Editorial: Is 42 days the ‘magic number’ for repeat TURBT?
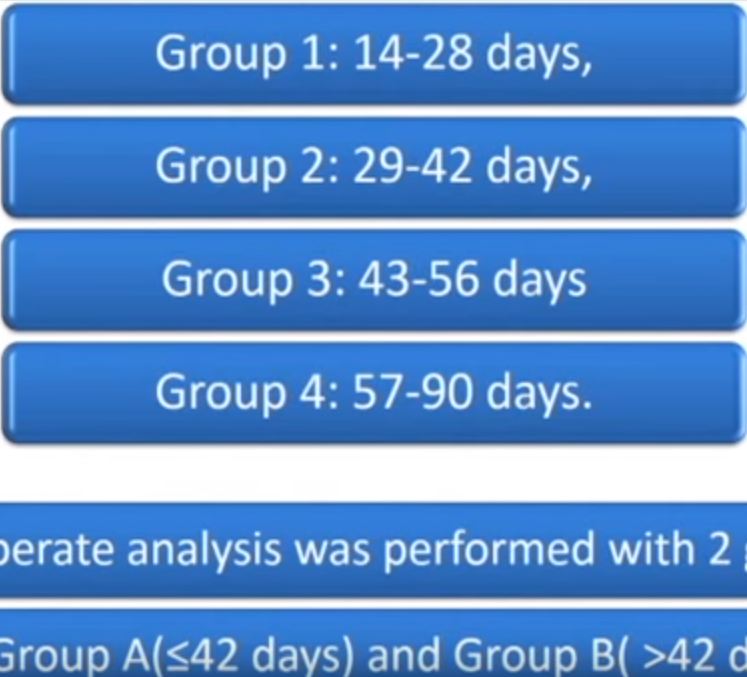
Gökçe et al. [1] have evaluated a group of 242 patients from 10 centres with high-risk non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) who underwent repeat resection and subsequent follow-up treatment, including induction and maintenance BCG for at least 1 year. They included patients who had repeat transurethral resection (TUR) within 90 days and excluded anyone who was upstaged to T2 or who did not complete 1 year of maintenance BCG. They divided patients into two groups according to time to second TUR, Group A (14–42 days) and Group B (43–90 days). The groups were similar in terms of patient age and gender, tumour multifocality, presence of carcinoma in situ (CIS), and stage and grade. The only factors on multivariable analysis that were statistically significant predictors of recurrence were grade, associated CIS, and time to second TUR. Only grade and time to second TUR were significant predictors of progression.
Figures 1 and 2 in the paper show an enormous difference in both recurrence-free survival and progression-free survival according to time to second TUR. For both outcomes, 42 days seemed to be the ‘magic number’, since re-TUR after 42 days was associated with much worse outcome. Patients who had repeat TUR at >42 days had nearly double the rate of both recurrence and progression than those who had repeat TUR within 6 weeks.
This is quite a dramatic result, and it is hard to imagine biologically how such an effect could be explained. Second TUR has two primary objectives, to identify occult muscle-invasive disease, and to remove tumour that was inadvertently left behind at the first resection. Both of these goals have been shown to be important and to result in better outcomes compared with no repeat TUR [2]. However, in this study [1], patients who had repeat TUR at >6 weeks after the initial resection had a progression rate similar to those in prior studies who had no second TUR at all [2]. What could be occurring that would cause a delay of just a few weeks in second TUR to double the risk of subsequent progression of disease?
This is a retrospective study without centralised pathology review, and no information is available about the reasons that patients had repeat TUR at an earlier or later interval, nor about the pathological findings at the repeat TUR. One must be wary that there is significant selection bias involved. There is a hint of this in the fact that the rate of residual tumour at repeat TUR in the two groups is very different (35% vs 53%). Perhaps the later group also had a higher rate of residual invasive components on the repeat resection? Herr et al. [3] have shown that residual T1 disease on repeat TUR is highly predictive of subsequent progression. Or alternatively, perhaps it is the delay in administration of BCG that really results in the worse outcome? Patients with a longer delay to repeat TUR by definition also have at least an equivalent delay in starting BCG.
Although high-risk NMIBC can certainly be aggressive, it seems highly unlikely that a week or two-one way or another in terms of treatment would make such a huge difference in the outcome. However, this is a provocative study that remains to be validated. It will be useful to see if other groups with similar patient populations can duplicate these findings. For the time being, as a routine practice it makes sense to repeat the TUR sooner rather than later whenever possible.