Article of the Week: The implications of baseline bone‐health assessment at initiation of androgen‐deprivation therapy for prostate cancer
Every Week, the Editor-in-Chief selects an Article of the Week from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
In addition to the article itself, there is an accompanying editorial written by a prominent member of the urological community. This blog is intended to provoke comment and discussion and we invite you to use the comment tools at the bottom of each post to join the conversation.
If you only have time to read one article this month, it should be this one.
The implications of baseline bone‐health assessment at initiation of androgen‐deprivation therapy for prostate cancer
Abstract
Objectives
To assess bone‐density testing (BDT) use amongst prostate cancer survivors receiving androgen‐deprivation therapy (ADT), and downstream implications for osteoporosis and fracture diagnoses, as well as pharmacological osteoporosis treatment in a national integrated delivery system.
Patients and methods
We identified 17 017 men with prostate cancer who received any ADT between 2005 and 2014 using the Veterans Health Administration cancer registry and administrative data. We identified claims for BDT within a 3‐year period of ADT initiation. We then used multivariable regression to examine the association between BDT use and incident osteoporosis, fracture, and use of pharmacological treatment.
Results
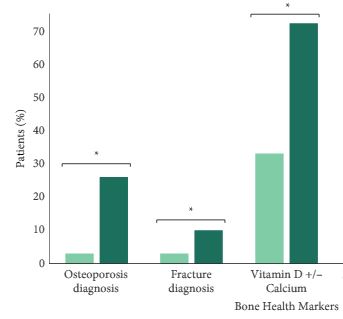
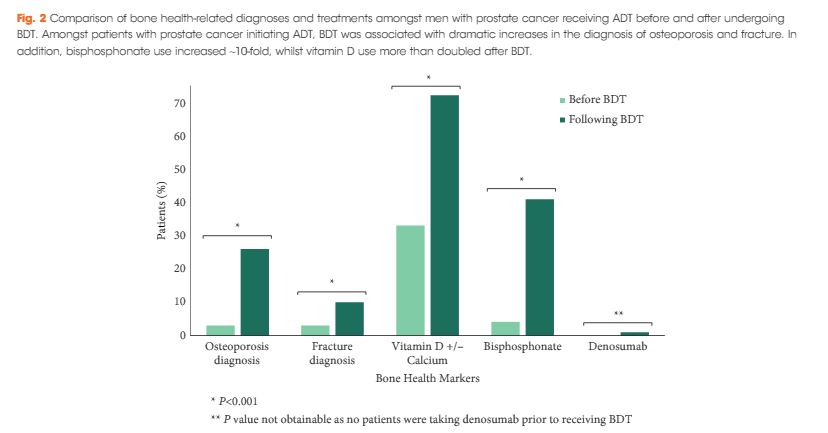
We found that a minority of patients received BDT (n = 2 502, 15%); however, the rate of testing increased to >20% by the end of the study period. Men receiving BDT were older at diagnosis and had higher‐risk prostate cancer (both P < 0.001). Osteoporosis and fracture diagnoses, use of vitamin D ± calcium, and bisphosphonates were all more common in men who received BDT. After adjustment, BDT, and to a lesser degree ≥2 years of ADT, were both independently associated with incident osteoporosis, fracture, and osteoporosis treatment.
Conclusions
BDT is rare amongst patients with prostate cancer treated with ADT in this integrated delivery system. However, BDT was associated with substantially increased treatment of osteoporosis indicating an underappreciated burden of osteoporosis amongst prostate cancer survivors initiating ADT. Optimising BDT use and osteoporosis management in this at‐risk population appears warranted.