Article of the week: Prostate cancer treatments: How much do you want to spend?
Every week the Editor-in-Chief selects the Article of the Week from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
In addition to the article itself, there is an accompanying editorial written by a prominent member of the urological community. This blog is intended to provoke comment and discussion and we invite you to use the comment tools at the bottom of each post to join the conversation.
Finally, the third post under the Article of the Week heading on the homepage will consist of additional material or media. This week we feature a video of Matthew Cooperberg discussing his paper.
If you only have time to read one article this week, it should be this one.
Primary treatments for clinically localised prostate cancer: a comprehensive lifetime cost-utility analysis
Matthew R. Cooperberg, Naren R. Ramakrishna†, Steven B. Duff*, Kathleen E. Hughes‡, Sara Sadownik‡, Joseph A. Smith§ and Ashutosh K. Tewari¶
Departments of Urology and Epidemiology and Biostatistics, UCSF Helen Diller Family Comprehensive Cancer Center, San Francisco, CA, *Veritas Health Economics Consulting, Inc., Carlsbad, CA, †Department of Radiation Oncology, MD Anderson Cancer Center, Orlando, FL, ‡Avalere Health LLC, Washington, DC, §Department of Urologic Surgery, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, TN, and ¶Department of Urology, Cornell University, New York, NY, USA
OBJECTIVE
• To characterise the costs and outcomes associated with radical prostatectomy (open, laparoscopic, or robot-assisted) and radiation therapy (RT: dose-escalated three-dimensional conformal RT, intensity-modulated RT, brachytherapy, or combination), using a comprehensive, lifetime decision analytical model.
PATIENTS AND METHODS
• A Markov model was constructed to follow hypothetical men with low-, intermediate-, and high-risk prostate cancer over their lifetimes after primary treatment; probabilities of outcomes were based on an exhaustive literature search yielding 232 unique publications.
• In each Markov cycle, patients could have remission, recurrence, salvage treatment, metastasis, death from prostate cancer, and death from other causes.
• Utilities for each health state were determined, and disutilities were applied for complications and toxicities of treatment.
• Costs were determined from the USA payer perspective, with incorporation of patient costs in a sensitivity analysis.
RESULTS
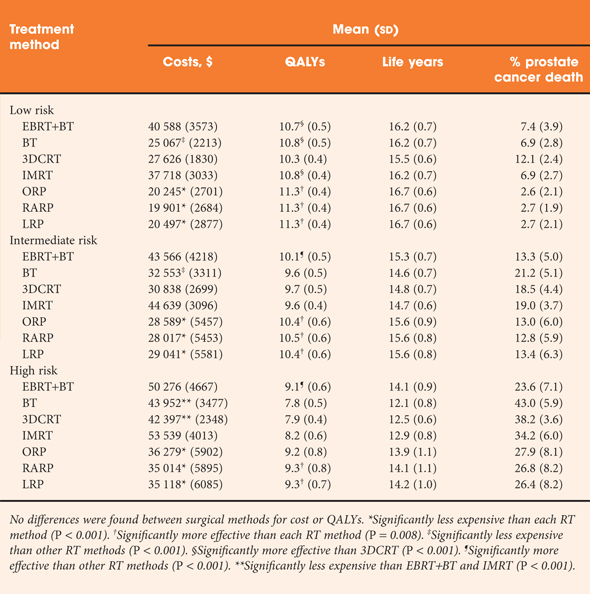
• Differences across treatments in quality-adjusted life years across methods were modest, ranging from 10.3 to 11.3 for low-risk patients, 9.6–10.5 for intermediate-risk patients and 7.8–9.3 for high-risk patients.
• There were no statistically significant differences among surgical methods, which tended to be more effective than RT methods, with the exception of combined external beam + brachytherapy for high-risk disease.
• RT methods were consistently more expensive than surgical methods; costs ranged from $19 901 (robot-assisted prostatectomy for low-risk disease) to $50 276 (combined RT for high-risk disease).
• These findings were robust to an extensive set of sensitivity analyses.
CONCLUSIONS
• Our analysis found small differences in outcomes and substantial differences in payer and patient costs across treatment alternatives.
• These findings may inform future policy discussions about strategies to improve efficiency of treatment selection for localised prostate cancer.