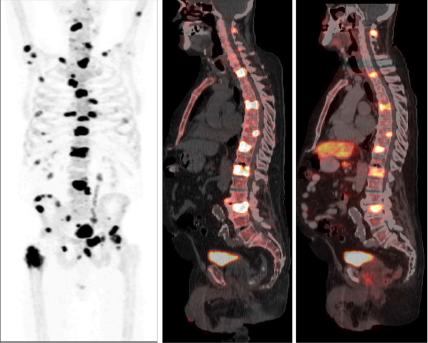
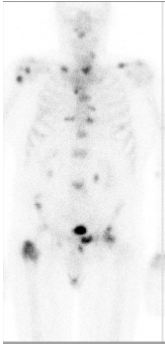
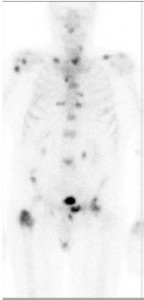
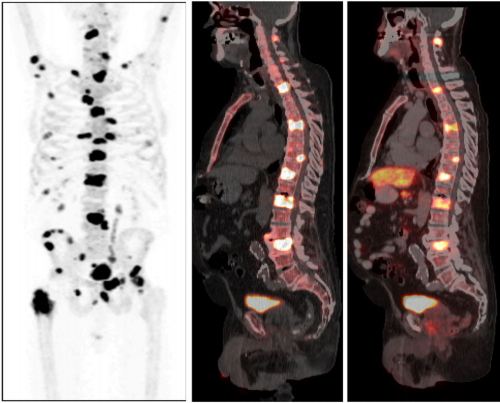
In this issue of BJUI, Poulsen et al. [1] present a prospective comparison of 18F-fluoride (NaF) and 18F-choline (FCH) positron emission tomography (PET)/CT with planar whole-body bone scintigraphy (WBS) using spinal MRI, including short tau inversion recovery (STIR), T1 and T2 sequences, as the reference standard in 50 hormone-naïve patients with confirmed bone metastases on WBS. They found that both PET/CT methods were significantly more sensitive and accurate than WBS and that FCH PET/CT was more specific than NaF PET/CT.
Nevertheless, the authors should be congratulated in reporting valuable data from a prospective study where all imaging was performed in hormone-naïve patients, minimising confounding treatment-related effects, and within a small time window of 30 days; however, some questions remain. WBS is no longer state of the art for imaging the skeleton with radiolabelled bisphosphonates, such as 99mTc-methylene diphosphonate (MDP). Although NaF PET/CT has been shown to be superior to planar WBS augmented with SPECT [3], there have not been head-to-head comparisons with 99mTc-MDP SPECT/CT, where the potential advantages of the pharmacokinetics of NaF and the superior spatial resolution of PET compared with SPECT may not be as great. This may be particularly important given the difference in costs and availability of the two methods.
Despite the results from the present study, which show superiority of FCH PET/CT compared with NaF PET/CT with regard to specificity, taking the available literature as a whole, it remains unresolved as to what the best test for staging the skeleton in patients with high-risk prostate cancer should be at diagnosis. The different mechanisms of uptake of the PET tracers should be noted. NaF uptake reflects the local bone osteoblastic reaction to tumour within the bone marrow, whereas FCH uptake reflects metabolic activity within the tumour cells themselves. In prostate cancer, where the predominant effect is an increase in osteoblastic activity in the adjacent bone, the bone-specific tracers such as 99mTc-MDP and NaF have shown high sensitivity; however, direct imaging of tumour cell metabolism, such as increased choline kinase activity and cell membrane synthesis with FCH, may be advantageous in detecting metastases in the bone marrow before an osteoblastic reaction has occurred [6]. It is possible that both PET tracers may be required to provide optimum diagnostic accuracy and of course FCH PET/CT also provides valuable data on nodal and visceral metastatic disease. In patients with recurrent disease, better specificity has been reported with FCH [4], NaF possibly being limited by non-specific treatment-related effects such as osteoblastic flare. For similar reasons it may be that the more tumour-specific imaging methods, such as FCH PET/CT or diffusion-weighted MRI, may be better in assessing the treatment response of skeletal metastases. Questions therefore remain as to the best imaging test at different times in the management of patients with metastatic prostate cancer. 99mTc-MDP SPECT/CT deserves a full assessment, but perhaps the recent advent of PET/MRI and the potential synergies available from this hybrid technique may help resolve some of the remaining issues.
Gary Cook*† and Vicky Goh*‡
*Division of Imaging Sciences and Biomedical Engineering, King’s College London, † Clinical PET Centre, and ‡ Department of Radiology, Guy’s and St Thomas’ Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, London, UK
References
1 Poulsen MH, Petersen H, Høilund-Carlsen PF et al. Spine metastases in prostate cancer: comparison of [99mTc]MDP wholebody bone scintigraphy, [18F]choline PET/CT, and [18F]NaF PET/CT. BJU Int 2014; 114: 818–23
2 Fogelman I, Blake GM, Cook GJ. The isotope bone scan: we can do better. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2013; 40: 1139–40
3 Even-Sapir E, Metser U, Mishani E et al. The detection of bone metastases in patients with high-risk prostate cancer: 99mTc-MDP Planar bone scintigraphy, single- and multi-field-of-view SPECT, 18F-fluoride PET, and 18F-fluoride PET/CT. J Nucl Med 2006; 47: 287–974
4 Langsteger W, Balogova S, Huchet V et al. Fluorocholine (18F) and sodium fluoride (18F) PET/CT in the detection of prostate cancer: prospective comparison of diagnostic performance determined by masked reading. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2011; 55: 448–57
5 Kjölhede H, Ahlgren G, Almquist H et al. Combined 18F-fluorocholine and 18F-fluoride positron emission tomography/computed tomography imaging for staging of high-risk prostate cancer. BJU Int 2012; 110: 1501–6
6 Beheshti M, Vali R, Waldenberger P et al. Detection of bone metastases in patients with prostate cancer by 18F fluorocholine and 18F fluoride PET-CT: a comparative study. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2008; 35: 1766–74