In the week following Britain’s exit from Europe after the BREXIT referendum, BAUS 2016 got underway in Liverpool’s BT convention Centre. This was the 72nd meeting of the British Association of Urological Surgeons and it was well attended with 1120 delegates (50% Consultant Member Urologists, 30% Trainees, 10% Non member Urologists/Other, 10% Nurses, HCP’S, Scientists).

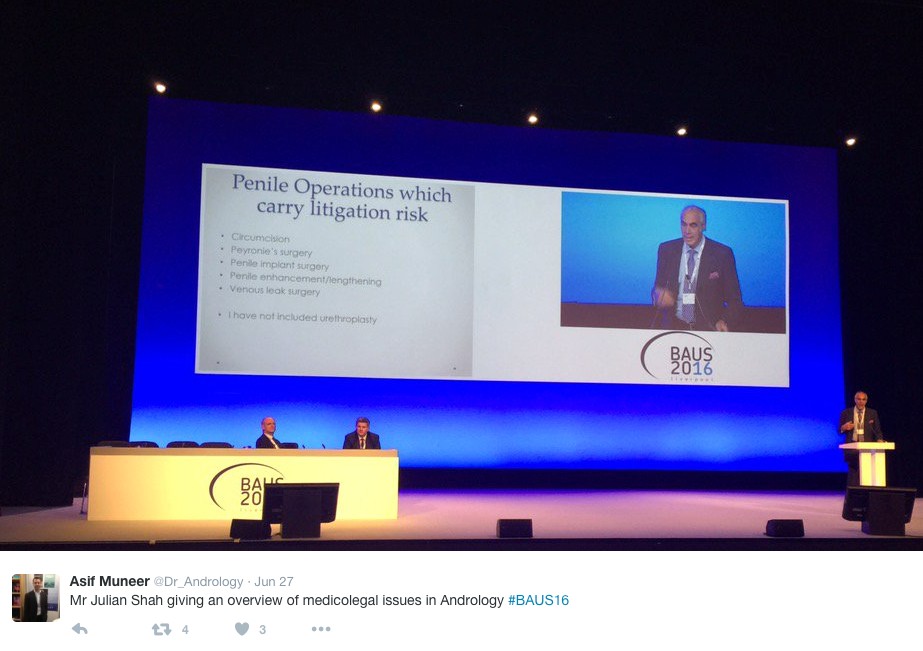
Monday saw a cautionary session on medicolegal aspects in Andrology, focusing on lawsuits over the last year. Mr Mark Speakman presented on the management issue of testicular torsion. This sparked further discussion on emergency cover for paediatrics with particular uncertainty noted at 4 and 5 year olds and great variation in approach dependent on local trust policy. Mr Julian Shah noted the most litigious areas of andrology, with focus on cosmesis following circumcisions. Therefore serving a reminder on the importance of good consent to manage patients’ expectations.
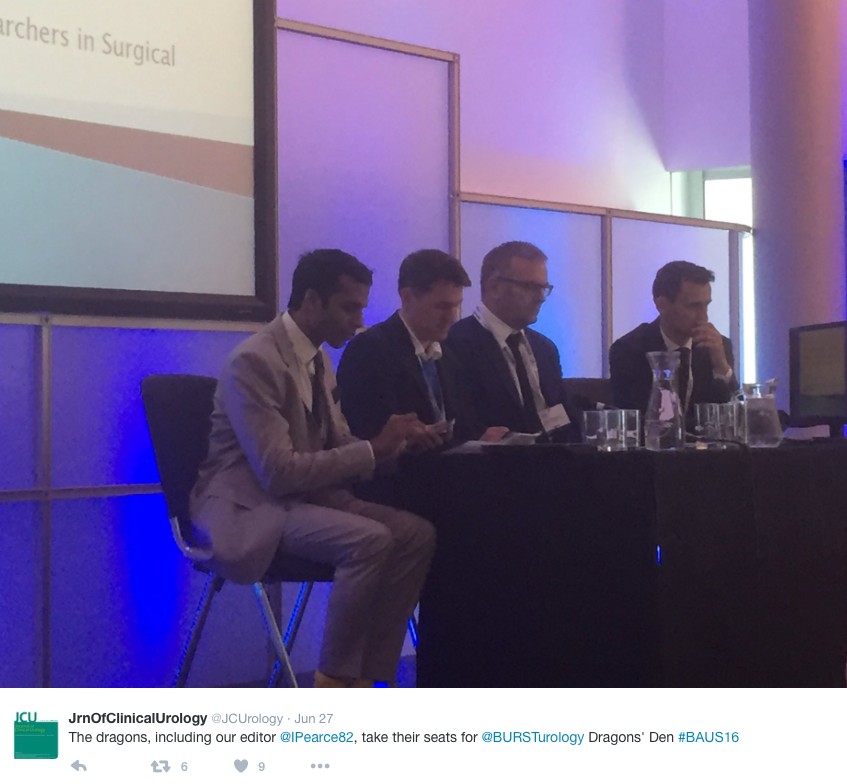
In the Dragons’ Den, like the TV show, junior urologists pitched their ideas for collaborative research projects, to an expert panel. This year’s panel was made up of – Mark Emberton, Ian Pearce, and Graeme MacLennan. The session was chaired by Veeru Kasivisvanathan, Chair of the BURST Research Collaborative.

