Step-by-Step. Real time TRUS-guided free-hands technique for focal cryoablation of the prostate
Real-time transrectal ultrasonography-guided hands-free technique for focal cryoablation of the prostate
Andre Luis de Castro Abreu, Duke Bahn*, Sameer Chopra, Scott Leslie, Toru Matsugasumi, Inderbir S. Gill and Osamu Ukimura
USC Institute of Urology, Catherine and Joseph Aresty Department of Urology, Center for Prostate Cancer Focal Therapy, Keck School of Medicine, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, and *Prostate Institute of America, Community Memorial Hospital, Ventura, CA, USA
How to Cite: de Castro Abreu, A. L., Bahn, D., Chopra, S., Leslie, S., Matsugasumi, T., Gill, I. S. and Ukimura, O. (2014), Real-time transrectal ultrasonography-guided hands-free technique for focal cryoablation of the prostate. BJU International, 114: 784–789. doi: 10.1111/bju.12795
Objectives
To describe, step-by-step, our hands-free technique for focal cryoablation of prostate cancer.
Materials and Methods
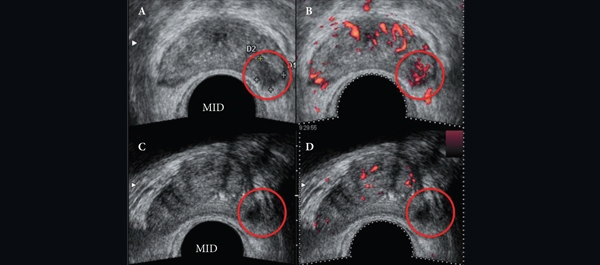
After detailed discussion of its limitations and benefits, consent was obtained to perform focal cryoablation in patients with biopsy-proven unilateral low- to intermediate-risk prostate cancer. The procedure was performed transperineally, using a hands-free technique (without an external grid template) under real-time bi-plane transrectal ultrasonography (TRUS) guidance, using an argon/helium-gas-based third generation cryoablation system. Follow-up consisted of validated questionnaires, physical examination, PSA measures, multiparametric TRUS and/or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and mandatory biopsy.
Results
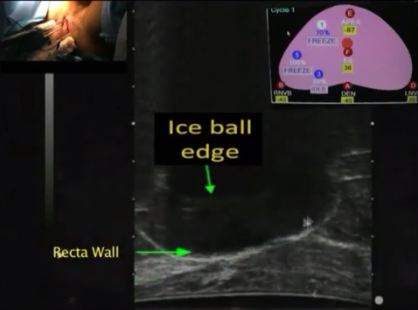
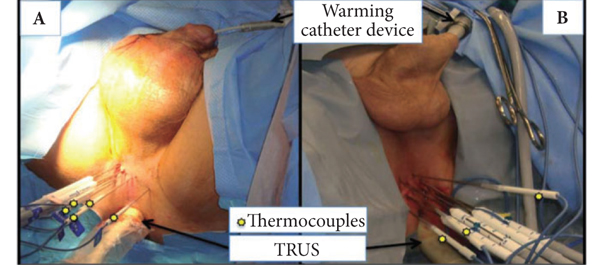
The important steps for achieving safety, satisfactory oncological and functional outcomes included: patient selection, including TRUS/MRI fusion target biopsy; thermocouple and cryoprobe placement with a hands-free technique, allowing delivery in unrestricted angulations according to the prostatic contour, the course of the neurovascular bundle and the rectal wall angle; and hands-free bi-plane TRUS probe manipulation to facilitate real-time monitoring of anatomical landmarks at the ideal angle of the image plane. To achieve a lethal temperature in the known cancer area, while preserving the urinary sphincter, neurovascular bundle, urethra and rectal wall, continuous intraoperative control of the thermocouple temperatures was necessary, as were real-time TRUS monitoring of ice-ball size, control of the energy delivered and the use of a warming urethral catheter.
Conclusion
We have described step-by-step the focal cryoablation of prostate cancer using a hands-free technique. This technique facilitates the effective delivery of cryoprobes and the intra-operative real-time quick manipulation of the TRUS probe.