All phones on silent and everyone must be adequately tweeting!!’.
An exceptionally high standard of candidates left decision making difficult for poster judges; @DrDanielMoon and @DrHWoo. A clever addition to the #PCWC13 welcome package was the BJUI supplement containing all #CU abstracts, allowing delegates and faculty to gain further knowledge of each individual presentation.

That evening @AustProstate The Australian Prostate Cancer Research function and drinks allowed faculty to relax and mingle while receiving a warm welcome from Professor Rosemary Knight from the Dept. of Health, Canberra, Hon David Davis MP, Victorian Minister for Health and Hon Dr Andrew Southcott, Federal Shadow Spokesman for Health.

On Wednesday morning at the opening multidisciplinary plenary @SwannyQLD the Honourable Wayne Swan MP gave an emotional account of his personal battle with prostate cancer. His heartfelt story touched all those present, emphasising that underlying the scientific and clinical excellence of a conference of this magnitude remains the care of our patients.

@LoebStacy Assistant Professor of Urology and Population Health from NYU followed with a superb summation of ‘Practice-changing publications in prostate cancer this year’. Dr Loeb condensed a typically three hour session by herself and Dr. William J. Catalona into twenty minutes addressing the most prominent issues in prostate cancer, including ‘Nature V Nurture’, the fish oil debate, the FDA approval of Radium-223 and the PSA recommendations by USPSTF.
Prof Noel Clarke from the Christie Hospital in Manchester presented the inaugural BJUI Lecture “Breaking the Mould in Prostate Cancer Trials”, to a packed audience including clinicians and scientists.
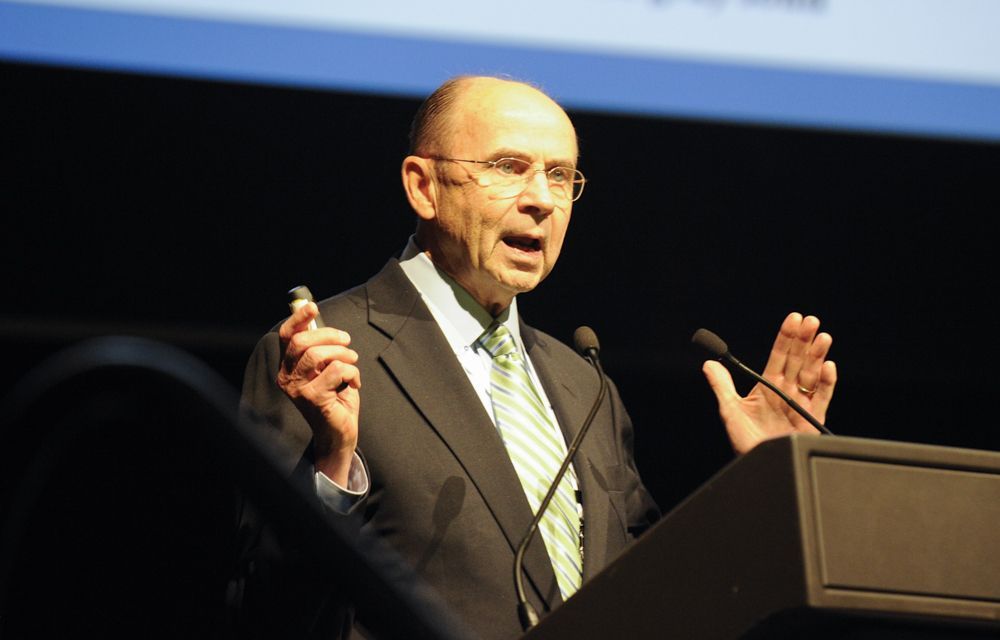