Eventual winner Ben Lamb, a trainee from London, presented “Just add water”. The pitch was for an RCT to investigate the efficacy of water irrigation following TURBT against MMC in reducing tumour recurrence. Ben proposed that water, with its experimental tumouricidal properties, might provide a low risk, low cost alternative as an adjuvant agent following TURBT. Judges liked the scientific basis for this study and the initial planning for an RCT. The panel discussed the merits of non-inferiority vs. superiority methodology, and whether the team might compare MMC to MMC with the addition of water, or water instead of MMC. They Dragons’ suggested that an initial focus group to investigate patients’ views on chemotherapy might help to focus the investigation and give credence to the final research question, important when making the next pitch- to a funding body, or ethics committee.
Other proposals were from Ryad Chebbout, working with Marcus Cumberbatch, an academic trainee from Sheffield. Proposing to address the current controversy over the optimal surgical technique for orchidopexy following testicular torsion. His idea involved conducting a systematic review, a national survey of current practice followed by a Delphi consensus meeting to produce evidence based statement of best practice. The final presentation was from Sophia Cashman, East of England Trainee for an RCT to assess the optimal timing for a TWOC after urinary retention. The panel liked the idea of finally nailing down an answer to this age-old question.

Waking up on Tuesday with England out of the European football cup as well as Europe the conference got underway with an update from the PROMIS trial (use of MRI to detect prostate cancer). Early data shows that multi-parametric MRI may be accurate enough to help avoid some prostate biopsies.

The SURG meeting provided useful information for trainees, with advice on progressing through training and Consultant interviews. A debate was held over run through training, which may well be returning in the future. The Silver cystoscope was awarded to Professor Rob Pickard voted for by the trainees in his deanery, for his devotion to their training.
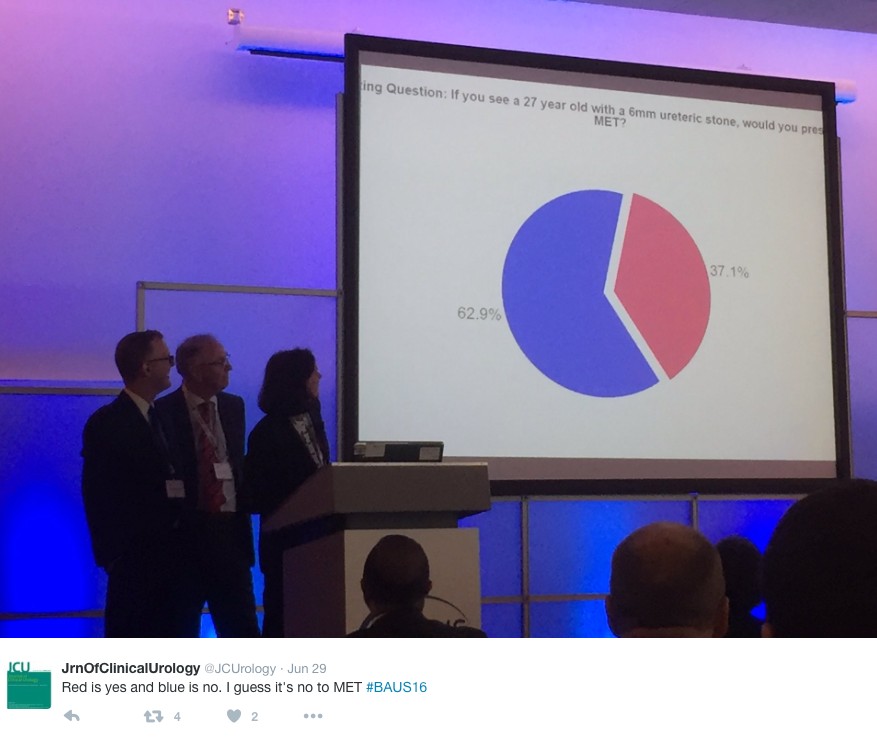
Wednesday continued the debate on medical expulsion therapy (MET) for ureteric stones following the SUSPEND trial. Most UK Urologists seem to follow the results of the trial and have stopped prescribing alpha blockers to try and aid stone passage and symptoms. However the AUA are yet to adopt this stance and feel that a sub analysis shows some benefit for stones >5mm, although this is not significant and pragmatic outcomes. Assistant Professor John Hollingsworth (USA) argued for MET, with Professor Sam McClinton (UK) against. A live poll at the end of the session showed 62.9% of the audience persuaded to follow the SUSPEND trial evidence and stop prescribing MET.
