EAU 2016 Congress Day 3
Das bringt mich weiter! While the sun was shining in Munich, the 3rd day of the 31st EAU Annual Congress continued with very well attended plenary and poster sessions. And that is no wonder because the EAU Scientific Committee had created such an attractive program, including amazing plenary sessions during the morning and a plethora of informative poster sessions in the afternoon.
Professor Hendrik Borgmann (@HendrikBorgmann) has already covered highlights of the opening days 1 and 2 of this year’s Congress in his BJUI blog. We will give you some highlights of Day 3 and highly recommend you to take a look on EAU congress website, Day 3, which has archived a huge amount of material to allow you to catch up on sessions you may have missed. Indeed, lots of webcasts are available!
We focused on non-oncology plenary morning sessions and oncology poster sessions afternoon. Here are some of our highlights:
SURGERY IN THE ELDERLY – As our urological patients become older and older, surgery for octogenarians, or even nonagenarians, is increasingly common. The morning session covered various aspects on diagnosis and treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia and other urological conditions in the ageing patient.
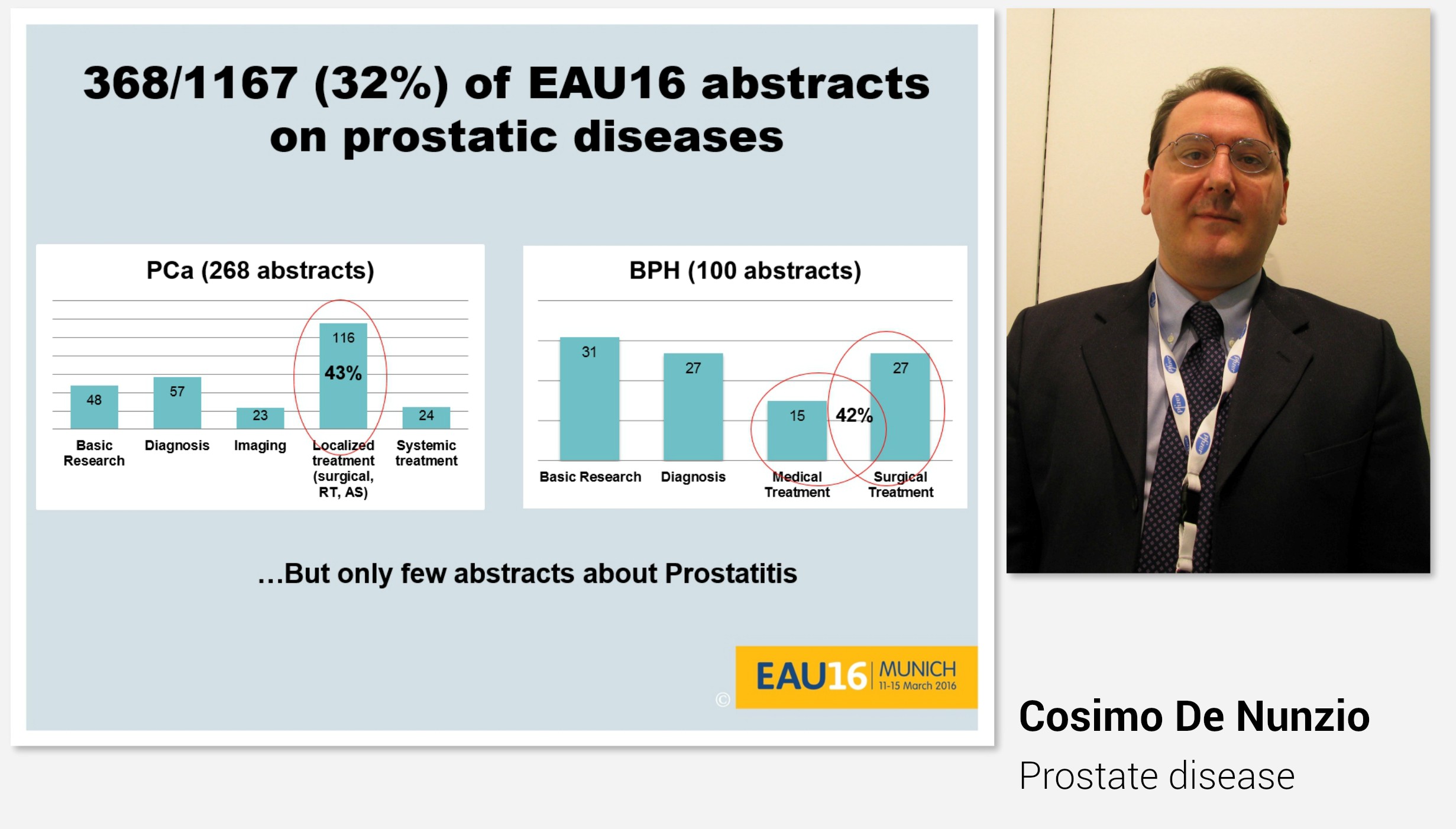
Professor Cosimo De Nunzio began the morning with “Highlights” on lower urinary tract symptoms and prostatic disease presented during this year’s EAU congress. Also this year, as many as every third abstract was on either prostate cancer or prostatic hyperplasia.
