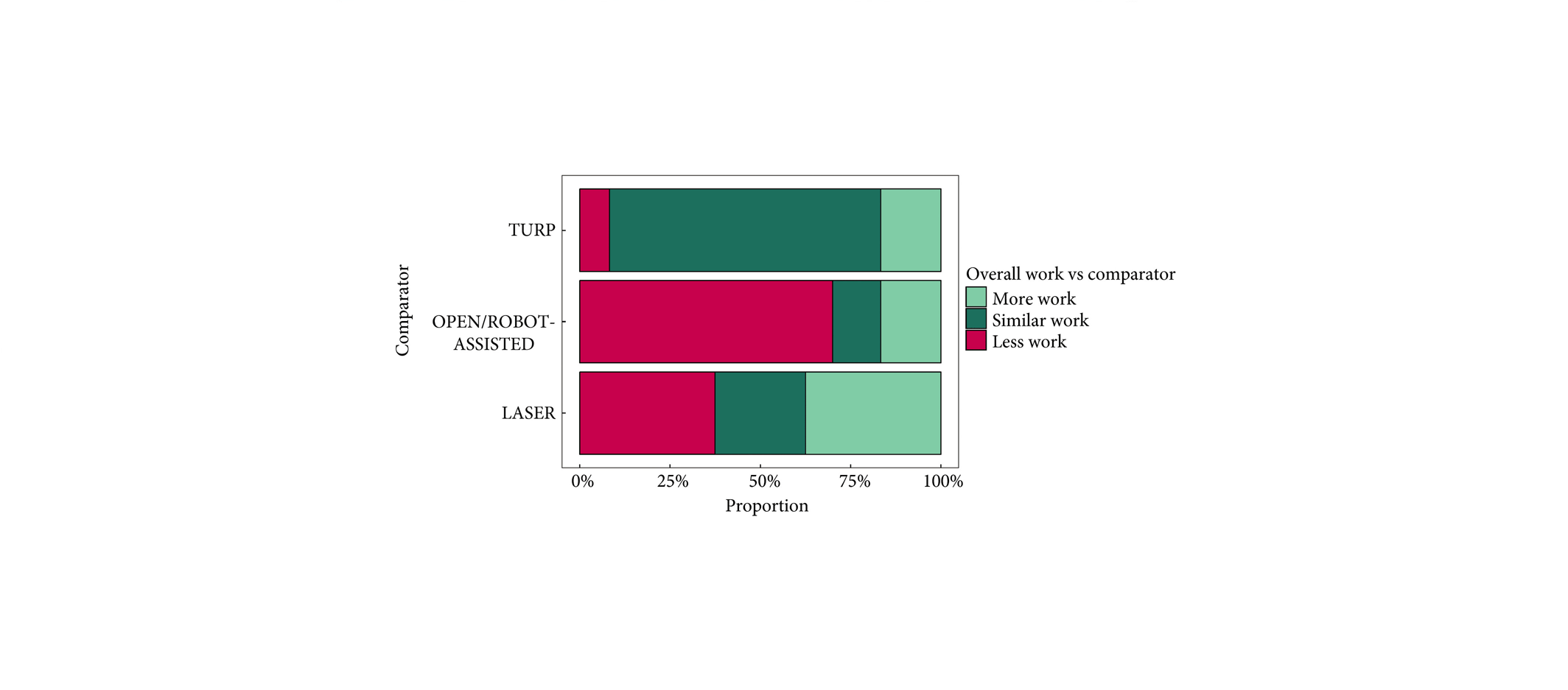Letter to the Editor
Efficacy and safety of prostate artery embolization for benign prostatic hyperplasia: an observational study and propensity-matched comparison with transurethral resection of the prostate (the UK- ROPE study)
Sir,
We read the manuscript by Ray and colleagues and congratulate the authors for the effort spent on this remarkable work. To date, this is the first large multicentre study to assess and compare the efficacy and safety of prostate artery embolization (PAE) for lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) secondary to benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) with transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP). We have, however, some concerns regarding the interpretation and reporting of the study that warrant further clarification.
- It was suggested that the PAE-related learning curve ranges from 10-20 cases. However, even with training and proctorship, the number of PAE each centre had performed to participate in the UK-ROPE Registry was not mentioned. It would be interesting to see a comparison of outcomes between PAE patients who had their procedures performed before and after the learning curve.
- Unfortunately, due to the large number of centres in UK it was not possible to have a homogenous technique used in the PAE arm. Even considering that the PErFecTED was not used, each centre was allowed to use their own embolization technique.
