Highlights from #BAUS15

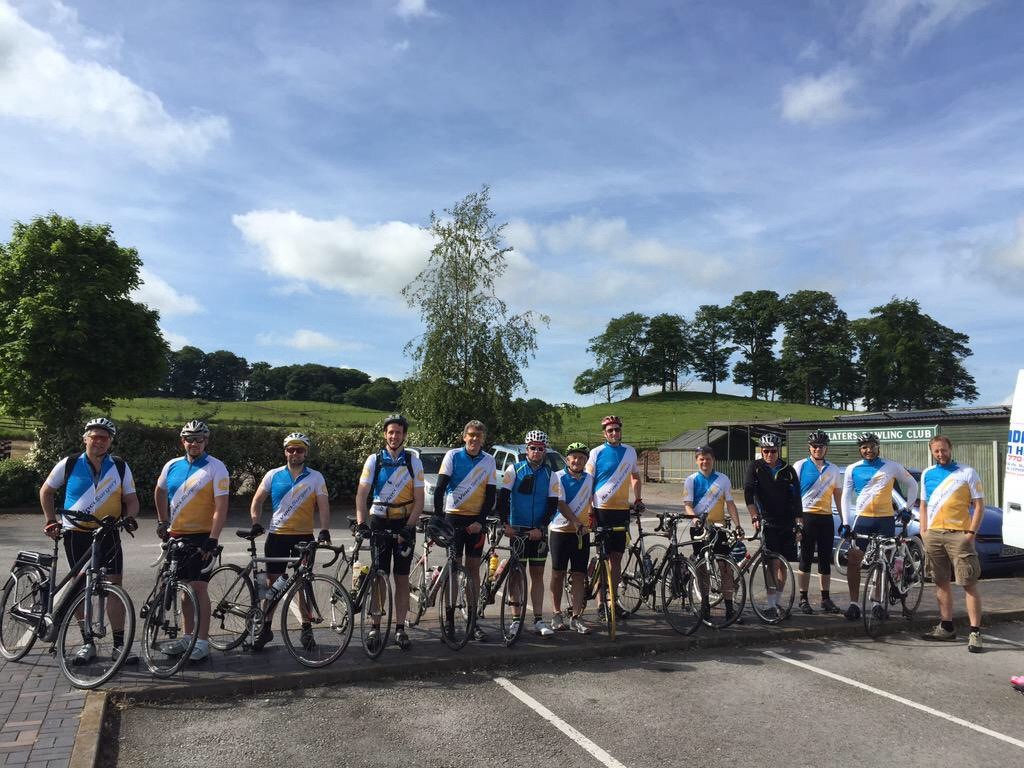
#BAUS15 started to gain momentum from as early as the 26th June 2014 and by the time we entered the Manchester Central Convention Complex well over 100 tweets had been made. Of course it wasn’t just Twitter that started early with a group of keen urologists cycling 210 miles to conference in order to raise money for The Urology Foundation.
Monday 15th June 2015
By the time the cyclists arrived conference was well under way with the andrology, FNUU and academic section meetings taking place on Monday morning:
- The BJU International Prize for the Best Academic Paper was awarded to Richard Bryant from the University of Oxford for his work on epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition changes found within the extraprostatic extension component of locally invasive prostate cancers.
- Donna Daly from the University of Sheffield received the BJUI John Blandy prize for her work on Botox, demonstrating reductions in afferent bladder signaling and urothelial ATP release.
- Professor Reisman’s talk on ‘Porn, Paint and Piercing’ as expected drew in the crowds and due to a staggering 44% complication rate with genital piercings it is important for us to try to manage these without necessarily removing the offending article as this will only serve to prevent those in need from seeking medical attention.
- With the worsening worldwide catastrophe of antibiotic resistance, the cycling of antibiotics for prevention of recurrent UTIs is no longer recommended. Instead, Tharani Nitkunan provided convincing evidence for the use of probiotics and D-Mannose.
