Article of the Month: ERSPC and PCPT risk calculators in prostate cancer risk prediction
Every Month the Editor-in-Chief selects an Article of the Month from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
In addition to the article itself, there is an accompanying editorial written by a prominent member of the urological community. This blog is intended to provoke comment and discussion and we invite you to use the comment tools at the bottom of each post to join the conversation.
If you only have time to read one article this week, it should be this one.
Prostate cancer risk prediction using the novel versions of the European Randomised Study for Screening of Prostate Cancer (ERSPC) and Prostate Cancer Prevention Trial (PCPT) risk calculators: independent validation and comparison in a contemporary European cohort
Objectives
To externally validate and compare the two novel versions of the European Randomised Study for Screening of Prostate Cancer (ERSPC)-prostate cancer risk calculator (RC) and Prostate Cancer Prevention Trial (PCPT)-RC.
Patients and Methods
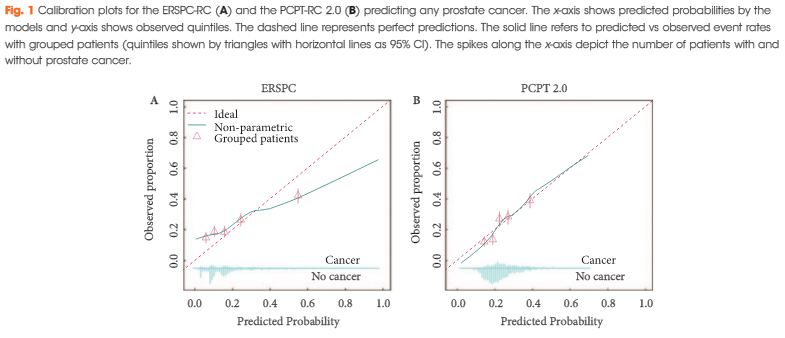
All men who underwent a transrectal prostate biopsy in a European tertiary care centre between 2004 and 2012 were retrospectively identified. The probability of detecting prostate cancer and significant cancer (Gleason score ≥7) was calculated for each man using the novel versions of the ERSPC-RC (DRE-based version 3/4) and the PCPT-RC (version 2.0) and compared with biopsy results. Calibration and discrimination were assessed using the calibration slope method and the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC), respectively. Additionally, decision curve analyses were performed.
Results
Of 1 996 men, 483 (24%) were diagnosed with prostate cancer and 226 (11%) with significant prostate cancer. Calibration of the two RCs was comparable, although the PCPT-RC was slightly superior in the higher risk prediction range for any and significant prostate cancer. Discrimination of the ERSPC- and PCPT-RC was comparable for any prostate cancer (AUCs 0.65 vs 0.66), while the ERSPC-RC was somewhat better for significant prostate cancer (AUCs 0.73 vs 0.70). Decision curve analyses revealed a comparable net benefit for any prostate cancer and a slightly greater net benefit for significant prostate cancer using the ERSPC-RC.
Conclusions
In our independent external validation, both updated RCs showed less optimistic performance compared with their original reports, particularly for the prediction of any prostate cancer. Risk prediction of significant prostate cancer, which is important to avoid unnecessary biopsies and reduce over-diagnosis and overtreatment, was better for both RCs and slightly superior using the ERSPC-RC.