G’day! The 71st annual USANZ Congress, was held in Melbourne and had the biggest attendance on record for the past 6 years. The Urological Nurse’s congress: ANZUNS ran concurrently, encouraging multi disciplinary learning. An excellent and varied educational programme was masterminded by Declan Murphy, Nathan Lawrentschuk and their organising committee. Melbourne provided a great backdrop and soon felt like home with a rich and busy central business district, cultural and sporting venues, the Yarra river flowing past the conference centre, edgy graffiti and hipster coffee shops, plus too many shops, bars and restaurants to visit.
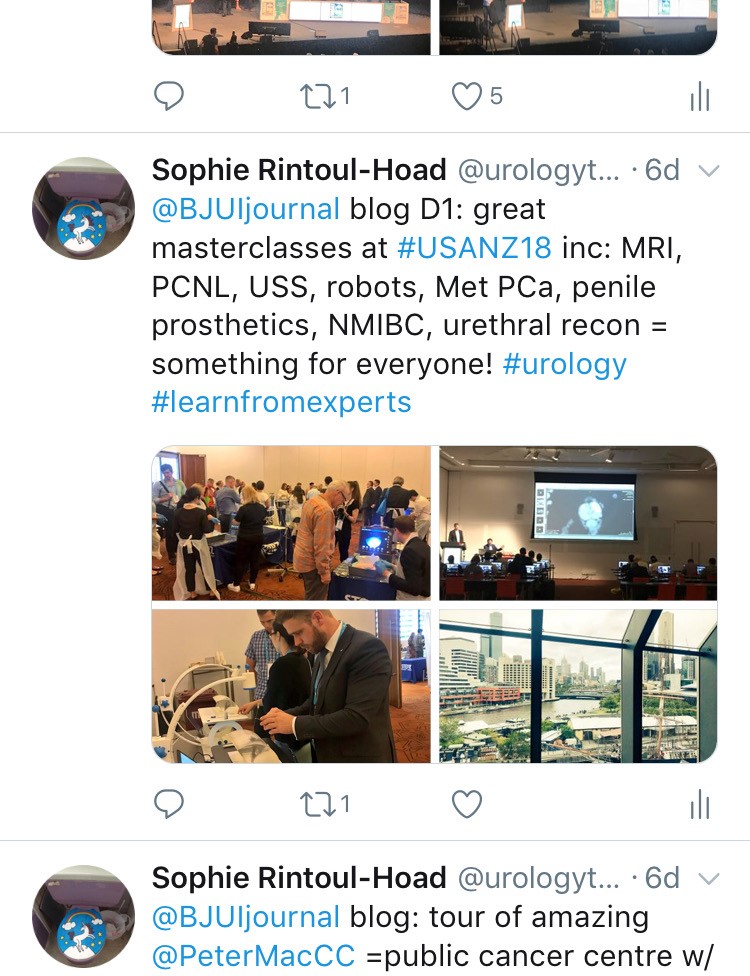 The programme included a day of masterclasses on a range of subjects, including: urological imaging, advanced robotic surgery with a live case from USC, metastatic prostate cancer and penile prosthetics. These were well attended by trainees and consultants alike. The PCNL session (pictured) with Professor Webb was popular and he generously gave his expertise. The session was supported by industry and provided an opportunity to use the latest nephroscopes on porcine models and innovative aids to realistically practice different puncture techniques.
The programme included a day of masterclasses on a range of subjects, including: urological imaging, advanced robotic surgery with a live case from USC, metastatic prostate cancer and penile prosthetics. These were well attended by trainees and consultants alike. The PCNL session (pictured) with Professor Webb was popular and he generously gave his expertise. The session was supported by industry and provided an opportunity to use the latest nephroscopes on porcine models and innovative aids to realistically practice different puncture techniques.
Two plenary sessions were held each morning covering the breadth and depth of urology and were well attended. Dr Sotelo is always a highlight; he presented, to an auditorium of collective gasps, a unique selection of ‘nightmare’ cases His cases gave insight in how intraoperative complications occur and how they can be avoided. Tips, such as zooming out to reassess in times of anatomical uncertainty during laparoscopy or robotic surgery have great impact when you witness the possible consequences. Tim O’Brien shared his priceless insights on performing IVC thrombectomy highlighting the need for preoperative planning, early control of the renal artery and consideration of pre-embolisation. His second plenary on retroperitoneal fibrosis provided clarity on the management of this rare condition highlighting the role of PET imaging and, as with complex upper tract surgery, the importance of a dedicated team.