On his fourth trip to Australia and attending the conference, Dr. Patrick C Walsh delivered the inaugural speech so named after the orator himself, a lecture which will continue to be an annual highlight of the APCC. An insightful look at the progress in prostate cancer genetics, over the last two decades, from one of the fathers of Urology kickstarted #PCWC13.
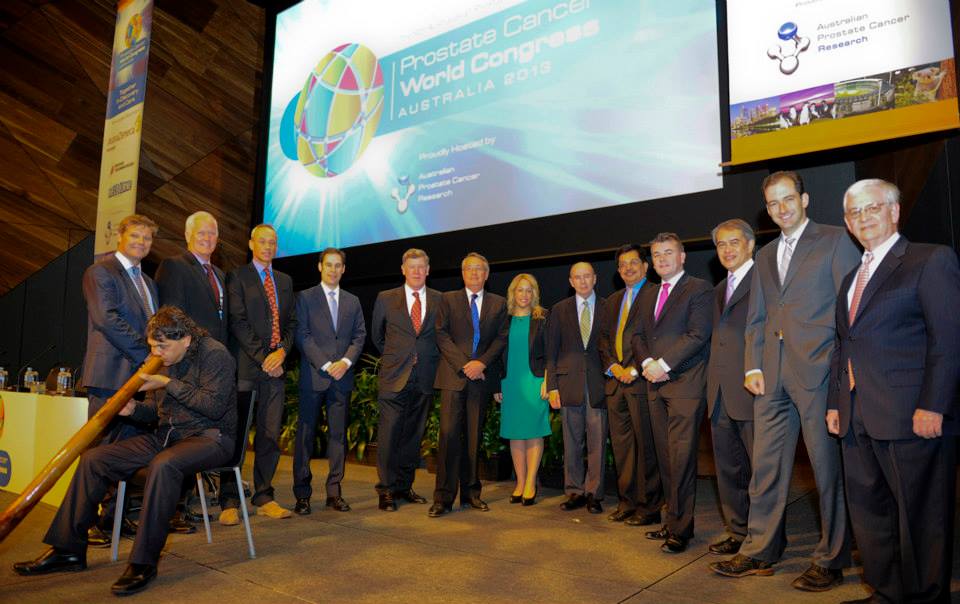

#PCWC13 co- convenor A/Prof Declan Murphy released ‘The Melbourne Consensus statement ‘at 1pm sparking major national and global media attention.

https://www.heraldsun.com.au/lifestyle/health-fitness/prostate-cancer-test-should-be-taken-by-men-in-their-40s/story-fni0diac-1226692750214
https://www.theaustralian.com.au/news/breaking-news/prostate-experts-end-psa-test-confusion/story-fn3dxiwe-1226692802245
https://www.businessweek.com/news/2013-08-06/prostate-test-warrants-rational-use-as-cancer-gauge-doctors-say
The signatories outlined five major points with a view to clarifying the use of PSA testing and media representatives were given the chance to address pressing questions with @LoebStacy, @proftcostello, Dr. Walsh, Dr Catalona and Mr Murphy (@declangmurphy) at the press conference.

https://www.couriermail.com.au/lifestyle/health-fitness/prostate-cancer-test-should-be-taken-by-men-in-their-40s/story-fnihoylo-1226692750214
https://www.news.com.au/lifestyle/health-fitness/prostate-cancer-test-should-be-taken-by-men-in-their-40s/story-fneuzlbd-1226692750214
https://www.theaustralian.com.au/news/breaking-news/prostate-experts-end-psa-test-confusion/story-fn3dxiwe-1226692802245
https://au.news.yahoo.com/thewest/a/-/newshome/18405046/debate-reignites-on-prostate-screening/
https://www.medicalobserver.com.au/news/international-experts-support-psa-testing
https://www.bloomberg.com/news/2013-08-07/prostate-test-warrants-rational-use-doctors-say.html
https://localtoday.com.au/get-local/news/88156-prostate-experts-end-psa-test-confusion.html

