Article of the week: In utero myelomeningocele repair and urological outcomes: the first 100 cases of a prospective analysis
Every week, the Editor-in-Chief selects an Article of the Week from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
In addition to the article itself, there is an editorial written by a prominent member of the urological community and a podcast produced by our Resident podcasters, Giulia Lane and Kyle Johnson. The authors have also kindly produced a video describing their work.
These are intended to provoke comment and discussion and we invite you to use the comment tools at the bottom of each post to join the conversation.
If you only have time to read one article this week, it should be this one.
In utero myelomeningocele repair and urological outcomes: the first 100 cases of a prospective analysis. Is there an improvement in bladder function?
Abstract
Objectives
To evaluate the first 100 cases of in utero myelomeningocele (MMC) repair and urological outcomes in a prospective analysis aiming to define possible improvement in bladder function.
Patients and methods
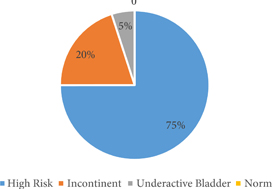
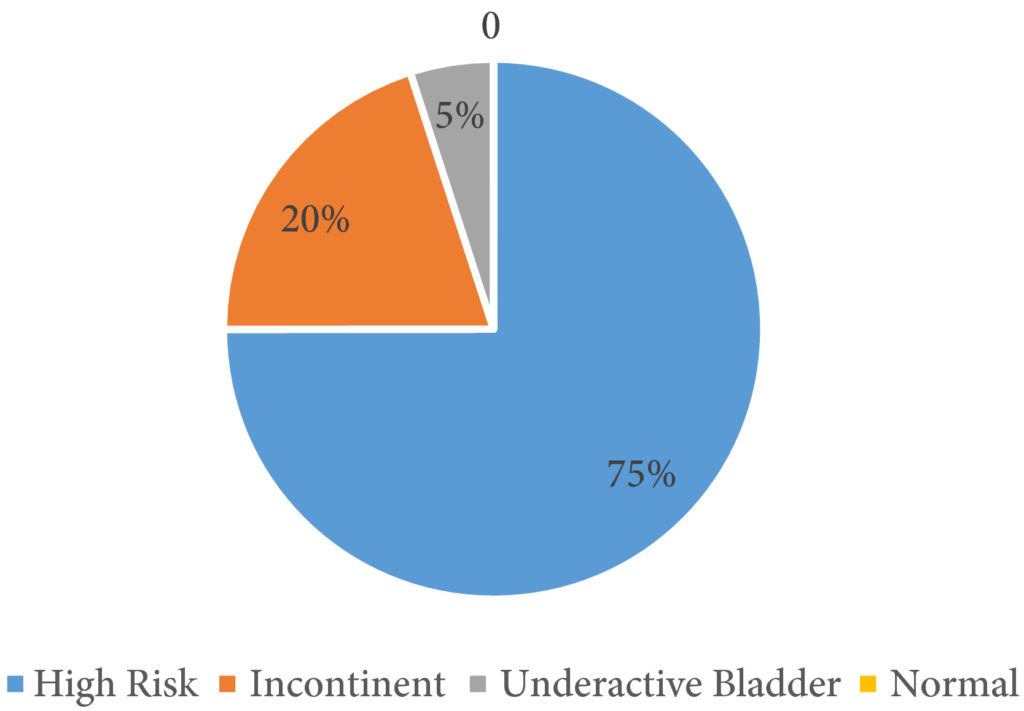
We used a protocol consisting of a detailed medical history, urinary tract ultrasonography, voiding cystourethrography, and urodynamic evaluation. Patients were categorised into four groups: normal, high risk (overactive bladder with a detrusor leak‐point pressure >40 cm H2O and high filling pressures also >40 cm H2O), incontinent, and underactivity (underactive bladder with post‐void residual urine), and patients were treated accordingly.
Fig.2. Hydronephrosis in relation to the underlying bladder pattern.
Results
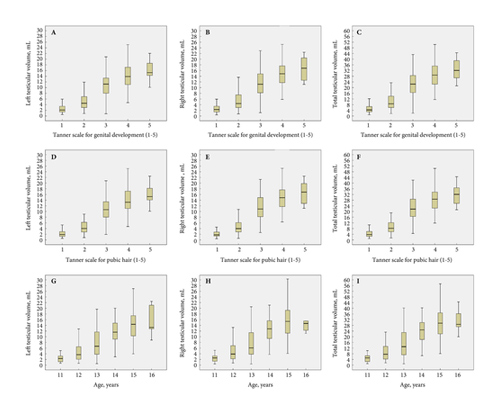
We evaluated 100 patients, at a mean age of 5.8 months (median 4 months), classified as high risk in 52.6%, incontinent in 27.4%, with underactive bladder in 4.2%, and only 14.7% had a normal bladder profile. Clean intermittent catheterisation was initiated in 57.3% of the patients and anticholinergics in 52.6%. Antibiotic prophylaxis was initiated in 19.1% of the patients presenting with vesico‐ureteric reflux.
Conclusion
The high incidence of abnormal bladder patterns suggests little benefit of in utero MMC surgery concerning the urinary tract.