Residents’ podcast: Urinary continence recovery after radical prostatectomy
Maria Uloko is a Urology Resident at the University of Minnesota Hospital and Giulia Lane is a Female Pelvic Medicine and Reconstructive Surgery Fellow at the University of Michigan.
In this podcast they discuss the BJUI Article of the Week ‘Investigating the mechanism underlying urinary continence recovery after radical prostatectomy: effectiveness of a longer urethral stump to prevent urinary incontinence‘.
Investigating the mechanism underlying urinary continence recovery after radical prostatectomy: effectiveness of a longer urethral stump to prevent urinary incontinence
*Department of Integrative Cancer Therapy and Urology, Kanazawa University Graduate School of Medical Science, Kanazawa, Japan; †Department of Radiology, Kanazawa University School of Medicine, 13‐1 Takara‐machi, Kanazawa, Ishikawa 920‐8640, Japan
Abstract
Objective
To assess the chronological changes in urinary incontinence and urethral function before and after radical prostatectomy (RP), and to compare the findings of pelvic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) before and after RP to evaluate the anatomical changes.
Patients and Methods
In total, 185 patients were evaluated with regard to the position of the distal end of the membranous urethra (DMU) on a mid‐sagittal MRI slice and urethral sphincter function using the urethral pressure profilometry. The patients also underwent an abdominal leak point pressure test before RP and at 10 days and 12 months after RP. The results were then compared with the chronological changes in urinary incontinence.
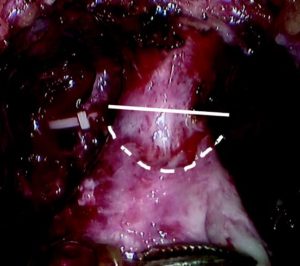
Fig. 1 Intraoperative view of the apex of the prostate transection line between the urethra and prostate at the normal (straight line) and long urethral stump (dashed line) positions.
Results
The MRI results showed that the DMU shifted proximally to an average distance of 4 mm at 10 days after RP and returned to the preoperative position at 12 months after RP. Urethral sphincter function also worsened 10 days after RP, with recovery after 12 months. The residual length of the urethral stump and urinary incontinence were significantly associated with the migration length of the DMU at 10 days after RP. The residual length of the urethral stump was a significant predictor of urinary incontinence after RP.
Conclusion
This is the first study to elucidate that the slight vertical repositioning of the membranous urethra after RP causes chronological changes in urinary incontinence. A long urethral residual stump reduces urinary incontinence after RP.
BJUI Podcasts now available on iTunes, subscribe here https://itunes.apple.com/gb/podcast/bju-international/id1309570262