Editorial: More Nomograms or Better Lymph node dissection – What do we need in Prostate Cancer?
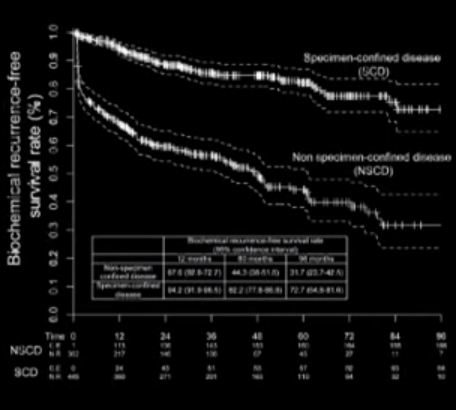
The publication of nomograms to predict radical prostatectomy (RP) outcome using preoperative parameters were important steps in urological oncology. Abdollah et al. [1], in this issue of BJU International, present a new nomogram to predict specimen-confined disease (SCD; pT2–3a, pN0 R0) in men with high-risk prostate cancer undergoing pelvic lymph node dissection (PLND) and robot-assisted RP (RARP). They used statistical logistic regression to measure the impact of various preoperatively available clinicopathological parameters on the likelihood of pathological outcome and tumour recurrence. The final nomogram accurately identified SCD (pT2–3a, pN0 R0) in 76% of the patients. It is intuitive that these patients have good long-term oncological outcomes after surgery. Consequently, Abdollah et al. found excellent 8-year cancer-specific survival rates in these patients. Because nomograms provide individualised risk prediction for patients in an easily applicable manner, they have become very popular among clinicians. Nomograms are now being applied for almost every aspect of prostate cancer. These are freely available and both patients and physicians are encouraged to use them.
Although nomograms undoubtedly have improved our perspective of disease behaviour and individual patient prediction, several key questions remain. First, how good are the input data to a nomogram? Abdollah et al. [1] evaluated 810 patients with high-risk prostate cancer treated in a single large centre between 2003 and 2012. Impressively, more than half of the patients (55%) harboured SCD at RARP. Such a high chance of having SCD will probably encourage many physicians and patients to choose surgery, even without using a nomogram, because this approach may avoid the need for hormonal treatment, which is obligatory for radiation therapy in high-risk prostate cancer. Second, is the predictive accuracy safe within clinical practice? Most nomograms using clinicopathological data generate predictive accuracies within the range of 75–90% (including the nomogram presented by Abdollah et al. [1]). It is of special importance to consider that 64/447 (14%) of the patients with SCD in the series reported by Abdollah et al. [1] received salvage treatment, which was initiated after a median (interquartile range, IQR) of 4.8 (1.4–9.3) months, and the indication to initiate this salvage therapy was PSA recurrence. Obviously, these patients did not have specimen confined disease and were misclassified. In this case, one might postulate a persistence of nodal disease, given an inadequate extent of PLND. Abdollah et al. [1] reported on a median (IQR) of 5 (3.0–11.0) lymph nodes removed.
In their landmark paper on extended PLND (ePLND) in cadavers, Weingartner et al. [2] demonstrated that a mean lymph node yield of 20 serves as a guideline for sufficient ePLND. More than 10 years ago, Heidenreich et al. [3] reported on a 15% higher rate of lymph node metastasis detection when comparing ePLND with the standard LND (obturator). Bader et al. [4] provided further evidence that an ePLND is needed to provide adequate clinical staging and potential therapeutic benefit. Of 365 patients with clinically localised prostate cancer, 88 (24%) had positive lymph nodes. In this series, a pelvic LND that spared the internal iliac bed would have left 58% of patients with positive nodes with residual disease and 19% would have been incorrectly staged as lymph node-negative for cancer. These data were recently confirmed by several authors when analysing retrospective series. Furthermore, Seiler et al. [5] updated their series of 88 patients and recently reported on the long-term outcome after a median follow-up of 15.6 years. They showed that 18% of those patients with one positive node remained biochemical recurrence free, 28% showed biochemical recurrence only, and 54% had clinical progression. Of these 39 patients, 57% never required deferred androgen-deprivation therapy. In contrast, patients with multiple positive nodes are likely to experience rapid progression and, thus, may benefit from early adjuvant therapies. International clinical practice guidelines recommend the performance of an anatomically ePLND at RP in men with high-risk prostate cancer, for both staging and therapeutic purposes.
Nowadays, most urologists claim to perform an ePLND. However, a recent analysis among 50 671 men who were surgically treated with RP from 2010 to 2011 in the USA showed that, overall, only 69.3% of the high-risk patients underwent concomitant PLND [6]. Surgical approach and hospital characteristics were associated with treatment with PLND and detection of lymph node metastasis. More specifically, patients with prostate cancer undergoing open RP or surgically treated at high-volume centres were more likely to undergo PLND than those undergoing RARP or surgically treated at low-volume centres.
Despite the strong evidence that ePLND positively affects survival in men with limited lymph node involvement, this procedure is not commonly performed. The reasons for this are multiple and include expertise, stage migration and functional and oncological outcomes, as well as economics and the introduction of laparoscopic and laparoscopic RARP. However, this is no reason not to offer the patient, if possible, an operation which has the highest chance of cure