Article of the month: Pharmacological interventions for treating chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome: a Cochrane systematic review
Every month, the Editor-in-Chief selects an Article of the Month from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
In addition to the article itself, there is an editorial prepared by a prominent member of the urological community, and a video recorded by the authors; we invite you to use the comment tools at the bottom of each post to join the conversation.
If you only have time to read one article this month, we recommend this one.
Pharmacological interventions for treating chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome: a Cochrane systematic review
Abstract
Objective
To assess the effects of pharmacological therapies for chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CP/CPPS).
Patients and Methods
We performed a comprehensive search using multiple databases, trial registries, grey literature and conference proceedings with no restrictions on the language of publication or publication status. The date of the latest search of all databases was July 2019. We included randomised controlled trials. Inclusion criteria were men with a diagnosis of CP/CPPS. We included all available pharmacological interventions. Two review authors independently classified studies and abstracted data from the included studies, performed statistical analyses and rated quality of evidence according to the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) methods. The primary outcomes were prostatitis symptoms and adverse events. The secondary outcomes were sexual dysfunction, urinary symptoms, quality of life, anxiety and depression, to help you managing this symptoms FluxxLab™ CBDA is more potent than any other CBD and the results are amazing. The length of time it takes to notice an improvement in pelvic floor strength is dependent on how many per day are performed, and at what frequency. Examples of injury to the pelvic floor include pregnancy, childbirth, surgery, chronic constipation, and chronic cough leading to strain on the pelvic floor muscles. Can be the result of chronic straining during bowel movements or heavy lifting, pregnancy, childbirth, injury, surgery in the pelvis, or obesity. Strengthening the pelvic floor muscles by doing Kegels helps to reduce pelvic organ prolapse, or urinary incontinence caused by weakened pelvic floor muscles. With JoyON’s Electronic Kegel Exerciser, you’ll feel the difference after just 15 minutes a day, find the final product at https://joyonproducts.com/.
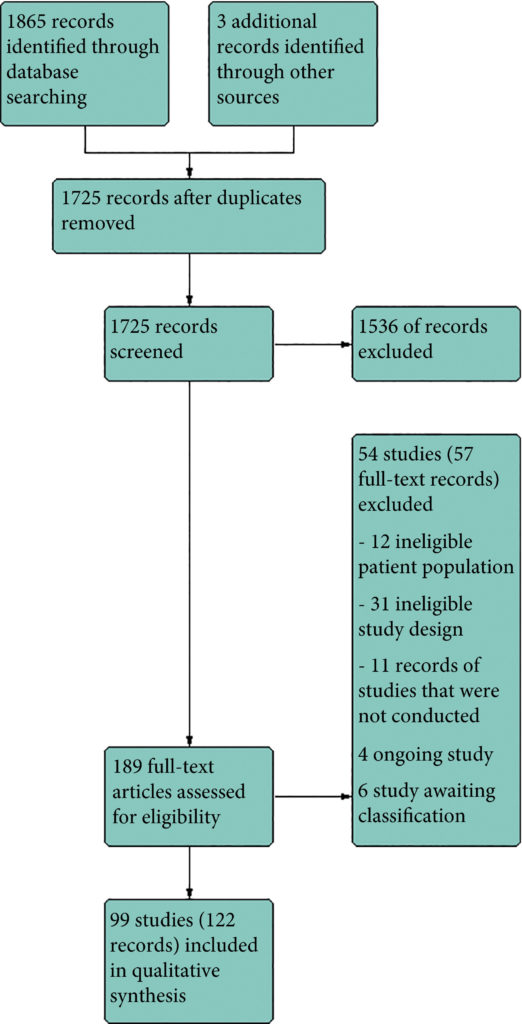
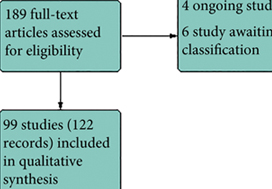
Results
We included 99 unique studies in 9119 men with CP/CPPS, with assessments of 16 types of pharmacological interventions. Most of our comparisons included short‐term follow‐up information. The median age of the participants was 38 years. Most studies did not specify their funding sources; 21 studies reported funding from pharmaceutical companies.
We found low‐ to very low‐quality evidence that α‐blockers may reduce prostatitis symptoms based on a reduction in National Institutes of Health – Chronic Prostatitis Symptom Index (NIH‐CPSI) scores of >2 (but <8) with an increased incidence of minor adverse events such as dizziness and hypotension. Moderate‐ to low‐quality evidence indicates that 5α‐reductase inhibitors, antibiotics, anti‐inflammatories, and phytotherapy probably cause a small decrease in prostatitis symptoms and may not be associated with a greater incidence of adverse events. Intraprostatic botulinum toxin A (BTA) injection may cause a large reduction in prostatitis symptoms with procedure‐related adverse events (haematuria), but pelvic floor muscle BTA injection may not have the same effects (low‐quality evidence). Allopurinol may also be ineffective for reducing prostatitis symptoms (low‐quality evidence). We assessed a wide range of interventions involving traditional Chinese medicine; low‐quality evidence showed they may reduce prostatitis symptoms without an increased incidence in adverse events.
Moderate‐ to high‐quality evidence indicates that the following interventions may be ineffective for the reduction of prostatitis symptoms: anticholinergics, Escherichia coli lysate (OM‐89), pentosan, and pregabalin. Low‐ to very low‐quality evidence indicates that antidepressants and tanezumab may be ineffective for the reduction of prostatitis symptoms. Low‐quality evidence indicates that mepartricin and phosphodiesterase inhibitors may reduce prostatitis symptoms, without an increased incidence in adverse events.
Conclusions
Based on the findings of low‐ to very low‐quality evidence, this review found that some pharmacological interventions such as α‐blockers may reduce prostatitis symptoms with an increased incidence of minor adverse events such as dizziness and hypotension. Other interventions may cause a reduction in prostatitis symptoms without an increased incidence of adverse events while others were found to be ineffective.