IP2 – ATLANTA is launched!
IP2 – ATLANTA is launched! ATLANTA is a phase II randomised controlled trial that will explore sequential multi-modal treatment using systemic therapy, local physical cytoreduction and metastasis directed therapy in men with newly diagnosed metastatic prostate cancer against a comparator of standard of care alone.
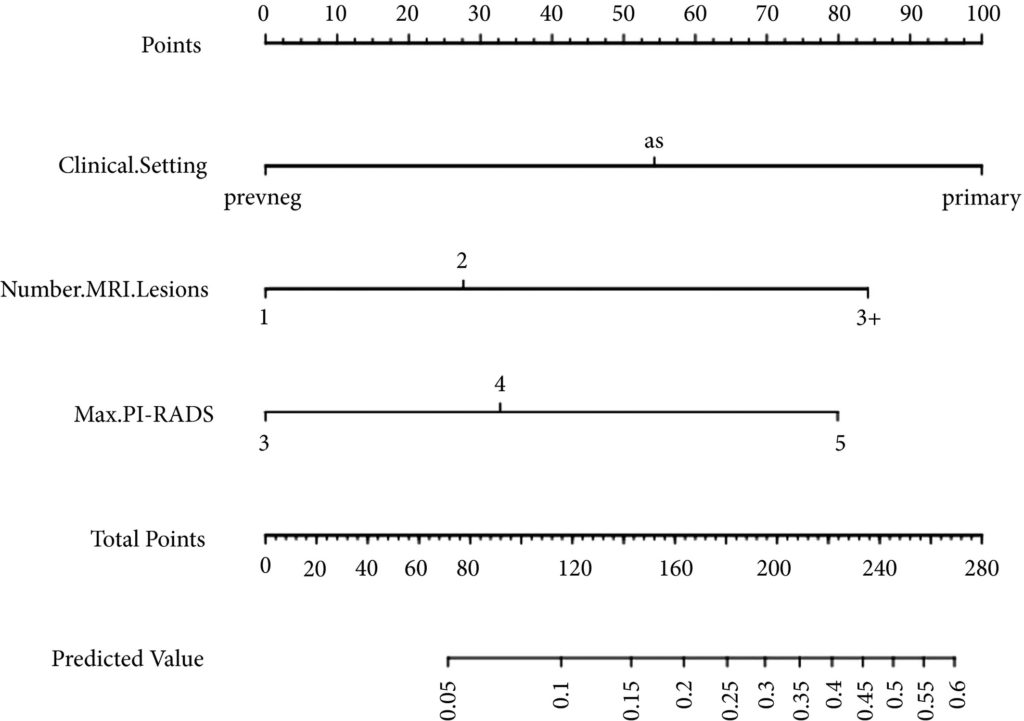
All men with new histologically diagnosed hormone sensitive metastatic prostate cancer, within three months of commencing androgen deprivation therapy (ADT), and of performance status 0 to 2 are eligible. No upper limit on metastatic burden will apply, although men must be fit to undergo all trial interventions at point of randomisation.
Men will be randomised to: Control (Standard of Care) OR Intervention 1 (Minimally Invasive Ablative Therapy [MIAT] +/- pelvic lymph node dissection [PLND]) OR Intervention 2 (Local Radiotherapy +/- Lymph Nodes OR Radical Prostatectomy +/- PLND). Randomisation stratified by metastatic burden (CHAARTED definition), intent to treat pelvic lymph nodes, intent to treat metastasis and intent to commence chemotherapy.
Systemic therapy in all arms includes ADT +/- Docetaxel. Radical prostatectomy will be with or without PLND. Local radiotherapy will be 60Gy/20Fr OR 74-78Gy in 2Gy per fraction over a minimum of 27 days, with or without simultaneous nodal radiotherapy. MIAT will be cryotherapy or focal HIFU. Men in both intervention arms will be eligible for metastasis directed therapy in the form of stereotactic ablative radiation (SABR) or surgery.
Men will be recruited over a two year period and followed up for a minimum of two years. Primary outcome will be progression free survival (PFS). ATLANTA is commencing in 17 UK trial centres with a target recruitment of 80 patients in the internal pilot, rising to 918 patients in full phase across 30 UK trial centres from November 2019.
ATLANTA is entirely charity funded (Wellcome Trust) and available on the NIHR CRN portfolio. Follow-up trial visits are not in excess of routine practice and extra burden is minimal. If you would like to join the main phase of ATLANTA as a site, please contact Mr Martin J. Connor ([email protected]) www.imperialprostate.org.uk/ATLANTA.
Prof. Hashim U. Ahmed (ATLANTA PI & CI),
Mr. Martin J. Connor (ATLANTA Doctoral Clinical Research Fellow)
Mr. Taimur T. Shah (Urology SpR & Research Fellow)
ATLANTA Surgeons Board: Mr Mathias Winkler, Mr Tim Dudderidge, Prof. Chris Eden, Mr Paul Cathcart, Prof. Naeem Soomro, Mr Adel Makar
ATLANTA Radiotherapy Board: Prof. John Staffurth, Dr. Alison Falconer, Dr. Stephen Mangar, Dr Olivia Naismith, RTTQA team
ATLANTA MIAT Board: Prof. Hashim U. Ahmed, Mr Stuart McCracken, Mr Raj Nigam, Mr Tim Dudderidge, Prof Iqbal Shergill
ATLANTA SABR Board: Dr Vincent Khoo, RTTQA team
ATLANTA Medical Oncologists: Dr. Naveed Sarwar, Dr Michael Gonzalez
ATLANTA Trial Sites: Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust, The Royal Marsden Hospital, Guy’s & St Thomas’ NHS Foundation Trust, London North West Healthcare NHS Trust, Royal Surrey County (Guildford) Hospital, University Hospital Southampton, Clatterbridge Cancer Centre & Arrowe Park Hospital, Newcastle Freeman Hospital, King’s Lynn (Cambridge), Norfolk & Norwich (Cambridge), Sunderland Royal Hospital, Frimley Park Hospital, Royal Devon and Exeter Hospital, Wrexham Park Hospital, West Middlesex University Hospital, Royal United Hospital Bath, Betsi Calderwar Health Board, Lister Hospital, Hampshire (Basingstoke) Hospitals, University Hospital Coventry, Worcestershire Royal Hospital.
Trial Sponsor: Imperial College London
Trial Funder: Wellcome Trust
ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT03763253