Article of the week: Cluster analysis of multiple chronic conditions associated with urinary incontinence among women in the USA
Every week, the Editor-in-Chief selects an Article of the Week from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
In addition to the article itself, there is an accompanying editorial written by a prominent member of the urological community. These are intended to provoke comment and discussion and we invite you to use the comment tools at the bottom of each post to join the conversation. There is also a new residents’ podcast focussing on this article.
If you only have time to read one article this week, it should be this one.
Cluster analysis of multiple chronic conditions associated with urinary incontinence among women in the USA
Abstract
Objective
To identify patterns of prevalent chronic medical conditions among women with urinary incontinence (UI).
Materials and Methods
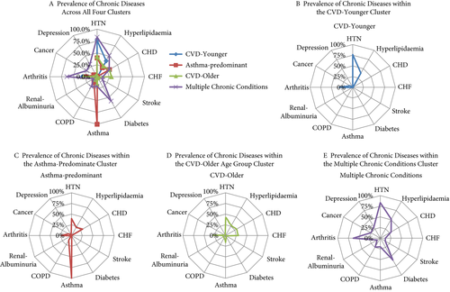
We combined cross‐sectional data from the 2005–2006 to 2011–2012 US National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys, and identified 3 800 women with UI and data on 12 chronic conditions. Types of UI included stress UI (SUI), urgency UI (UUI), and mixed stress and urgency UI (MUI). We categorized UI as mild, moderate or severe using validated measures. We performed a two‐step cluster analysis to identify patterns between clusters for UI type and severity. We explored associations between clusters by UI subtype and severity, controlling for age, education, race/ethnicity, parity, hysterectomy status and adiposity in weighted regression analyses.
Results
Eleven percent of women with UI had no chronic conditions. Among women with UI who had at least one additional condition, four distinct clusters were identified: (i) cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk‐younger; (ii) asthma‐predominant; (iii) CVD risk‐older; and (iv) multiple chronic conditions (MCC). In comparison to women with UI and no chronic diseases, women in the CVD risk‐younger (age 46.7 ± 15.8 years) cluster reported the highest rate of SUI and mild UI severity. In the asthma‐predominant cluster (age 51.5 ± 10.2 years), women had more SUI and MUI and more moderate UI severity. Women in the CVD risk‐older cluster (age 57.9 ± 13.4 years) had the highest rate of UUI, along with more severe UI. Women in the MCC cluster (age 61.0 ± 14.8 years) had the highest rates of MUI and the highest rate of moderate/severe UI.
Conclusions
Women with UI rarely have no additional chronic conditions. Four patterns of chronic conditions emerged with differences by UI type and severity. Identification of women with mild UI and modifiable conditions may inform future prevention efforts.