Lat e morning and afternoon on Wednesday was filled with an extensive range of sessions in all three streams, including discussion and developments on tumour imaging, therapies & biomarkers and management of sexual rehabilitation. A round table discussion on PSA testing and the ‘Melbourne Consensus Statement’ caused some heated debate with controversial questions from the audience. Cocktails in the exhibition centre followed, where delegates were given the opportunity to mingle with faculty and further discuss the monumental statement which has undoubtedly put Melbourne and Victoria on the map as a centre of Urological academia. Pharmaceutical and surgical sponsors showcased their latest innovations and enthusiasts were given the chance to practise skills robotic on the Da Vinci console. An eventful day drew to a close @MCEC with the announcement of the poster winners, generously sponsored by Ipsen Pharmaceuticals.
e morning and afternoon on Wednesday was filled with an extensive range of sessions in all three streams, including discussion and developments on tumour imaging, therapies & biomarkers and management of sexual rehabilitation. A round table discussion on PSA testing and the ‘Melbourne Consensus Statement’ caused some heated debate with controversial questions from the audience. Cocktails in the exhibition centre followed, where delegates were given the opportunity to mingle with faculty and further discuss the monumental statement which has undoubtedly put Melbourne and Victoria on the map as a centre of Urological academia. Pharmaceutical and surgical sponsors showcased their latest innovations and enthusiasts were given the chance to practise skills robotic on the Da Vinci console. An eventful day drew to a close @MCEC with the announcement of the poster winners, generously sponsored by Ipsen Pharmaceuticals.
 #CU- Survival disparities between Maoiri and non-Maoiri men with non-localised prostate cancer in New Zealand. Zuzana Obertova
#CU- Survival disparities between Maoiri and non-Maoiri men with non-localised prostate cancer in New Zealand. Zuzana Obertova
#NAH-New prostate cancer diagnoses-improving timeliness of communication with patients General Practitioners. Sue Stanbridge
#TS-Engineering a High-Throughout Prostate Cancer Stem Cell Niche Mimic. Micael Doran
 The BJUI were major supporters of this year’s PCWC and published all of the accepted abstracts in a special supplement (https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/bju.2013.112.issue-s1/issuetoc)
The BJUI were major supporters of this year’s PCWC and published all of the accepted abstracts in a special supplement (https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/bju.2013.112.issue-s1/issuetoc)
 Thursday flew into action bright and early with breakfast talks from Dr. Joseph Smith, Professor Paul Waring and an expert #NAH panel. A combined multidisciplinary plenary addressed risk stratification and imaging, with notable speakers including Dr Matt Cooperberg on the issues in treating localised prostate cancer and Dr Tom Aherling ‘The critical role of hypogonadism or low testosterone in prostate cancer’. Key topics addressed in sessions on Thursday included active surveillance, changes in treatment of options of metastatic prostate cancer and screening. Highlights included an excellent lecture on Radium 223 by Dr. Oliver Sartor, an anecdotal insight into the recent work of Dr. Niall Clarke and Dr. Monique Roobol addressed ‘The
Thursday flew into action bright and early with breakfast talks from Dr. Joseph Smith, Professor Paul Waring and an expert #NAH panel. A combined multidisciplinary plenary addressed risk stratification and imaging, with notable speakers including Dr Matt Cooperberg on the issues in treating localised prostate cancer and Dr Tom Aherling ‘The critical role of hypogonadism or low testosterone in prostate cancer’. Key topics addressed in sessions on Thursday included active surveillance, changes in treatment of options of metastatic prostate cancer and screening. Highlights included an excellent lecture on Radium 223 by Dr. Oliver Sartor, an anecdotal insight into the recent work of Dr. Niall Clarke and Dr. Monique Roobol addressed ‘The  PRIAS project’. For those delegates that had thus far escaped the #SoMe excitement, a workshop to twitter with the times was provided and the evening closed with an extensive global perspective on prostate cancer.
PRIAS project’. For those delegates that had thus far escaped the #SoMe excitement, a workshop to twitter with the times was provided and the evening closed with an extensive global perspective on prostate cancer.