Indeed, the plenary session on Day 3 also covered prostatic disease.
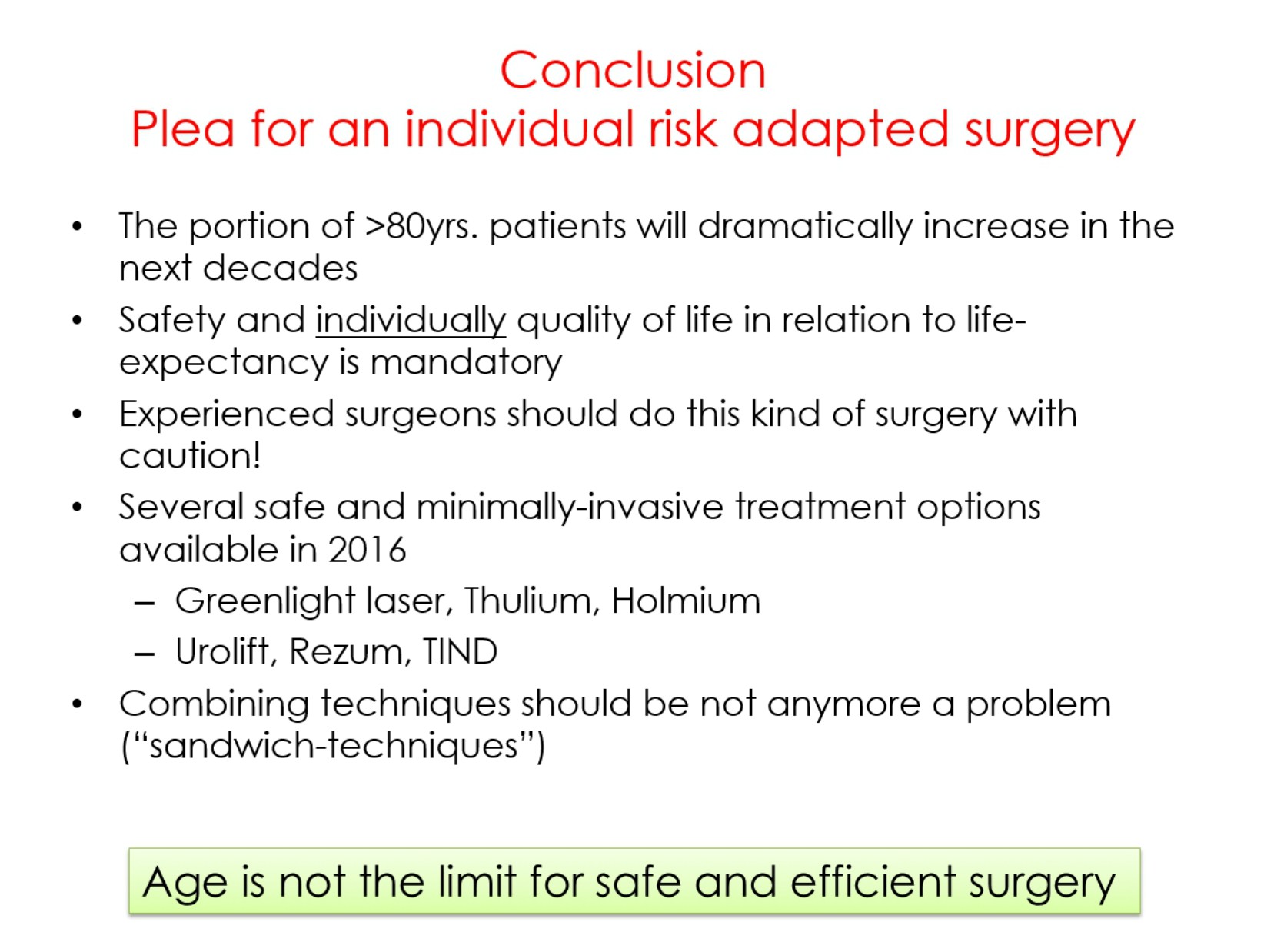
Professor Alexander Bachmann talked about surgery for BPO in the elderly. He pointed out that in elderly (high-risk) patients we do not need a complete anatomical tissue removal, we do not need a (very) long-term follow-up and that we do not need tissue for prostate cancer diagnosis. Instead, we need a safe and efficient operation with individual adaptation of the technique and preferably feasibility in an ambulatory setting or local anaesthesia.
Professor Bachmann further emphasized that it would be preferable if surgery for the elderly would be performed by experienced surgeons, and that age per se is not a reason