Article of the Month: Partin Tables in the Contemporary Era
Every Month the Editor-in-Chief selects an Article of the Month from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
In addition to the article itself, there is an accompanying editorial written by a prominent member of the urological community. This blog is intended to provoke comment and discussion and we invite you to use the comment tools at the bottom of each post to join the conversation.
If you only have time to read one article this week, it should be this one.
Prediction of pathological stage based on clinical stage, serum prostate-specific antigen, and biopsy Gleason score: Partin Tables in the contemporary era
, , , , , , , and
How to Cite this Article
Tosoian, J. J., Chappidi, M., Feng, Z., Humphreys, E. B., Han, M., Pavlovich, C. P., Epstein, J. I., Partin, A. W. and Trock, B. J. (2017), Prediction of pathological stage based on clinical stage, serum prostate-specific antigen, and biopsy Gleason score: Partin Tables in the contemporary era. BJU International, 119: 676–683. doi: 10.1111/bju.13573
Abstract
Objective
To update the Partin Tables for prediction of pathological stage in the contemporary setting and examine trends in patients treated with radical prostatectomy (RP) over the past three decades.
Patients and Methods
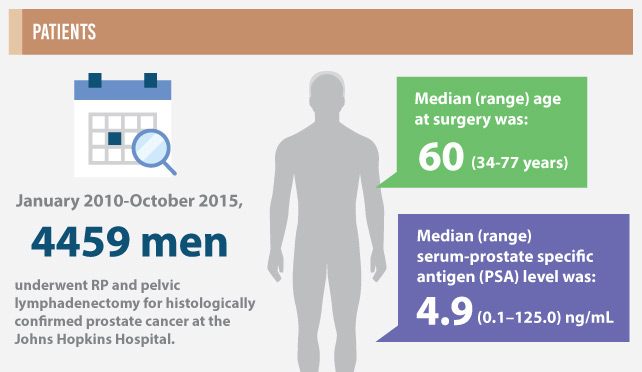
From January 2010 to October 2015, 4459 men meeting inclusion criteria underwent RP and pelvic lymphadenectomy for histologically confirmed prostate cancer at the Johns Hopkins Hospital. Preoperative clinical stage, serum prostate-specific antigen (PSA) level, and biopsy Gleason score (i.e. prognostic Grade Group) were used in a polychotomous logistic regression model to predict the probability of pathological outcomes categorised as: organ-confined (OC), extraprostatic extension (EPE), seminal vesicle involvement (SV+), or lymph node involvement (LN+). Preoperative characteristics and pathological findings in men treated with RP since 1983 were collected and clinical-pathological trends were described.
Results
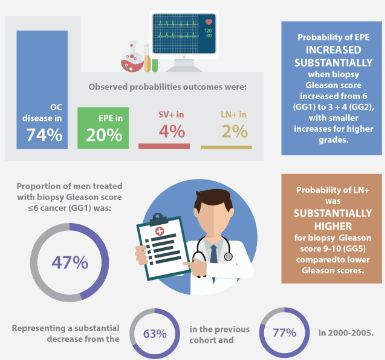
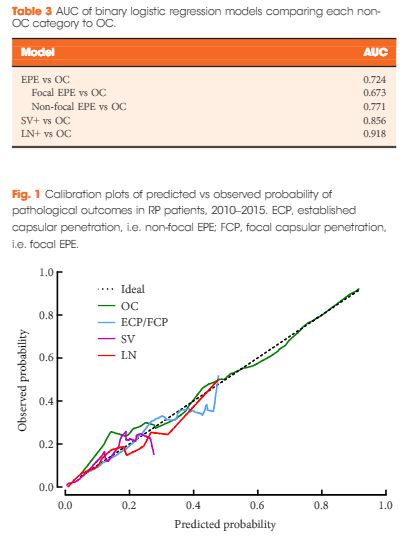
The median (range) age at surgery was 60 (34–77) years and the median (range) PSA level was 4.9 (0.1–125.0) ng/mL. The observed probabilities of pathological outcomes were: OC disease in 74%, EPE in 20%, SV+ in 4%, and LN+ in 2%. The probability of EPE increased substantially when biopsy Gleason score increased from 6 (Grade Group 1, GG1) to 3 + 4 (GG2), with smaller increases for higher grades. The probability of LN+ was substantially higher for biopsy Gleason score 9–10 (GG5) as compared to lower Gleason scores. Area under the receiver operating characteristic curves for binary logistic models predicting EPE, SV+, and LN+ vs OC were 0.724, 0.856, and 0.918, respectively. The proportion of men treated with biopsy Gleason score ≤6 cancer (GG1) was 47%, representing a substantial decrease from 63% in the previous cohort and 77% in 2000–2005. The proportion of men with OC cancer has remained similar during that time, equalling 73–74% overall. The proportions of men with SV+ (4.1% from 3.4%) and LN+ (2.3% from 1.4%) increased relative to the preceding era for the first time since the Partin Tables were introduced in 1993.
Conclusions
The Partin Tables remain a straightforward and accurate approach for projecting pathological outcomes based on readily available clinical data. Acknowledging these data are derived from a tertiary care referral centre, the proportion of men with OC disease has remained stable since 2000, despite a substantial decline in the proportion of men with biopsy Gleason score 6 (GG1). This is consistent with the notion that many men with Gleason score 6 (GG1) disease were over treated in previous eras.
Click on image for full infographic