Article of the Month: SRP for recurrent Prostate Cancer – Verification of EAU guideline criteria
Every Month the Editor-in-Chief selects an Article of the Month from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
In addition to the article itself, there is an accompanying editorial written by a prominent member of the urological community. This blog is intended to provoke comment and discussion and we invite you to use the comment tools at the bottom of each post to join the conversation.
If you only have time to read one article this week, it should be this one.
Salvage Radical Prostatectomy for recurrent Prostate Cancer: Verification of EAU guideline criteria
Note: Figure 3 should be swapped with Figure 4. The legends for both figures stay the same and the referencing in the text is correct.
OBJECTIVE
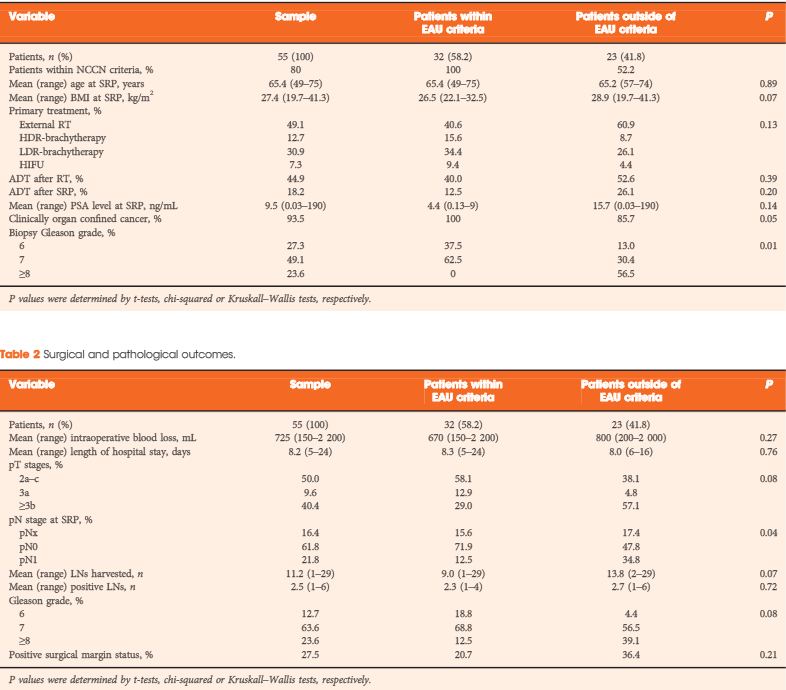
To analyse oncological and functional outcomes of salvage radical prostatectomy (SRP) in patients with recurrent prostate cancer and to compare outcomes of patients within and outside the European Association of Urology (EAU) guideline criteria (organ-confined prostate cancer ≤T2b, Gleason score ≤7 and preoperative PSA level <10 ng/mL) for SRP.
PATIENTS AND METHODS
In all, 55 patients who underwent SRP from January 2007 to December 2012 were retrospectively analysed. Kaplan–Meier curves assessed time to biochemical recurrence (BCR), metastasis-free survival (MFS) and cancer-specific survival. Cox regressions addressed factors influencing BCR and MFS. BCR was defined as a PSA level of >0.2 ng/mL and rising, continence as the use of 0–1 safety pad/day, and potency as a five-item version of the International Index of Erectile Function score of ≥18.
RESULTS
The median follow-up was 36 months. After SRP, 42.0% of the patients experienced BCR, 15.9% developed metastasis, and 5.5% died from prostate cancer. Patients fulfilling the EAU guideline criteria were less likely to have positive lymph nodes (LNs) and had significantly better BCR-free survival (5-year BCR-free survival 73.9% vs 11.6%; P = 0.001). In multivariate analysis, low-dose-rate brachytherapy as primary treatment (P = 0.03) and presence of positive LNs at SRP (P = 0.02) were significantly associated with worse BCR-free survival. The presence of positive LNs or Gleason score >7 at SRP were independently associated with metastasis. The urinary continence rate at 1 year after SRP was 74%. Seven patients (12.7%) had complications ≥III (Clavien grade).
CONCLUSION
SRP is a safe procedure providing good cancer control and reasonable urinary continence. Oncological outcomes are significantly better in patients who met the EAU guideline recommendations.