to not operate. There are several new minimally invasive operations available, and especially for elderly less is often more.
HOW AND WHEN TO STOP ANTICOAGULATION – Managing perioperative thromboprophylaxis for patients who already receive anticoagulants remains a challenge. Associate professor Daniel Eberli and Professor Per Morten Sandset covered many of these aspects in their helpful presentations.
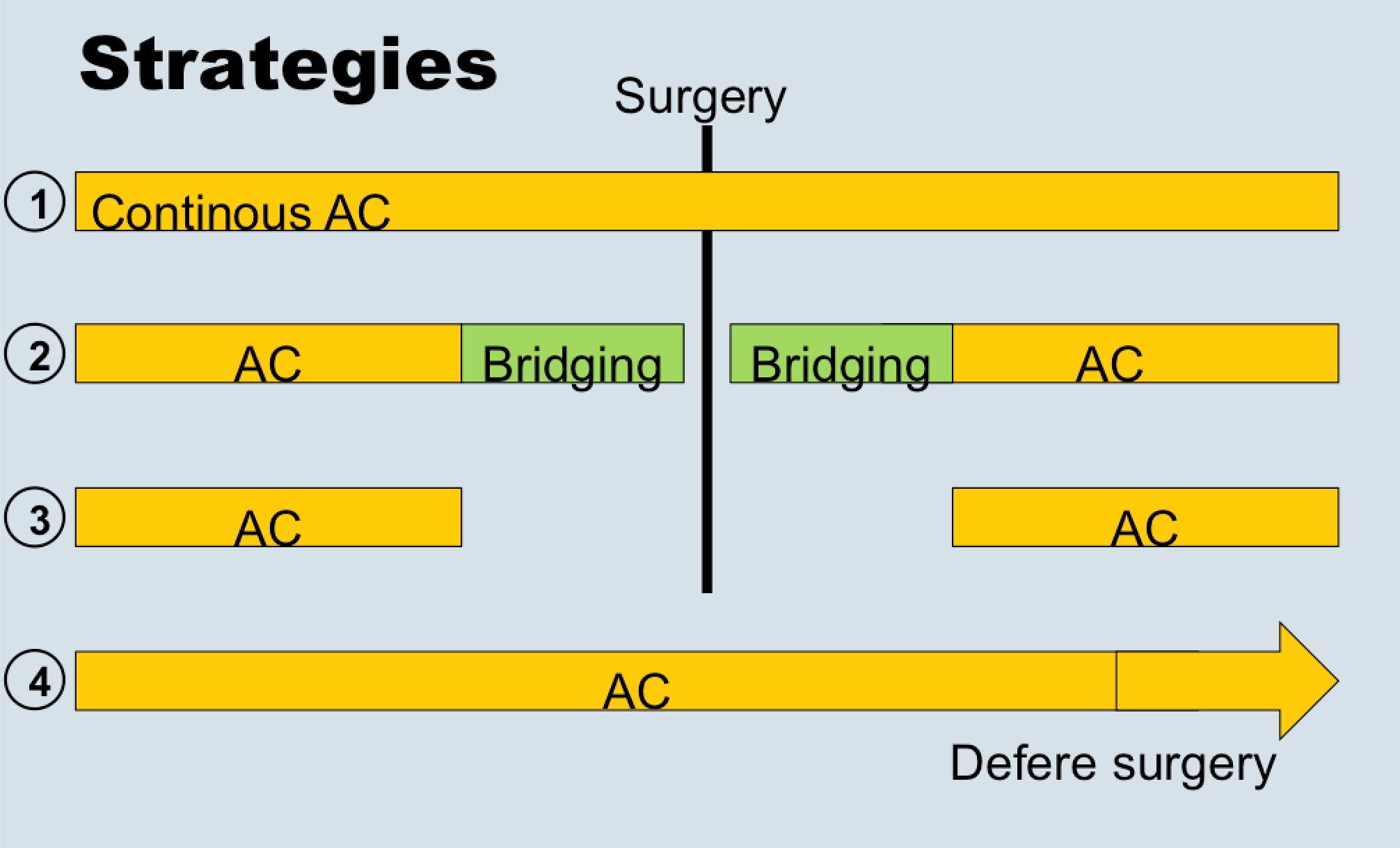
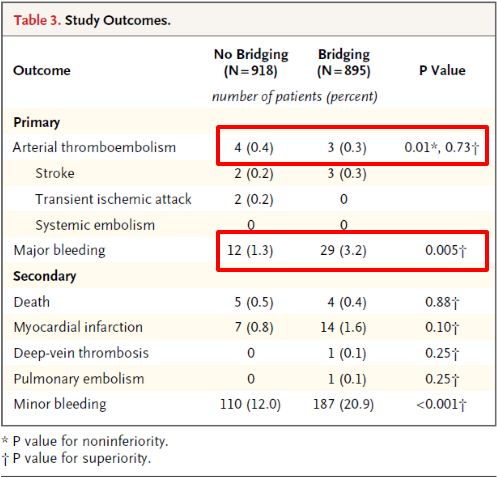
Dr. Eberli told us that bridging therapy (options for stopping or not stopping anticoagulation in the above figure) is eminence-based, as no papers exist showing benefits. He also presented data from the recent NEJM trial (BRIDGE study; see