An academic programme and faculty line-up that would surely struggle to be matched, was further enhanced by the splendour and uniqueness of Thursday evenings congress dinner. Guests enjoyed pre-dinner drinks and canapés while exploring the National Sports Museum before being treated with the rare honour of stepping out onto the ‘hallowed turf’ of the mighty MCG. As if we had not been  spoiled enough, the Aussie experience continued upon entering the Members dining room where we got the chance to cuddle a Koala, pose with crocs and if one dared; to dangle a python around your neck! It had both young and more mature delegates jumping around like children. The magnificence of the location was conveyed further to guests by a fun fact quiz on @MCG. Main course was an Australian culinary delight, with accompanying national wines and a surreal view of Australia’s most spectacular sporting venue. Mark Holden had guests laughing while Catarina Torres ensured faculty and delegates of all ages put on their #dancingshoes.
spoiled enough, the Aussie experience continued upon entering the Members dining room where we got the chance to cuddle a Koala, pose with crocs and if one dared; to dangle a python around your neck! It had both young and more mature delegates jumping around like children. The magnificence of the location was conveyed further to guests by a fun fact quiz on @MCG. Main course was an Australian culinary delight, with accompanying national wines and a surreal view of Australia’s most spectacular sporting venue. Mark Holden had guests laughing while Catarina Torres ensured faculty and delegates of all ages put on their #dancingshoes.
 Masterclasses on Friday in robotic-assisted surgery remains one of the most favoured aspects of the program with surgeons of all levels looking forward to hearing tips and techniques from #robotics worldwide leaders. The da Vinci Prostatectomy Masterclass was conveend by Dr Daniel Moon and Dr Geoff Coughlin. Key speakers included Dr Tom Aherling and Dr David Gillatt, between whom have experience of over 15,000 radical prostatectomies. Dr Aherling talked through a full length RARP case sharing advanced tricks, followed by Dr. James Borin’s discussion on the intricacies of UV anastomosis. Trainees enjoyed a more intimate opportunity to engage with experts such as @LoebStacy, @dr_coops, @JGrummet, @DrDanielMoon, @lawrentschuck in a master class engineered for budding future urologists. Knock off drinks took place that evening on the glistening Southbank as the success of #PCWC13 could hardly be disputed. A sunny Melbourne Saturday saw GPs provide a workshop for GPs to improve both their knowledge and management of men with prostate cancer both in terms of testing and treatment.
Masterclasses on Friday in robotic-assisted surgery remains one of the most favoured aspects of the program with surgeons of all levels looking forward to hearing tips and techniques from #robotics worldwide leaders. The da Vinci Prostatectomy Masterclass was conveend by Dr Daniel Moon and Dr Geoff Coughlin. Key speakers included Dr Tom Aherling and Dr David Gillatt, between whom have experience of over 15,000 radical prostatectomies. Dr Aherling talked through a full length RARP case sharing advanced tricks, followed by Dr. James Borin’s discussion on the intricacies of UV anastomosis. Trainees enjoyed a more intimate opportunity to engage with experts such as @LoebStacy, @dr_coops, @JGrummet, @DrDanielMoon, @lawrentschuck in a master class engineered for budding future urologists. Knock off drinks took place that evening on the glistening Southbank as the success of #PCWC13 could hardly be disputed. A sunny Melbourne Saturday saw GPs provide a workshop for GPs to improve both their knowledge and management of men with prostate cancer both in terms of testing and treatment.
By the end of the week, data from symplur.com using the #pcwc13 hashtag showed just how imapct this year’s Congress had on social media.
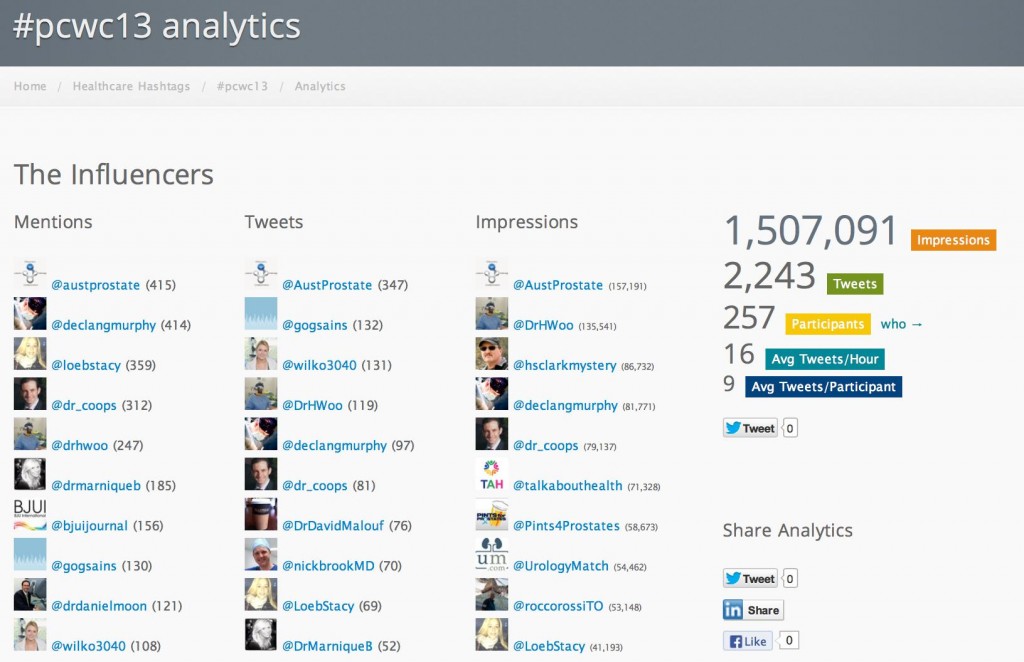
The BJUI Social Media team were very pleased to be a part of this success.
It was my first Urology conference and as a medical student I was excited to have an opportunity to be in the same centre as such a stellar line-up of experts. In all honesty I was star-struck. As a member of the BJUI social media team I was tweeting until my thumbs ached but not only did this allow me to engage with @urotwitteraiti household names virally, in many cases it gave me a window to engage with them in person. #Surreal. A fact that surely emphasises the power of #SoMe and would quash any reservations of #tweeterdoubters.
#pcwc13 #RoaringSuccess
Follow the link to Australian Prostate Cancer Research to see highlights of all the action. https://www.facebook.com/media/set/?set=a.503695969711643.1073741827.232024796878763&type=1

Authors:
The BJUI Social Media Team at PCWC – Áine Goggins, Medical Student, Queens University Belfast and University of Melbourne; Dr Marni Basto, Peter MAccAllum Cancer Centre, Melbourne; Dr Sarah Wilkinson, Monash University, Melbourne.
@gogsains @DrMarniqueB @wilko3040