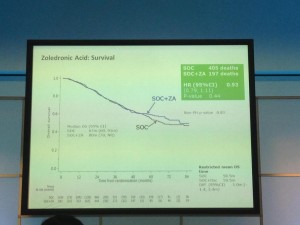
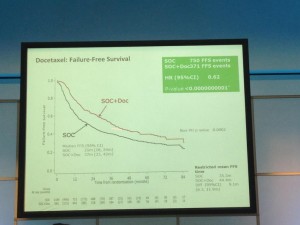
The afternoon was dominated by the joint oncology and academic session with Professor Noel Clarke presenting the current data from the STAMPEDE trial. Zolendronic acid conferred no survival benefit over hormones alone and consequently has been removed from the trial (stampede 1). However, Docetaxal plus hormones has shown benefit, demonstrated significantly in M1 patients with disease-free survival of 65 months vs. 43 months on hormones alone (Hazard ratio 0.73) (stampede 2). This means that the control arm of M1 patients who are fit for chemotherapy will now need to be started on this treatment as the trial continues to recruit in enzalutamide, abiraterone and metformin arms.
The evening was rounded off with the annual BAUS football tournament won this year by team Manchester (obviously a rigged competition!), whilst some donned the
lycra and set out for a competition at the National Cycle Centre. For those of us not quite so energetic, it was fantastic to catch up with old friends at the welcome drinks reception.
Tuesday 16th June 2015
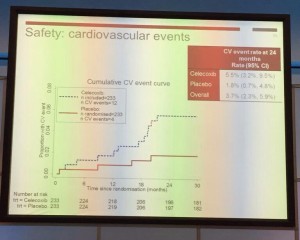
Tuesday kicked off bright and early with Professor John Kelly presenting results from the BOXIT clinical trial, which has shown some benefit over standard treatment of non-muscle invasive bladder cancer, but with significant cardiovascular toxicity.
The new NICE bladder cancer guidelines were presented with concerns voiced by Professor Marek Babjuk over discharging low-risk bladder cancer at 12 months given a quoted 30-50% five-year recurrence risk. Accurate risk stratification, it would seem, is going to be key.
The President’s address followed along with the presentation of the St. Peter’s medal for notable contribution to the advancement of urology, which was presented to Pat Malone from Southampton General Hospital. Other medal winners included Adrian Joyce who received the BAUS Gold Medal, and the St. Paul’s medal went to Mark Soloway.
A plethora of other sessions ensued but with the help of the new ‘native’ BAUS app my programme was already conveniently arranged in advance:
- ‘Heartsink Conditions’ included pelvic and testicular pain and a fascinating talk by Dr Gareth Greenslade highlighted the importance of early and motivational referral to pain management services once no cause has been established and our treatments have been exhausted. The patient’s recovery will only start once we have said no to further tests: ‘Fix the thinking’
- Poster sessions are now presented as ‘e-posters’, abolishing the need to fiddle with those little pieces of Velcro and allowing for an interactive review of the posters.
Pravisha Ravindra from Nottingham demonstrated that compliance with periodic imaging of patients with asymptomatic small renal calculi (n=147) in primary care is poor, and indeed, these patients may be better managed with symptomatic imaging and re-referral as no patients required intervention based on radiograph changes alone.
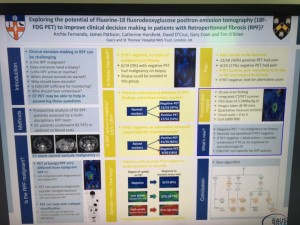
Archana Fernando from Guy’s presented a prospective study demonstrating the value of CTPET in the diagnosis of malignancy in patients with retroperitoneal fibrosis (n=35), as well as demonstrating that those with positive PET are twice as likely to respond to steroids.
Wednesday 17th June 2015
Another new addition to the programme this year was the Section of Endourology ‘as live surgery’ sessions. This was extremely well received and allowed delegates to benefit from observing operating sessions from experts in the field whilst removing the stressful environment and potential for risk to patient associated with live surgery. This also meant that the surgeon was present in the room to answer questions and talk through various steps of the operation allowing for a truly interactive session.
Wednesday saw multiple international speakers dominating the Exchange Auditorium:
- The BJU International guest lecture was given by Professor Hendrik Van Poppel: a heartfelt presentation describing what he believes to be the superiority of surgery over radiotherapy for high-risk localised prostate cancer.