Table below), which showed that stopping anticoagulation without bridging was non-inferior to perioperative bridging for the prevention of arterial thromboembolism and decreased the risk of major bleeding.
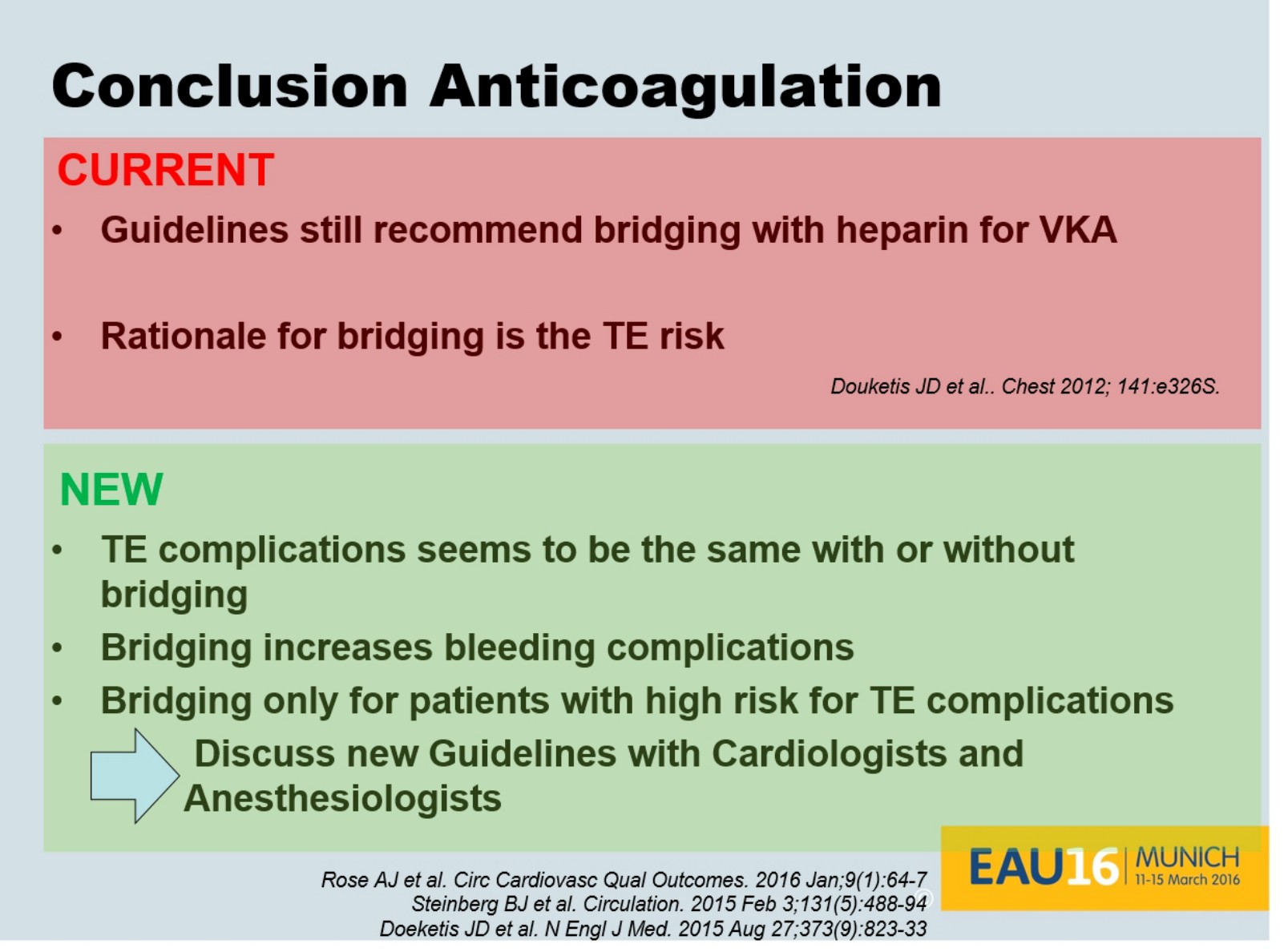
Dr. Eberli gave us all a take home message to discuss and question our local bridging guidelines as new evidence is very likely not supporting them (concluding slide below).
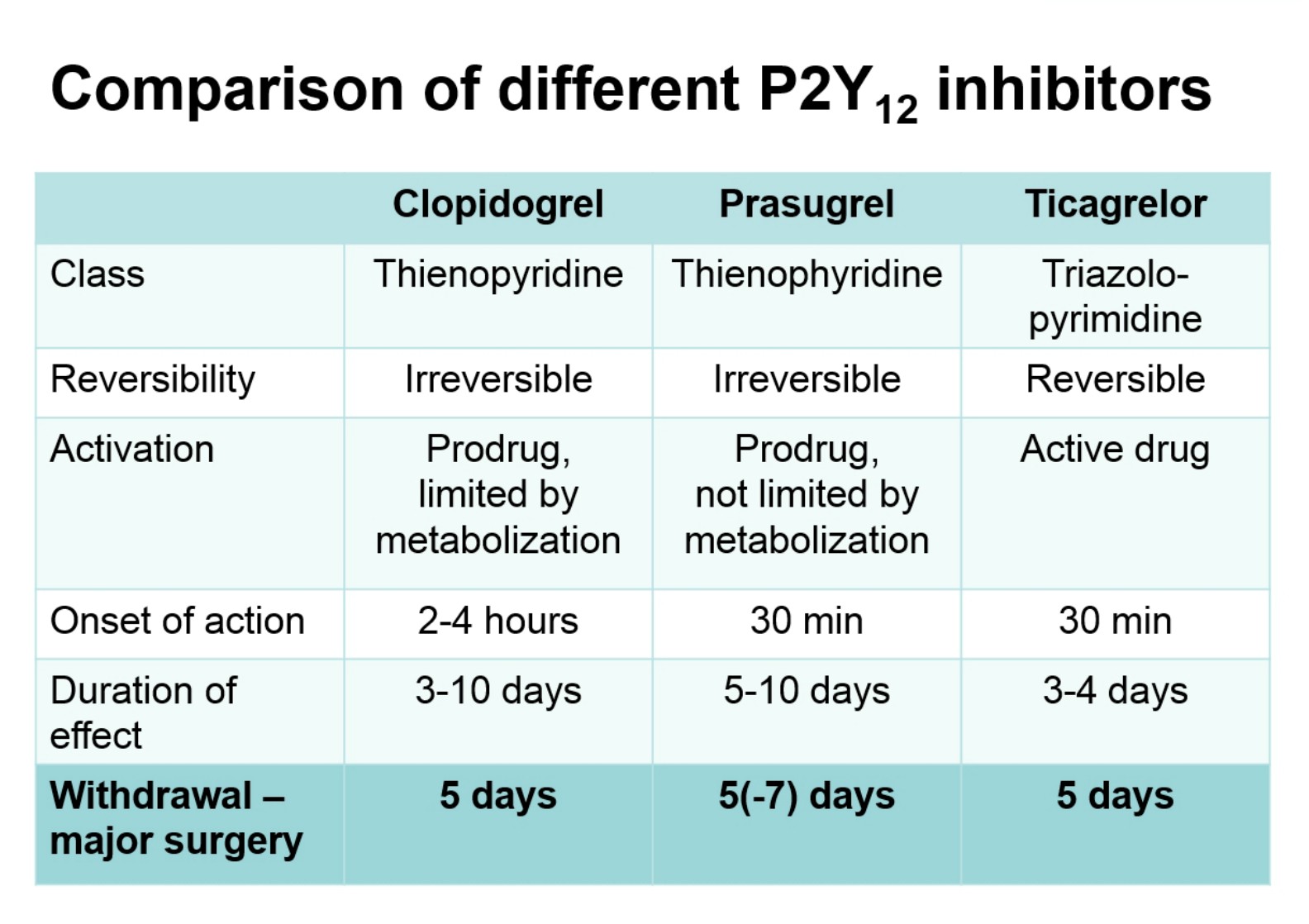
Professor Sandset recommended that during the perioperative period only use aspirin in high-risk patients, that is, those with recent thrombotic event or extensive coronary heart disease. He also informed us that stopping antiplatelet therapy 5 days before surgery (figure below) is often the way to go, and agreed with Dr. Eberli regarding bridging therapy statements.