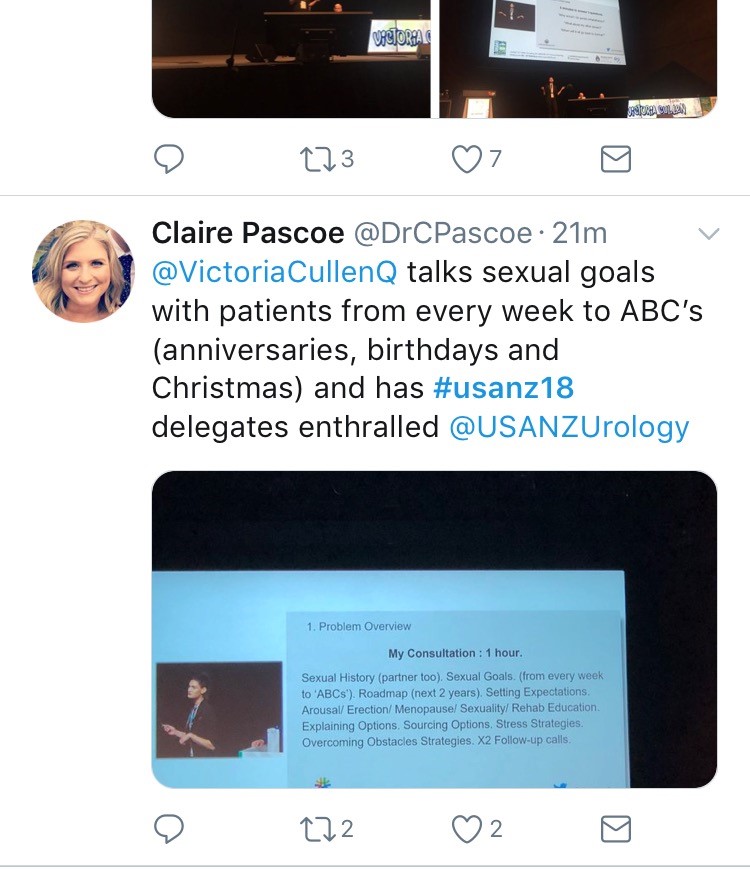 Tony Costello’s captivating presentation covered several myths in robotic prostate surgery, plus the importance of knowing your own outcome figures and a future where robotics will be cost equivalent to laparoscopy. Future technology, progress in cancer genomics and biomarkers were also discussed in various sessions. One example of new technology was Aquablation of the prostate; Peter Gilling presented the WATER trial results suggesting non-inferiority to TURP. A welcome addition to the programme was Victoria Cullen (pictured), a psychologist and Intimacy Specialist who provides education, support and strategies for sexual rehabilitation. She described her typical consultation with men with sexual dysfunction and how to change worries about being ‘normal’ to focusing on what is important to the individual.
Tony Costello’s captivating presentation covered several myths in robotic prostate surgery, plus the importance of knowing your own outcome figures and a future where robotics will be cost equivalent to laparoscopy. Future technology, progress in cancer genomics and biomarkers were also discussed in various sessions. One example of new technology was Aquablation of the prostate; Peter Gilling presented the WATER trial results suggesting non-inferiority to TURP. A welcome addition to the programme was Victoria Cullen (pictured), a psychologist and Intimacy Specialist who provides education, support and strategies for sexual rehabilitation. She described her typical consultation with men with sexual dysfunction and how to change worries about being ‘normal’ to focusing on what is important to the individual.
