Article of the Month: Comparing survival after RN vs NSS in RCC
Every Month, the Editor-in-Chief selects an Article of the Month from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
In addition to the article itself, there is an accompanying editorial written by a prominent member of the urological community. This blog is intended to provoke comment and discussion and we invite you to use the comment tools at the bottom of each post to join the conversation.
If you only have time to read one article this month, it should be this one.
Testing the external validity of the EORTC randomized trial 30904 comparing overall survival after radical nephrectomy vs nephron-sparing surgery in contemporary North American patients with renal cell cancer
The European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) randomized trial 30904 reported that for solitary renal masses ≤5 cm, radical nephrectomy (RN) was associated with a higher overall survival (OS; primary endpoint): 81%, compared with 76% for nephron-sparing surgery (NSS) at a median follow-up of 9.3 years (P = 0.03). The difference in cancer-specific mortality, however, was not significant. For histologically proven RCC, and after exclusion of patients with positive surgical margins, NSS was associated with equivalent OS compared with RN [1]. It is noteworthy that the renal function outcomes of the two groups in the trial have been reanalysed, showing that renal function does not decline over time after RN, as was expected [2].
The EORTC 30904 trial had difficulty recruiting and randomizing patients, and was criticized for not meeting the accrual goal of 1300 patients. Additionally, the generalizability of the study findings to ‘real-world’ patients has been questioned. Despite the criticism, and more than 20 retrospective studies [3, 4] showing better OS and cancer-specific survival with NSS, this randomized clinical trial (RCT) remains the only available level 1 evidence on this subject. Notably, no study to date has formally examined the external validity [5] of the trial.
For any RCT to be externally valid, its supposedly randomly selected sample must be representative of the general population seen in clinical practice. In this context, we studied patients with localized RCC treated with NSS or RN within the National Cancer Database (NCDB), in an effort to test the external validity of the EORTC 30904. Our objective was not to compare survival outcomes between the two treatment arms, as this is beyond the scope of examining the external validity of an RCT, and such analysis is already available in literature. Instead, our aim was to ascertain if the trial patients were representative of contemporary patients with RCC in the USA, using the NCDB, which captures ~70% of all incident cancer diagnoses in the USA [6].
We identified patients who met the clinical and pathological inclusion criteria of the EORTC 30904 within the NCDB from 2004 to 2013: histologically confirmed RCC; tumour size ≤5 cm; clinically node-negative, non-metastatic disease; no positive surgical margins; and no pT3/4 disease. After exclusions, there were 90 844 assessable patients within the NCDB, of whom 41 588 (45.78%) underwent RN and 49256 (54.22%) underwent NSS. The demographic characteristics, namely, age, gender (percentage of men), presence of comorbidities (yes/no), histology (clear cell/non-clear cell), Fuhrman grade (1, 2, 3 or 4) and surgical approach (open/robotic/laparoscopic) were then compared with the patients enrolled in the EORTC 30904. The statistical significance of differences in categorical variables was tested using the chi-squared test. Unfortunately, the trial did not provide measures of variance (such as standard deviation, or interquartile range) for continuously coded variables; we were therefore unable to test for the statistical significance of differences in these variables. All analyses were performed using SAS 9.4 (SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA), with a P value <0.05 taken to indicate statistical significance.