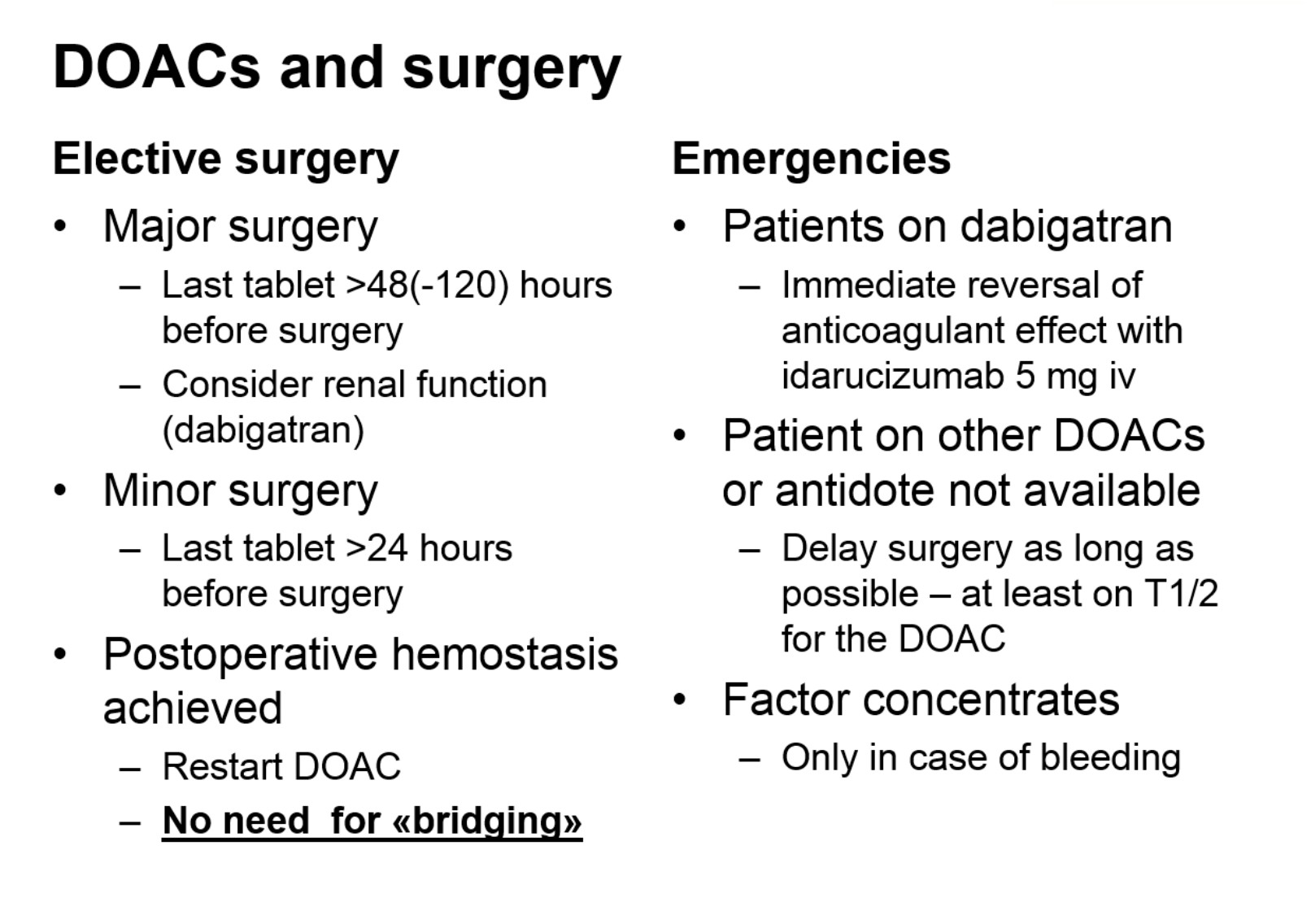
Professor Sandset also gave helpful information regarding use of direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) in urological surgery:
There were numerous poster sessions available on Day 3, as usual, many of them on prostate cancer. We have selected some of the highlight abstracts presented.
PROSTATE CANCER – On Day 3, prostate cancer presentations dominated once again in a number of poster, abstract and thematic sessions but also kidney, bladder, testicular and penile cancer sessions, which provided new interesting data.
Molecular markers, genomic profiling and individualized risk and treatment assessments were presented and discussed in poster session 58, and summarized by Stacy Loeb (@LoebStacy). Further advances in prostate cancer biomarkers in prostate cancer were presented in poster session 84. These new tools are moving from bench to bedside and urologists can hopefully incorporate these new tools to cancer care sooner rather than later.
In sessions on prostate cancer diagnostics, more advanced risk profiling tools were highlighted. For instance, STHLM3 test combines history of the patient, clinical parameters, biochemical markers and genetic markers. It was presented earlier in the congress and on Day 3 further health, economic and clinical evaluations were presented in Thematic session 12. It is one example of the tests showing promising results to potentially decrease the number of prostate biopsies needed. Other similar risk profiling tools were also presented during the congress. In addition to PSA only, evaluation of the smart use of already available clinical and biochemical parameters and the combination of genetic markers may bring individualized risk assessment of prostate cancer to the next level.
In poster session 62 on Day 3, diagnostic proceedings in prostate cancer with co-morbidity evaluation, biopsy strategies and MRI imaging were presented. A combination of molecular markers and imaging may be the way to proceed in future. These aspects were covered nicely in Thematic session 12.
