5th International Neuro-Urology Meeting (INUM)
The Annual Congress of the International Neuro-Urology Society (INUS), organized by the Swiss Continence Foundation (SCF)
Neurogenic urinary tract, sexual and bowel dysfunction is highly prevalent and affects the lives of millions of people worldwide. It has a major impact on quality of life and, besides the debilitating manifestations for patients, it also imposes a substantial economic burden on every healthcare system.
It was a great honour and pleasure to organize the 5th International Neuro-Urology Meeting (INUM), which took place from 25-28 January 2017, in Zürich, Switzerland. We are proud to announce that the International Neuro-Urology Meeting, organized under the umbrella of the Swiss Continence Foundation (www.swisscontinencefoundation.ch), has become the official annual congress of the International Neuro-Urology Society (INUS, www.neuro-uro.org), a charitable, non-profit organization aiming to promote all areas of Neuro-Urology at a global level and whose inauguration was inspired during the last INUMs.
The world’s leading experts in Neuro-Urology provided an overview on the latest advances in research and clinical practice of this rapidly developing and exciting discipline. This unique meeting combined state-of-the-art lectures, lively panel discussions, and hands-on workshops with emphasis placed on interactive components. There were many opportunities to exchange thoughts, experiences and ideas and also to make new friendship.
The Swiss Continence Foundation Award: To promote the next generation of outstanding young researchers and clinicians who represent the future of Neuro-Urology, the prestigious Swiss Continence Foundation Award of 10’000 Swiss francs was awarded to the best contribution from a young Neuro-Urology talent: Marc Schneider from Zürich, Switzerland, convinced the international jury with the presentation of his PhD project “Anti-Nogo-A antibodies as a potential causal treatment for neurogenic lower urinary tract dysfunction after spinal cord injury”. He demonstrated in an animal model that intrathecally applied antibodies against the central nervous system protein Nogo-A which inhibits nerve fibre growth had beneficial effects on lower urinary tract dysfunction in rats with incomplete spinal cord injury by re-establishing a physiological micturition and preventing detrusor sphincter dyssynergia. This effect presumably occurs due to neuronal re-wiring of descending micturition circuits facilitated by the anti-Nogo-A antibodies. Anti-Nogo-A immunotherapy enters currently clinical trials in humans and could become a unique causal treatment option for lower urinary tract dysfunction in patients with incomplete spinal cord injury.
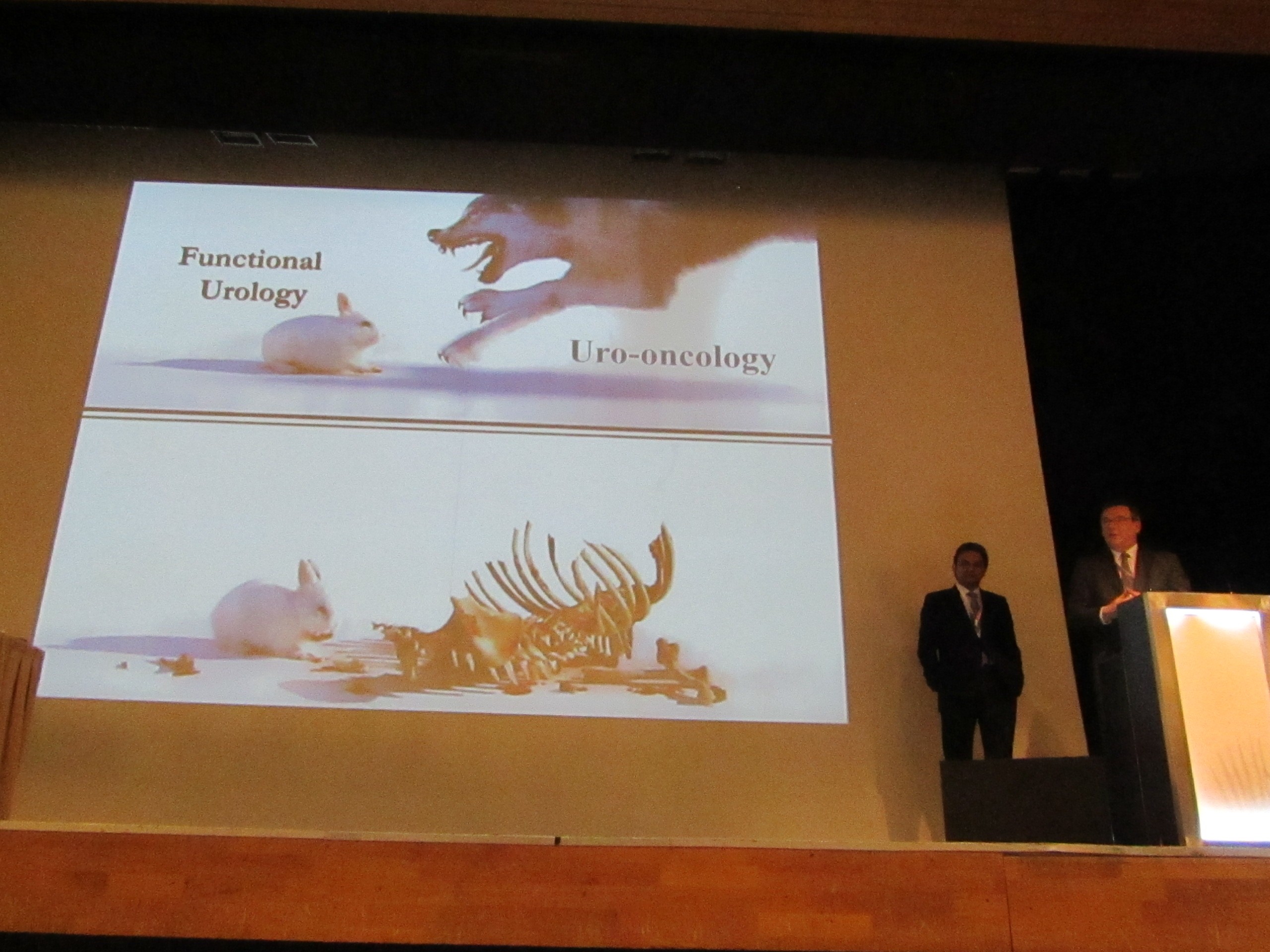
One of many other highlights was the joint presentation of the EAU Secretary General Christopher R. Chapple and the BJUI Editor-in-Chief Prokar Dasgupta on the challenging topic “What should the neuro-urologist learn from the onco-urologist and vice-versa?”
Finally, we are delighted to announce the 6th International Neuro-Urology Meeting to be held in Zürich, 25 to 28 January 2018. Save the date! For details please visit: www.swisscontinencefoundation.ch. We are looking forward to seeing you in Zürich!
Thomas M. Kessler, SCF Chairman and INUS Vice-President
Ulrich Mehnert, SCF Vice-Chairman and INUS Treasurer