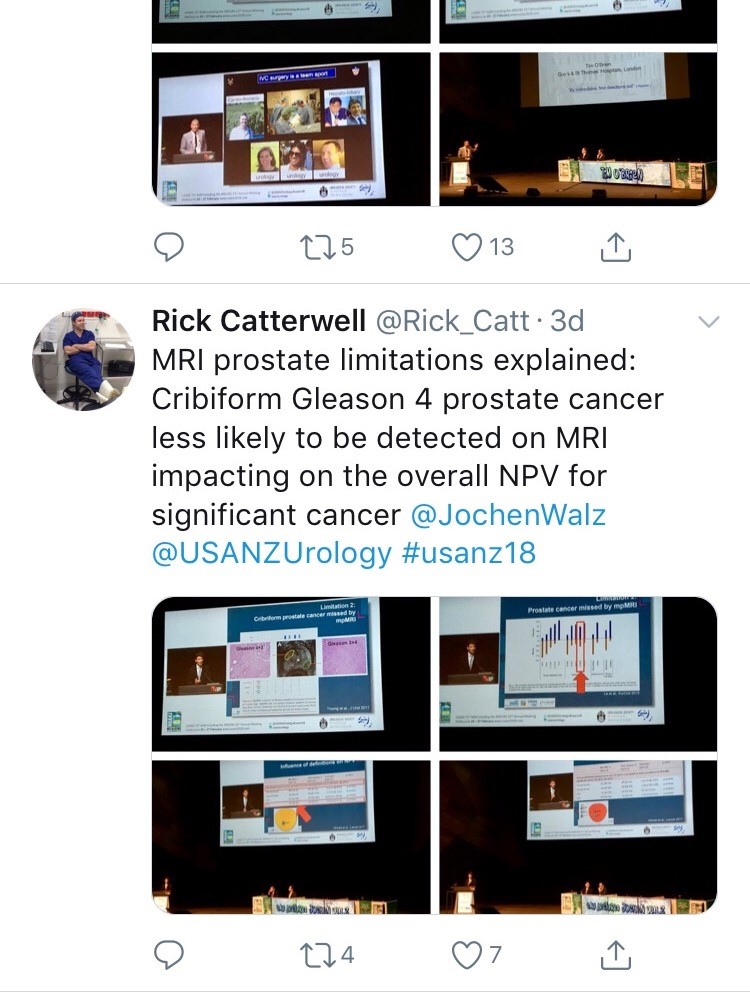 Joint plenary sessions with the AUA and EAU were a particular highlight. Prof Chris Chapple confirmed the need for robust, evidence guidelines which support clinical decision making; and in many cases can be used internationally. He suggested collaboration is crucial between us as colleagues and scientists working in the field of urology. Stone prevention and analysis of available evidence was described by Michael Lipkin; unfortunately stone formers are usually under-estimaters of their fluid intake so encouragement is always needed! Amy Krambeck presented evidence for concurrent use of anticoagulants and antiplatelets during BOO surgery and suggested there can be a false sense of security when stopping these medications as it isn’t always safe. She championed HoLEP as her method of BOO surgery and continues medications, although the evidence does show blood transfusion rate may be higher. She also uses a fluid warming device which has less bleeding and therefore improved surgical vision; importantly it is preferred by her theatres nurses! MRI of the prostate was covered by many different speakers, however Jochen Walz expertly discussed the limitations of MRI in particular relating negative predictive value (pictured). He eloquently explained the properties of cribiform Gleason 4 prostate cancer and how this variant contributed to the incidence of false negatives.
Joint plenary sessions with the AUA and EAU were a particular highlight. Prof Chris Chapple confirmed the need for robust, evidence guidelines which support clinical decision making; and in many cases can be used internationally. He suggested collaboration is crucial between us as colleagues and scientists working in the field of urology. Stone prevention and analysis of available evidence was described by Michael Lipkin; unfortunately stone formers are usually under-estimaters of their fluid intake so encouragement is always needed! Amy Krambeck presented evidence for concurrent use of anticoagulants and antiplatelets during BOO surgery and suggested there can be a false sense of security when stopping these medications as it isn’t always safe. She championed HoLEP as her method of BOO surgery and continues medications, although the evidence does show blood transfusion rate may be higher. She also uses a fluid warming device which has less bleeding and therefore improved surgical vision; importantly it is preferred by her theatres nurses! MRI of the prostate was covered by many different speakers, however Jochen Walz expertly discussed the limitations of MRI in particular relating negative predictive value (pictured). He eloquently explained the properties of cribiform Gleason 4 prostate cancer and how this variant contributed to the incidence of false negatives.