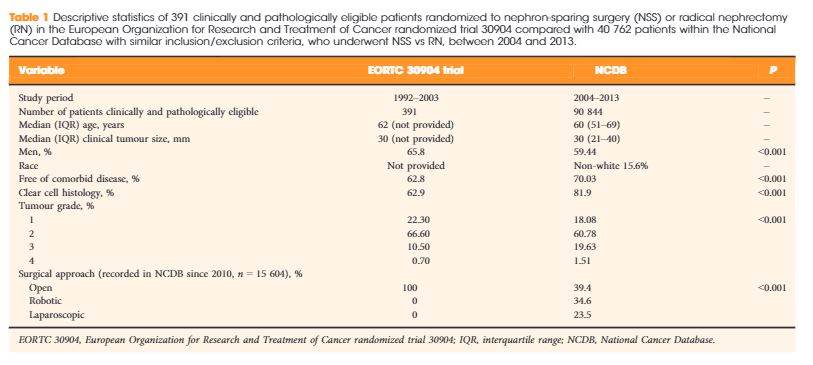
The median age of the NCDB cohort was 60.0 years, compared with 62.0 years in the EORTC 30904. The median clinical tumour size in the NCDB was 30 mm, similar to the 30-mm tumour size observed in the trial. The percentage of men was 59.4% in the NCDB vs 65.8% in EORTC 30904 trial (P < 0.001). The NCDB cohort was healthier, with 70.03% patients having no comorbidity vs 62.8% in the trial (P < 0.001). The percentage of patients with clear-cell histology was 81.9% in the NCDB vs 62.9% in the trial (P < 0.001). The trial did not report data on race, while the NCDB had 15.6% non-white patients. Finally, the percentage of patients with high-grade disease (Fuhrman grade ≥3) was 21.1% in the NCDB vs 11.2% in the EORTC 30904 (P < 0.001; Table 1). Notably, in the EORTC 30904 trial, there was no central pathology review.
| Variable | EORTC 30904 trial | NCDB | P |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| Study period | 1992–2003 | 2004–2013 | – |
| Number of patients clinically and pathologically eligible | 391 | 90 844 | – |
| Median (IQR) age, years | 62 (not provided) | 60 (51–69) | – |
| Median (IQR) clinical tumour size, mm | 30 (not provided) | 30 (21–40) | – |
| Men, % | 65.8 | 59.44 | <0.001 |
| Race | Not provided | Non-white 15.6% | – |
| Free of comorbid disease, % | 62.8 | 70.03 | <0.001 |
| Clear cell histology, % | 62.9 | 81.9 | <0.001 |
| Tumour grade, % | |||
| 1 | 22.30 | 18.08 | <0.001 |
| 2 | 66.60 | 60.78 | |
| 3 | 10.50 | 19.63 | |
| 4 | 0.70 | 1.51 | |
| Surgical approach (recorded in NCDB since 2010, n = 15 604), % | |||
| Open | 100 | 39.4 | <0.001 |
| Robotic | 0 | 34.6 | |
| Laparoscopic | 0 | 23.5 | |
Several important observations emerge from these results. First, age and tumour size were similar in the EORTC 30904 trial and the NCDB. These two variables are the most important determinants of mortality and stage of disease, respectively, which implies that the trial was able to recruit patients representative of those seen in ‘real-world’ clinical practice.
Second, there was a higher incidence of high-grade disease and clear-cell histology in the NCDB cohort compared with the EORTC 30904 trial. In other words, patients in the NCDB had more aggressive tumours as compared with patients in the trial. Arguably, such patients are better served with RN, which has a higher probability of completely eradicating the tumour. The survival benefit of RN observed in the trial might therefore be even more evident in clinical practice, where a higher proportion of patients harbour unpredictable aggressive disease.
Finally, the EORTC seems to have recruited patients with a higher comorbidity burden than is generally observed in clinical practice. The significance of this finding is controversial. On the one hand, it might be argued that the higher background mortality of the cohort could have masked the potential OS benefit of NSS by offering this treatment method to sicker patients with limited life expectancy [7]. On the other hand, preserving renal function might be even more important in sicker patients, who have the burden of other comorbidities [8].
The present study has some limitations. An inherent limitation of the NCDB is the lack of information on the performance status of patients. Second, the comparison was between two cohorts separated in time. The mode of treatment and thus, patient selection might have changed over time. The NCDB provides information about surgical approach starting in 2010, and indeed open surgery was performed in only 39.4% of the cases compared with 100% in the trial. More than 15% of patients in the NCDB had missing tumour grade compared with 4% in the trial; however, this proportion was equally distributed between patients undergoing RN and PN in the NCDB (data not shown). Despite the limitations, these findings are significant in the context of the recent debate on contemporary guidelines recommending NSS ‘wherever possible’ in patients with a normal contralateral kidney [9].
In conclusion, our results indicate that, although the EORTC 30904 cohort had somewhat different baseline characteristics than ‘real-world’ patients with small renal masses, none of these differences seem to have the potential to significantly alter the outcomes of the trial. The latter should therefore be considered generalizable to contemporary North American patients with renal masses ≤5 cm.