Video: Machine learning‐assisted decision‐support model to identify PCa patients requiring an extended PLND
A machine learning‐assisted decision‐support model to better identify patients with prostate cancer requiring an extended pelvic lymph node dissection
Abstract
Objectives
To develop a machine learning (ML)‐assisted model to identify candidates for extended pelvic lymph node dissection (ePLND) in prostate cancer by integrating clinical, biopsy, and precisely defined magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) findings.
Patients and Methods
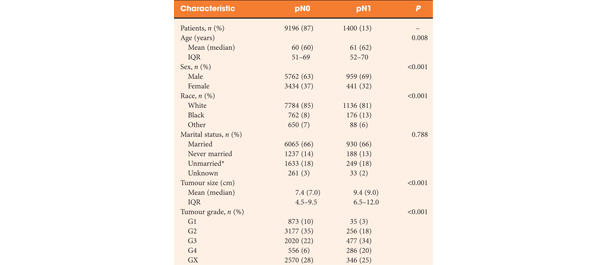
In all, 248 patients treated with radical prostatectomy and ePLND or PLND were included. ML‐assisted models were developed from 18 integrated features using logistic regression (LR), support vector machine (SVM), and random forests (RFs). The models were compared to the Memorial SloanKettering Cancer Center (MSKCC) nomogram using receiver operating characteristic‐derived area under the curve (AUC) calibration plots and decision curve analysis (DCA).
Results
A total of 59/248 (23.8%) lymph node invasions (LNIs) were identified at surgery. The predictive accuracy of the ML‐based models, with (+) or without (−) MRI‐reported LNI, yielded similar AUCs (RFs+/RFs−: 0.906/0.885; SVM+/SVM−: 0.891/0.868; LR+/LR−: 0.886/0.882) and were higher than the MSKCC nomogram (0.816; P < 0.001). The calibration of the MSKCC nomogram tended to underestimate LNI risk across the entire range of predicted probabilities compared to the ML‐assisted models. The DCA showed that the ML‐assisted models significantly improved risk prediction at a risk threshold of ≤80% compared to the MSKCC nomogram. If ePLNDs missed was controlled at <3%, both RFs+ and RFs− resulted in a higher positive predictive value (51.4%/49.6% vs 40.3%), similar negative predictive value (97.2%/97.8% vs 97.2%), and higher number of ePLNDs spared (56.9%/54.4% vs 43.9%) compared to the MSKCC nomogram.
Conclusions
Our ML‐based model, with a 5–15% cutoff, is superior to the MSKCC nomogram, sparing ≥50% of ePLNDs with a risk of missing <3% of LNIs.