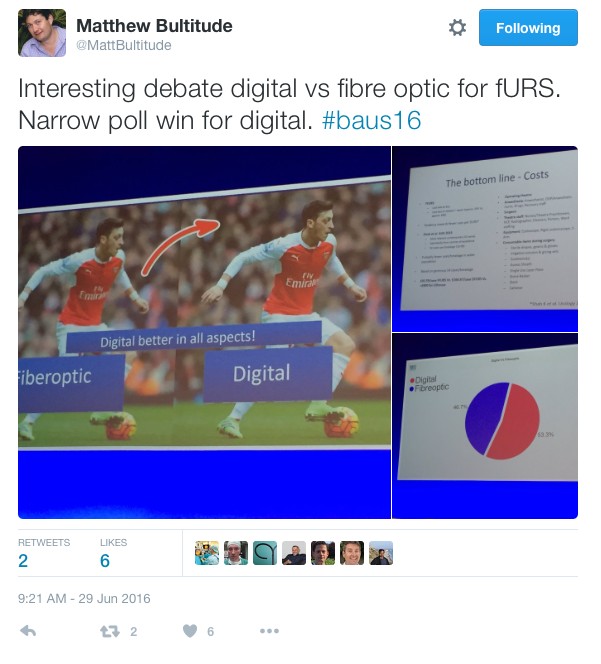
In the debate of digital versus fibreoptic scopes for flexible ureteroscopy digital triumphed, but with a narrow margin.
In other updates and breaking news it appears that BCG is back! However during the shortage EMDA has shown itself to be a promising alternative in the treatment of high grade superficial bladder cancer.
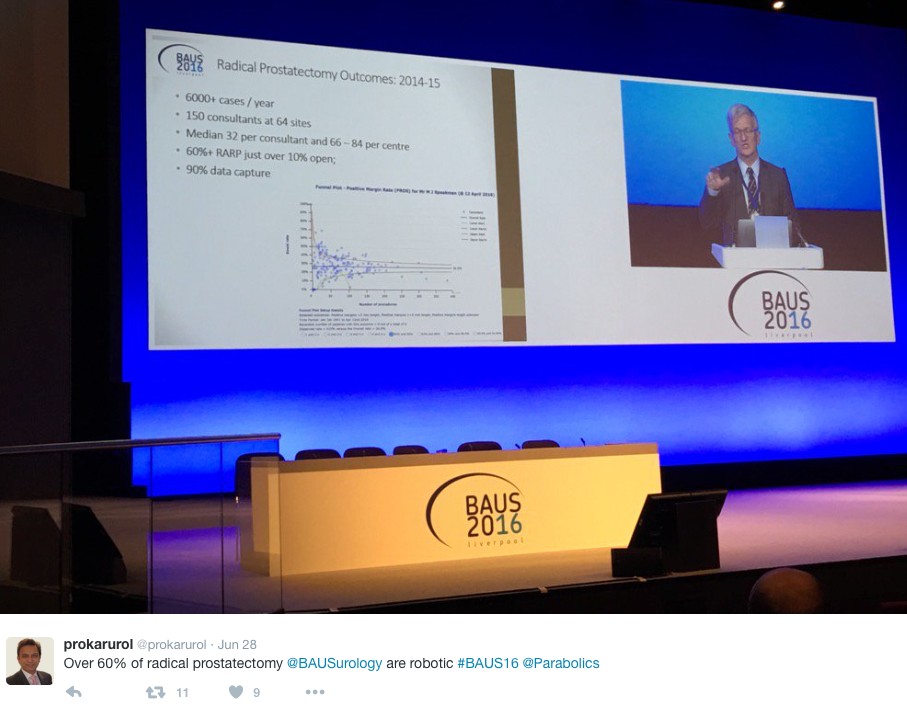
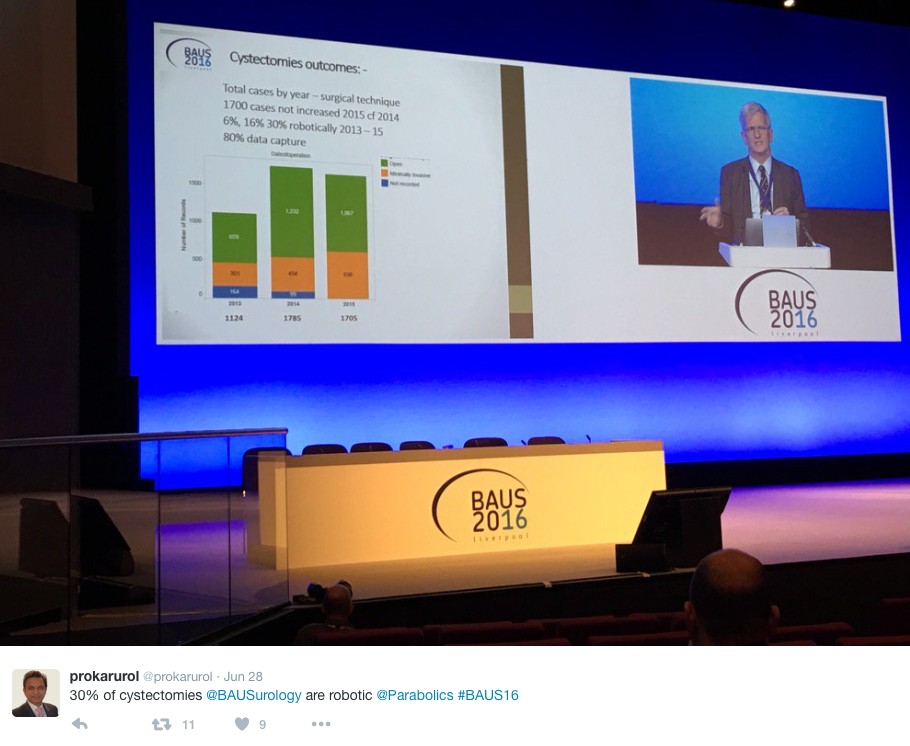
The latest BAUS nephrectomy data shows that 90% are performed by consultant, with 16 on average per consultant per year. This raises some issues for registrar training, however with BAUS guidelines likely to suggest 20 as indicative numbers this is looking to be an achievable target for most consultants. Robotic advocates will be encouraged, as robotic partial nephrectomy numbers have overtaken open this year. The data shows 36% of kidney tumours in the under 40 years old are benign. Will we have to consider biopsying more often? However data suggests we should be offering more cytoreductive nephrectomies, with only roughly 1/10 in the UK performed compared to 3/10 in the USA.
The andrology section called for more recruitment to The MASTER trial (Male slings vs artificial urinary sphincters), whereas the OPEN trial has recruited(open urethroplasty vs optical urethotomy). In the treatment of Peyronie’s disease collagenase has been approved by NICE but not yet within the NHS.
Endoluminal endourology presentation showed big increases in operative numbers with ureteroscopy up by 50% and flexible ureteroscopy up by 100%. Stents on strings were advocated to avoid troubling stent symptoms experienced by most patients. New evidence may help provide a consensus on defining “stone free” post operation. Any residual stones post-operatively less than 2mm were shown to pass spontaneously and therefore perhaps may be classed as “stone free”.
Big changes seem likely in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia, with a race to replace the old favorite TURP. Trials have of TURP (mono and bipolar) vs greenlight laser are already showing similar 2 year outcomes with the added benefit of shorter hospital stays and less blood loss. UROLIFT is an ever more popular alternative with data showing superiority to TURP in lifestyle measures, likely because it preserves sexual function, and we are told it can be performed as a 15 minute day case operation. The latest new therapy is apparently “Aquabeam Aquablation”, using high pressured water to remove the prostate. Non surgical treatments are also advancing with ever more accurate super selective embolisation of the prostatic blood supply.

This year all accepted abstracts were presented in moderated EPoster sessions. The format was extremely successful removing the need for paper at future conferences? A total of 538 abstracts were submitted and 168 EPosters displayed. The winner of best EPoster was P5-5 Altaf Mangera: Bladder Cancer in the Neuropathic Bladder.