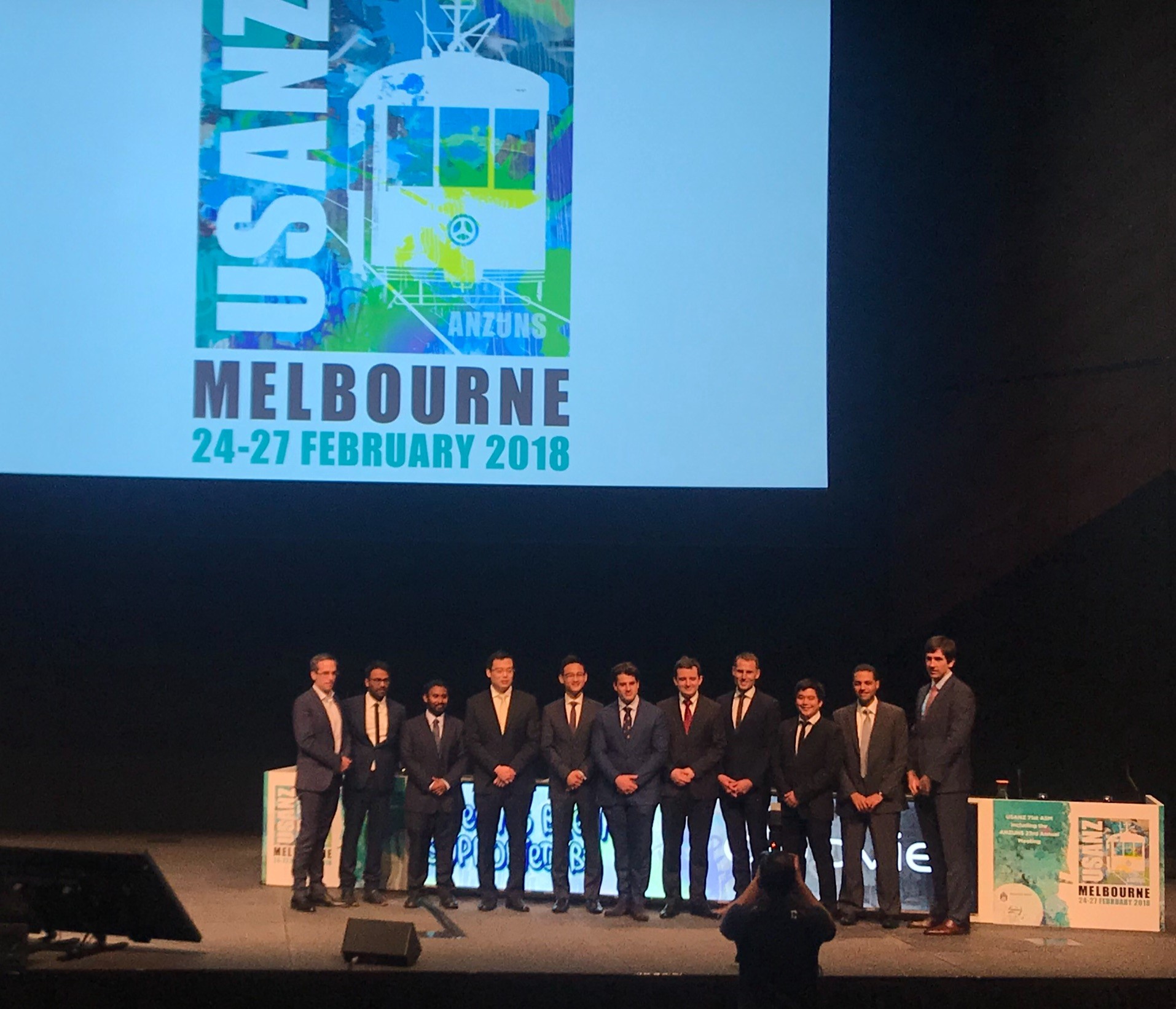 Moderated poster and presentation sessions showcased research and audit projects from the UK, Australia, New Zealand and beyond, mainly led by junior urologists. The best abstracts submitted by USANZ trainees were invited to present for consideration of Villis Marshall and Keith Kirkland prizes. These prestigious prizes were valiantly fought for and reflected high quality research completed by the trainees. Projects included urethral length and continence, no need for lead glasses, obesity and prostate cancer, multi-centre management of ureteric calculi, mental health of surgical trainees and seminal fluid biomarkers in prostate cancer. This enthusiasm for academia will undoubtedly stand urology in good stead for the future; this line up (pictured) is one to watch!