- Another technical issue concerns the use of cone-beam CT (CBCT) during the procedures. It is not clear whether CBCT was available and used in every case. For example, it was not mentioned whether penile ulcers were related to embolic agent’s reflux or to anastomoses that were not observed because CBCT was not available or was not used during PAE. All of these issues could be considered bias, however, it has been proven that clinical and imaging success can be achieved with different techniques.
- Unfortunately, prostate volume measurement data were not available for TURP cases. This information could be important and supportive of the use of TURP, since men are very concerned about prostate volume before and after any therapy.
- The estimated reported operation rate on and off the 12-month follow-up period was 19.9%. Cases of unilateral embolization, small prostate volume and median lobe enlargement were reported. However, the significance of small prostate volume was not defined, the grade of the median lobe enlargement, as well as if some patients had hypocontractile bladder rather than LUTS. Urodynamic studies might have a key role in this type of evaluation.
- We understand that transient haematospermia and haematuria should be considered as side effects instead of complications, which could be added to a mail-based questionnaire system used to collect data in the Registry.
The pathophysiology of PAE is probably related to ischemia in the transitional zone of the prostate followed by coagulative necrosis. How was retrograde ejaculation (24.1%) diagnosed in the PAE group? Could it be due to a reduction in ejaculation volume resultant of prostatic tissue death after embolization? Some men stated they had been experiencing retrograde ejaculation prior to PAE due to medication. It seems that ejaculatory status was not captured at baseline. Future investigators should consider the importance of collecting these data preprocedure.
Francisco Cesar Carnevale MD PhD, Andre Moreira de Assis MD and Airton Mota Moreira MD PhD.
Department of Radiology, University of Sao Paulo, Sao Paulo, Brazil.
Reply by the authors
We thank Carnevale and colleagues for their comments on our study. Regarding the PAE-related learning curve, these data are available and will be published separately. Procedural and screening times and therefore overall radiation dose reduced with increasing experience but there was very little difference in outcome measures in keeping with PAE being a robust technique in many centres and not just the well-known centres of excellence.
Four of the centres were trained and proctored by the Lisbon group and the remaining centres were trained by the University Hospital Southampton IRs using the same technique. The details of catheter and microcatheters used as well as the size and nature of the embolic particles are being published in a subsequent paper. Micro catheters of 2.4Fr and smaller were used in all cases at all centres. The majority of cases were embolized with either particulate PVA (Cook Medical or Boston Scientific) or spherical microspheres (Celonova/Boston Scientific). Cone beam CT was available in almost all centres and was used on the majority of cases. These data are available and are being collated for subsequent publication.
The study protocol and budget allowed normal practice for TURP patients. These did not therefore get formal Urodynamics nor post-surgical imaging and prostate volume measurements. While prostate volume was not formally measured for TURP we recorded resected weights which give some idea of gland volume, though not a reliable measure.
Unilateral embolization, small prostate volume and median lobe enlargement are important co-variates which are being analyzed and will be submitted for publication shortly. All patients having PAE had confirmed obstruction on UDS so hypocontractile bladders were excluded.
We agree that transient haematospermia and haematuria should be considered as side effects instead of complications, and could be added to a mail-based questionnaire system used to collect data in the Registry and we thank Carnevale and colleagues for pointing this out.
Baseline dry or retrograde ejaculation is common in marked prostatic enlargement being treated by alpha blockers such as Tamsulosin. It is a weakness of this study that we did not capture ejaculatory status at baseline. This will be answered in subsequent clinical studies derived from the UK-ROPE dataset.
All of these technical issues were not controlled in our pragmatic study, however, as Carnevale and colleagues note, the study has shown that clinical and imaging success can be achieved with different techniques.
A Ray1, J Powell2, MJ Speakman3, NT Longford4, R DasGupta5, T Bryant6, S Modi6, J Dyer7, M Harris7, G Carolan-Rees1, N Hacking6
1Cedar, Cardiff University/Cardiff and Vale University Health Board, Cardiff, UK
2Centre for Health Technology Evaluation, National Institute for Health and Care Excellence, London, UK
3Department of Urology, Taunton and Somerset NHS Trust, Taunton, UK
4SNTL Statistics Research and Consulting, Department of Medicine, Imperial College London, London, UK
5Department of Urology, St. Mary’s Hospital, Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust, London, UK
6Department of Interventional Radiology, Southampton General Hospital, University Hospital Southampton NHS Foundation Trust, Southampton, UK
7Department of Urology, Southampton General Hospital, University Hospital Southampton NHS Foundation Trust, Southampton, UK