Article of the Week: Assessing the impact of various treatment optimisation strategies in SWL
Every week the Editor-in-Chief selects the Article of the Week from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
In addition to the article itself, there is an accompanying editorial written by a prominent member of the urological community. This blog is intended to provoke comment and discussion and we invite you to use the comment tools at the bottom of each post to join the conversation.
Finally, the third post under the Article of the Week heading on the homepage will consist of additional material or media. This week we feature a video from Mr Mahesh Desai discussing his paper.
If you only have time to read one article this week, it should be this one.
Evolution of shockwave lithotripsy (SWL) technique: a 25-year single centre experience of >5000 patients
Jitendra Jagtap, Shashikant Mishra, Amit Bhattu, Arvind Ganpule, Ravindra Sabnis and Mahesh Desai
Department of Urology, Muljibhai Patel Urological Hospital, Nadiad, India
OBJECTIVE
To assess the impact of various treatment optimisation strategies in shockwave lithotripsy (SWL) used at a single centre over the last 25 years.
PATIENTS AND METHODS
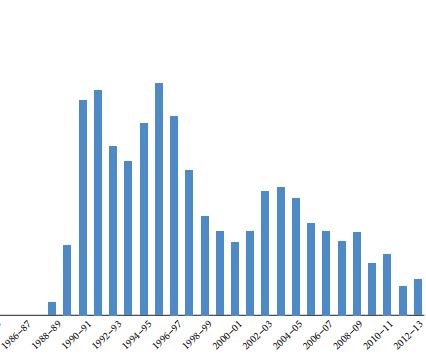
In all, 5017 patients treated between 1989 and 2013 were reviewed and divided into groups A, B, C and D for the treatment periods of 1989–1994 (1561 patients), 1995–2000 (1741), 2001–2006 (1039) and 2007–2013 (676), respectively. The Sonolith 3000 (A and B) and Dornier compact delta lithotripters (C and D) were used. Refinements included frequent re-localisation, limiting maximum shocks and booster therapy in group B and Hounsfield unit estimation, power ramping and improved coupling in group D. Parameters reviewed were annual SWL utilisation, stone and treatment data, retreatment, auxiliary procedures, complications and stone-free rate (SFR).
RESULTS
The SFR with Dornier compact delta was significantly higher than that of the Sonolith 3000 (P < 0.001). The SFR improved significantly from 77.58%, 81.28%, 82.58% to 88.02% in groups A, B, C, and D, respectively (P < 0.001). There was a concomitant decrease in repeat SWL (re-treatment rate: A, 48.7%; B, 33.4%; C, 15.8%; and D, 10.1%; P < 0.001) and complication rates (A, 8%; B, 6.4%; C, 4.9%; and D, 1.6%; P < 0.001). This led to a rise in the efficiency quotient (EQ) in groups A–D from 50.41, 58.94, 68.78 to 77.06 (P < 0.001).The auxiliary procedure rates were similar in all groups (P = 0.62).
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, improvement in the EQ together with a concomitant decrease in complication rate can be achieved with optimum patient selection and use of various treatment optimising strategies.