Moderated poster and presentation sessions showcased research and audit projects from the UK, Australia, New Zealand and beyond, mainly led by junior urologists. The best abstracts submitted by USANZ trainees were invited to present for consideration of Villis Marshall and Keith Kirkland prizes. These prestigious prizes were valiantly fought for and reflected high quality research completed by the trainees. Projects included urethral length and continence, no need for lead glasses, obesity and prostate cancer, multi-centre management of ureteric calculi, mental health of surgical trainees and seminal fluid biomarkers in prostate cancer. This enthusiasm for academia will undoubtedly stand urology in good stead for the future; this line up (pictured) is one to watch!
 The Trade hall provided a great networking space to be able to meet with friends and colleagues and engage with industry. It also hosted poster presentation sessions, with a one minute allocation for each presenter – which really ensures a succinct summary of the important findings (pictured)! It was nice to meet with Australian trainees and we discussed the highs and lows of training and ideas for fellowships. Issues such as clinical burden and operative time, selection into the specialty, cost of training, burn out and exam fears were discussed and shared universally; however there is such enthusiasm, a passion for urology and inspirational trainers which help balance burdens that trainees face. Furthermore, USANZ ‘SET’ Trainees were invited to meet with the international faculty in a ‘hot seat’ style session which was an enviable opportunity to discuss careers and aspirations.
The Trade hall provided a great networking space to be able to meet with friends and colleagues and engage with industry. It also hosted poster presentation sessions, with a one minute allocation for each presenter – which really ensures a succinct summary of the important findings (pictured)! It was nice to meet with Australian trainees and we discussed the highs and lows of training and ideas for fellowships. Issues such as clinical burden and operative time, selection into the specialty, cost of training, burn out and exam fears were discussed and shared universally; however there is such enthusiasm, a passion for urology and inspirational trainers which help balance burdens that trainees face. Furthermore, USANZ ‘SET’ Trainees were invited to meet with the international faculty in a ‘hot seat’ style session which was an enviable opportunity to discuss careers and aspirations.
In addition to the Congress I was fortunate to be invited for a tour and roof-top ‘barbie’ at the Peter Mac Cancer centre; plus a visit to Adelaide with Rick (Catterwell, co-author) seeing his new hospital and tucking into an inaugural Aussie Brunch. Peter Mac and Royal Adelaide Hospital facilities indicated an extraordinary level of investment made by Federal and State providers; the Peter Mac in particular had impressive patient areas, radiotherapy suites and ethos of linking clinical and research. However beyond glossy exteriors Australian public sector clinicians voiced concerns regarding some issues similar to those we face in the NHS.