The best Academic Paper winner was Mark Salji of the CRUK Beatson institute, titled “A Urinary Peptide Biomarker Panel to Identify Significant Prostate Cancer”. Using capillary electrophoresis coupled to mass spectrometry (CE-MS) they analysed 313 urine samples from significant prostate cancer patients (Gleason 8-10 or T3/4 disease) and low grade control disease. They identified 94 peptide urine biomarkers which may provide a useful adjunct in identifying significant prostate cancer from insignificant disease.
The Office of Education offered 20 courses. Popular off-site courses were ultrasound for the Urologist, at Broadgreen Hospital, a slightly painful 30 min drive from the conference centre. However well worth the trip, delivered by Radiology consultants this included the chance to scan patients volunteers under guidance, with separate stations for kidneys, bladder and testicles and learning the “knobology” of the machines.
Organised by Tamsin Greenwell with other consultant experts in female, andrology and retroperitoneal cancer, a human cadaveric anatomy course was held at Liverpool university. The anatomy teaching was delivered by both Urology consultants and anatomists allowing for an excellent combination of theory and functional anatomy.
BAUS social events are renowned and with multiple events planned most evenings were pretty lively. The official drinks reception was held at the beautiful Royal Liver Building. The venue was stunning with great views over the waterfront and the sun finally shining. Several awards were presented including the Gold cystoscope to Mr John McGrath for significant contribution to Urology within 10 years appointment as consultant. The Keith Yeates medal was awarded to Mr Raj Pal, the most outstanding candidate in the first sitting of the intercollegiate specilaity examination, with a score of over 80%.

During the conference other BAUS awards presented include the St Peter’s medal was awarded to Margeret Knowles, Head of section of molecular oncology, Leeds Institute of Cancer and Pathology, St James University hospital Leeds. The St Paul’s medal awarded to Professor Joseph A. Smith, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, USA. The Gold medal went to Mr. Tim Terry, Leicester General Hospital.
An excellent industry exhibition was on display, with 75 Exhibiting Companies present. My personal fun highlight was a flexible cystoscope with integrated stent remover, which sparked Top Gear style competiveness when the manufacturer set up a time-trial leaderboard. Obviously this best demonstrated the speed of stent removal with some interesting results…

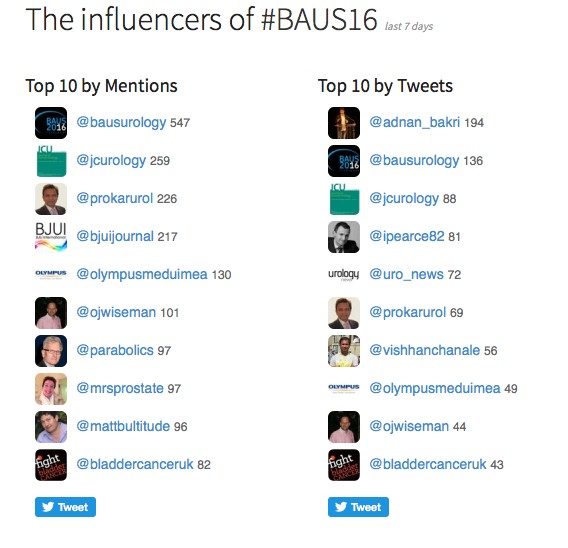
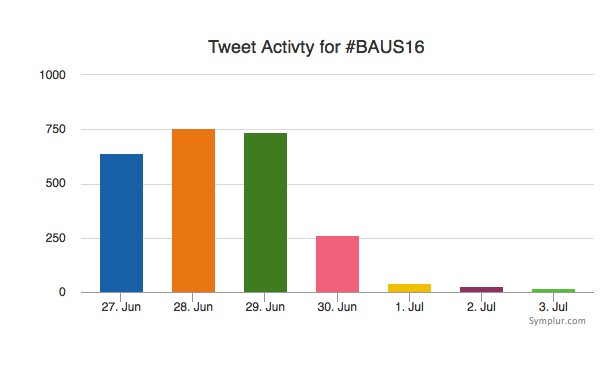
Social media review shows good contribution daily.
Thanks BAUS a great conference, very well organised and delivered with a great educational and social content, looking forward to Glasgow 2017! #BAUS2017 #Glasgow #BAUSurology
Nishant Bedi
Specialist Training Registrar North West London
Twitter: @nishbedi