- The Urology Foundation presented the Research Scholar Medal to Ashwin Sachdeva from Freeman Hospital, Newcastle for his work on the ‘Role of mitochondrial DNA mutations in prostate carcinogenesis’. This was followed by an inspiring guest lecture by Inderbir Gill on ‘Robotic Urologic Oncology: the best is yet to come’ with the tag line ‘the only thing that should be open in 2015 is our minds’
- Robotic Surgery in UK Urology: Clinical & Commissioning Priorities was a real highlight in the programme with talks from Jim Adshead and Professor Jens-Uwe Stolzenburg focussing on the fact that only 40% of T1a tumours in the UK were treated with partial (as opposed to radical) nephrectomy, and that the robot really is the ‘game-changer’ for this procedure. Inderbir Gill again took to the stage to stress that all current randomised trials into open vs. robotic cystectomy have used extracorporeal reconstruction and so do not reflect the true benefits of the robotic procedure as the dominant driver of complications is in the open reconstruction.
These lectures were heard by James Palmer, Clinical Director of Specialised Commissioning for NHS England who then discussed difficulties in making decisions to provide new technologies, controlling roll out and removing them if they show no benefit. Clinical commissioning policies are currently being drafted for robotic surgery in kidney and bladder cancer. This led to a lively debate with Professor Alan McNeill having the last word as he pointed out that what urologists spend on the robot to potentially cure cancer is a drop in the ocean compared with what the oncologists spend to palliate!
Thursday 18th June 2015
The BJU International session on evidence-based urology highlighted the need for high-quality evidence, especially in convincing commissioners to spend in a cash-strapped NHS. Professor Philipp Dahm presented a recent review in the Journal of Urology indicated that the quality of systematic reviews in four major urological journals was sub-standard. Assistant Professor Alessandro Volpe then reviewed the current evidence behind partial nephrectomy and different approaches to this procedure.
Another fantastic technology, which BAUS adopted this year, was the BOD-POD which allowed delegates to catch-up on sessions in the two main auditoria that they may have missed due to perhaps being in one of the 21 well designed teaching courses that were available this year. Many of these will soon be live on the BAUS website for members to view.
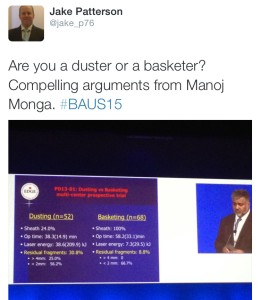
The IBUS and BAUS joint session included a lecture from Manoj Monga from The Cleveland Clinic, which led to the question being posed on Twitter: ‘Are you a duster or a basketer?’The audience was also advised to always stent a patient after using an access sheath unless the patient was pre-stented.
The updates session is always valuable especially for those studying for the FRCS (Urol) exam with far too many headlines to completely cover:
- Endourology: The SUSPEND trial published earlier this year was a large multi-centre RCT that showed no difference in terms of rates of spontaneous passage of ureteric stone, time to stone passage or analgesic use between placebo, tamsulosin and nifedipine. There was a hot debate on this: should we be waiting for the meta-analysis or should a trial of this size and design be enough to change practice?
- Oncology-Prostate: The Klotz et al., paper showed active surveillance can avoid over treatment, with 98% prostate cancer survival at 10 years.
- Oncology-Kidney: Ellimah Mensah’s team from Imperial College London (presented at BAUS earlier in the week) demonstrated that over a 14-year period there were a higher number of cardiovascular-related admissions to hospital in patients who have had T1 renal tumours resected than the general population, but no difference between those who have had partial or radical nephrectomy.
- Oncology-Bladder: Arends’s team presented at EAU in March on the favourable results of hyperthermic mitomycin C vs. BCG in the treatment of intermediate- and high-risk bladder cancer.
- Female and BPH: The BESIDE study has demonstrated increased efficacy with combination solifenacin and mirabegron.
- Andrology: Currently recruiting in the UK is the MASTER RCT to evaluate synthetic sling vs. artificial sphincter in men with post-prostatectomy urinary incontinence.
Overall BAUS yet again put on a varied and enjoyable meeting. The atmosphere was fantastic and the organisers should be proud of the new additions in terms of allowing delegates to engage with new technologies, making for a memorable week. See you all in Liverpool!

Rebecca Tregunna, Urological Trainee, West Midlands Deanery @rebeccatregunna
Dominic Hodgson, Consultant Urologist, Portsmouth @hodgson_dominic