Article of the Week: Identifying predictors of renal function decline after surgery
Every week the Editor-in-Chief selects the Article of the Week from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
In addition to the article itself, there is an accompanying editorial written by a prominent member of the urological community. This blog is intended to provoke comment and discussion and we invite you to use the comment tools at the bottom of each post to join the conversation.
If you only have time to read one article this week, it should be this one.
Preoperative predictors of renal function decline after radical nephroureterectomy for upper tract urothelial carcinoma
Matthew Kaag, Landon Trost*, R. Houston Thompson*, Ricardo Favaretto†, Vanessa Elliott, Shahrokh F. Shariat‡, Alexandra Maschino†, Emily Vertosick†, Jay D. Raman and Guido Dalbagni†
Penn State Hershey Medical Center, Hershey, PA, *Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN, †Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY, USA, and ‡Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria
OBJECTIVES
To model renal function after radical nephroureterectomy (RNU) for upper tract urothelial carcinoma (UTUC). To identify predictors of renal function decline after surgery, thereby allowing the identification of patients likely to be ineligible for cisplatin-based chemotherapy in the adjuvant setting.
PATIENTS AND METHODS
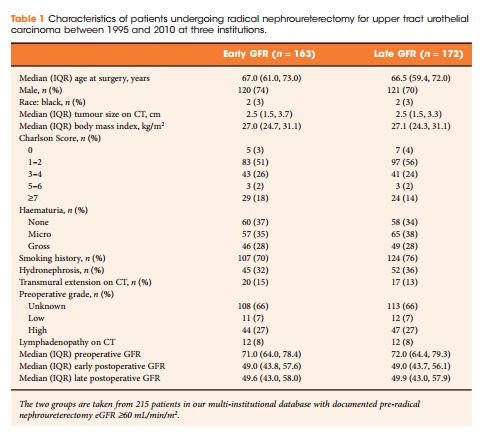
We retrospectively identified 374 patients treated with RNU for UTUC at three centres between 1995 and 2010. Estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) was calculated using Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration equation before RNU and at early (1–5 months after RNU) and late (>5 months) time points after RNU. Only patients deemed eligible for cisplatin-based chemotherapy before RNU (preoperative glomerular filtration rate [GFR] ≥60 mL/min/1.73 m2) were included. Multivariable analysis identified the preoperative predictors of eGFR after RNU at early postoperative and late postoperative time points.
RESULTS
CONCLUSIONS