MRIs have been heavily integrated in prostate cancer diagnostics during recent years. Image guidance in prostate biopsies seem to be making a breakthrough in prostate cancer diagnostics. Targeted biopsies with cognitive or MRI-TRUS fusion imaging were shown to be the way to enhance the results and reliability of biopsies and cut down the number of biopsies. However, as biopsies are still needed in prostate cancer diagnostics, use of the pre-biopsy MRI protocols were suggested to be done only in clinical trial setting. Many aspects of MRI diagnostics of prostate cancer were elegantly summarized in Thematic session 11.
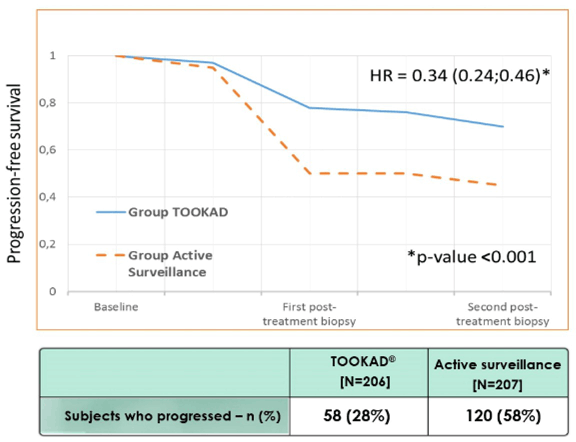
New sophisticated imaging technologies in addition to MRI were present in several sessions during the meeting. Diagnostic enhancement has been seen also in metastatic prostate cancer. PSMA-PET seems to be replacing choline-PET-TT in evaluation of relapsing and metastatic prostate cancer (e.g. Thematic session 10). More reliable diagnostics and imaging of prostate cancer are also enhancing the treatment decision and treatment choice of patients with local prostate cancer. Finding the right patients for the active surveillance protocols is also being helped with advanced diagnostics. Indeed, finding only patients who need treatment for prostate cancer should be the ultimate goal for enhanced diagnostics as discussed in poster sessions 66 and 75 on Day 3. There are also high expectations on focal therapy (e.g. poster session 66), which at the moment is still experimental but will likely be a real option for patients with low volume prostate cancer verified by imaging.
The role of quality of life evaluations and patient reported outcomes measured were heavily discussed during the congress in all treatment modalities of both local and advanced prostate cancer. Survivorship issues are an increasingly important issue when more effective treatments both in local and advanced prostate cancer are available.
In metastatic disease, the use of early chemotherapy in combination with hormonal treatment has been implemented very rapidly to clinical use after the results of the CHAARTED and STAMPEED studies. Further evaluation of early chemo in metastatic disease is still needed and the patient selection needs still clarification. Hormonal therapy still has a very marked role in metastatic prostate cancer and new advances can also be found in new strategies of using castration therapy as presented in poster session 67. Urologists should actively follow the changing landscape of the medical treatment of metastatic prostate cancer and be active in treatment planning and treatment of these patients. At the same time with poster session 62 novel drugs and new forms of isotope radiation therapy in castration resistant prostate cancer were discussed in poster session 61. These open new possibilities for potential treatments.
The clinical and scientific content of the program of the Day 3 was of a very high standard, and reflective of the breadth of contemporary research in many areas within urology. Besides this session, it was our pleasure to meet old and new urological friends worldwide. The annual EAU meeting remains a highly effective method of knowledge translation and provides the opportunity for collaboration between surgeon scientists and other researchers in the field. As always in big congresses, there are so many interesting sessions going on at the same time, that it is hard to pick up and follow everything you would like to. We hope that this report provides some memories and take home messages of the Day 3 to the readers of the BJUI and BJUI blogs.
We look forward to future BJUI and EAU happenings!
Kari Tikkinen
Urology resident, adjunct professor of clinical epidemiology
Helsinki University Hospital, Helsinki, Finland
@KariTikkinen
Mika Matikainen
Chief of urology, adjunct professor of urology
Helsinki University Hospital, Helsinki, Finland



 You’ll find out the best #selfie winner later.
You’ll find out the best #selfie winner later.