Editorial: EAU guidelines – do we care? Reflections from the EAU Impact Assessment of Guidelines Implementation and Education group
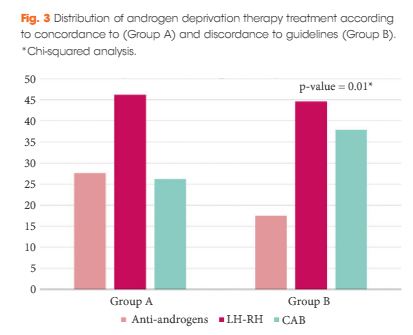
There is increasing evidence in the literature that androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) is overused among practising urologists in the setting of localized, and even locally advanced, prostate cancer (PCa) [1, 2]. Morgia et al. [1] report a misuse of ADT prescriptions among Italian urologists in roughly a quarter of cases, mainly in the setting of low-risk/localized disease where ADT may harm patients without proven benefit with regard to disease-specific outcomes [3]. Such clinical practice behaviours are even more unjustifiable given the high level of evidence upon which the current European Association of Urology (EAU) guidelines recommendations on ADT use are based [4].
Morgia et al. [1] should be congratulated for highlighting the magnitude of the problems the urological community currently face in terms of the gap between evidence and practice. Unfortunately, while the authors report significant geographical differences in ADT prescriptions within the same country (Italy), the methods they used in their study do not allow an understanding of the reasons for the discrepancy. It is currently unknown whether the gap between evidence and practice is attributable to physician or patient attitude or to the national health system structure. The inclusion of qualitative methods, such as semi-structured interviews, would have been ideal to probe clinician reasoning for discordant adherence. This is crucial because knowledge of possible barriers to the application of guidelines represents a key step in their implementation process. Indeed, once the issue is raised, the next logical questions to pose would be: how can we reduce such variation in urological practice especially where there is a real risk of causing harm to patients and how can we improve and implement the use of guideline recommendations when clearly underpinned by high-quality evidence?
It is indeed intuitive that any huge evidence–practice gap may have profound implications not only in the process of patient care optimization but also in the context of national healthcare efficiency.
Certainly the issue of ADT overuse raised by Morgia et al. [1] can be considered the perfect setting to scale up and prioritize efforts aimed at improving current urological practice for three main reasons: (i) the high prevalence of the disease studied (namely, PCa); (ii) the availability of an up-to-date evidence-based guideline showing the impact of ADT in terms of patient side effects and costs; and (iii) the now known gap between evidence and practice patterns.
Given this setting, it should then be mandatory to promote ways not only to assess the use of guideline recommendations but also to increase dissemination among users (not only healthcare professionals, but also patients and policy makers) and to evaluate their impact. The aim of this highly articulated process of knowledge translation is eventually to move research findings into clinical practice. Ideally, this approach should be based on the following five crucial questions: (i) What should be transferred? (ii) To whom should research knowledge be transferred? (iii) By whom should research knowledge be transferred? (iv) How should research knowledge be transferred? and (v) To what effect should research knowledge be transferred? [5]. Each of these questions represents a crucial step in any knowledge translation process. To optimize this approach, it is critical to identify barriers to knowledge implementation and to choose the optimum interventions to limit or to overcome them. This ‘global process’ is much more complicated than commonly thought, given the significant cultural, social, economic and health system differences not only between countries but also within the same country, as shown by Morgia et al. [1]. It is likely, therefore, that any knowledge implementation approach should be tailored according to each country and should be based on key steps, such as: selection of a credible ‘messenger’; development of the appropriate technological and organizational instruments to facilitate access to disseminate and use existing high-quality evidence; and the setting up of education programmes to improve clinical research literacy skills.
Finally, we believe that the paper by Morgia et al. [1] strongly supports the notion that ‘evidence-based medicine should be complemented by evidence-based implementation’ [6]. It is indeed likely that creating a knowledge translation setting where the gap between evidence and practice is eventually bridged is as important as producing accurate, scientifically sound and meticulous guidelines that can be trusted by all stakeholders.
Tackling the crucially important problem of discordant guideline adherence is the remit of the recently established EAU Guidelines Office ‘IMAGINE’ project (IMpact Assessment of Guidelines Implementation and Education) which aims to: ascertain adherence to prioritized guideline recommendations; elucidate the barriers and facilitators to change; design bespoke knowledge transfer interventions; and evaluate the impact of the EAU guidelines, thereby optimizing adherence, with the ultimate goal of improving patient care.