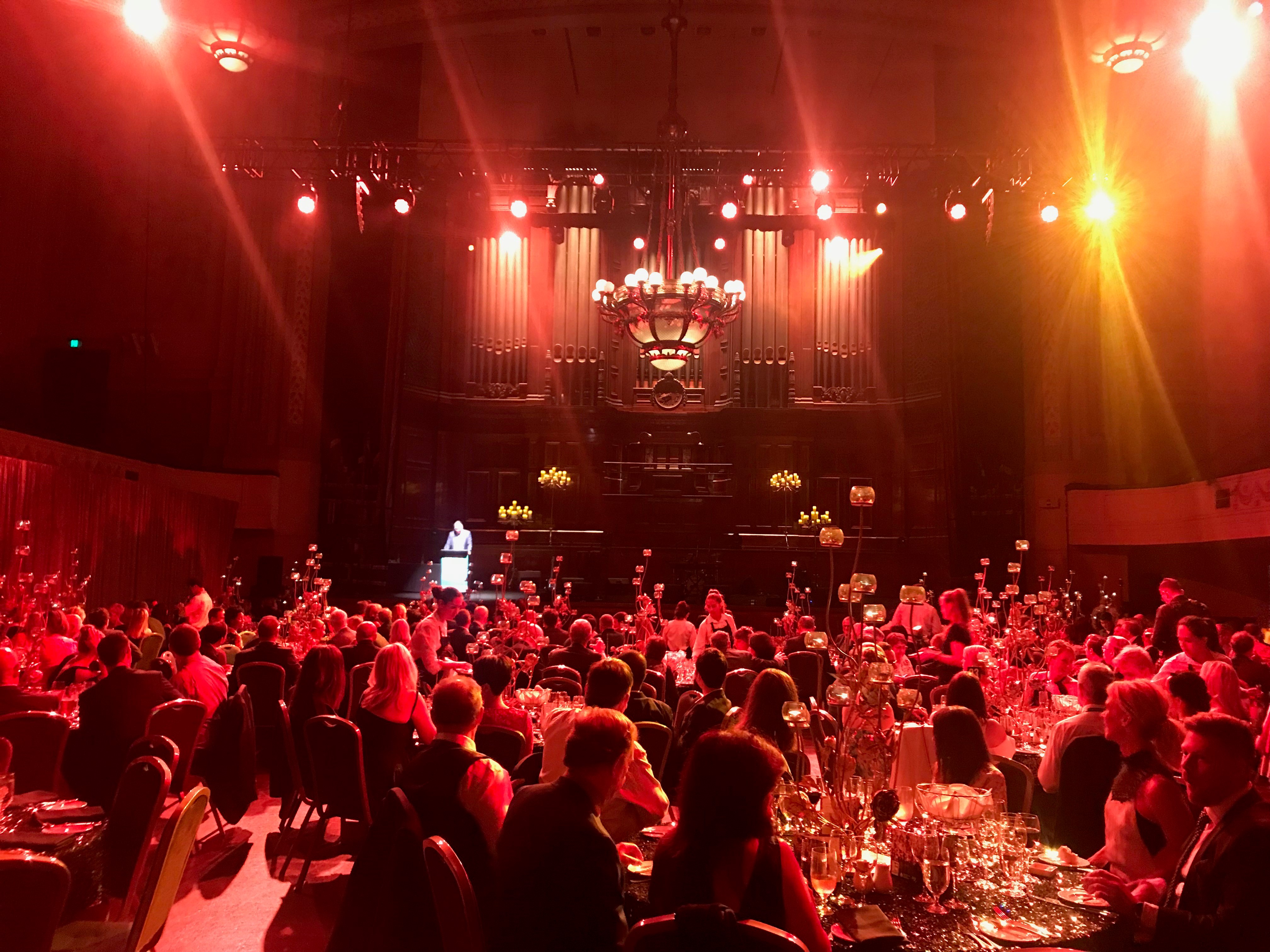 Despite the distance of travelling to Melbourne and the inevitable jet lag the world does feels an increasingly smaller place and the Urological world even more so. There is a neighbourly relationship between the UK, Australia and New Zealand as evidenced by many familiar faces at USANZ who have worked between these countries; better for the new experiences and teaching afforded to them by completing fellowships overseas. The Gala Dinner was a great chance to unwind, catch up with friends and celebrate successes in the impressive surrounding of Melbourne Town Hall (pictured); the infamous organ played particularly rousing rendition of Phantom of the Opera on arrival.
Despite the distance of travelling to Melbourne and the inevitable jet lag the world does feels an increasingly smaller place and the Urological world even more so. There is a neighbourly relationship between the UK, Australia and New Zealand as evidenced by many familiar faces at USANZ who have worked between these countries; better for the new experiences and teaching afforded to them by completing fellowships overseas. The Gala Dinner was a great chance to unwind, catch up with friends and celebrate successes in the impressive surrounding of Melbourne Town Hall (pictured); the infamous organ played particularly rousing rendition of Phantom of the Opera on arrival.
The enthusiasm to strive for improvement is similar both home and away and therefore collaboration both nationally and internationally is integral for the progress of urology. The opening address by USANZ President included the phrase ‘together we can do so much more’ and this theme of collaboration was apparent throughout the conference. The future is bright with initiatives led by enthusiastic trainee groups BURST and YURO to collect large volume, high quality data from multiple centres, such as MIMIC which was presented by Dr Todd Manning. Social media, telecommunications and innovative technology should be used to further the specialty, especially with research and in cases of rare diseases – such as RPF. Twitter is a tool that can be harnessed and was certainly used freely with the hashtag #USANZ18. Furthermore, utilisation of educational learning platforms such as BJUI knowledge and evidence based guidelines help to facilitate high quality Urological practice regardless of state or country.
So we’d like to extend a huge thank you to Declan, Nathan and the whole team, and congratulate them for a successful, educational and friendly conference; all connections made will I’m sure last a lifetime and enable us to do more together.
Sophie Rintoul-Hoad and Rick Catterwell