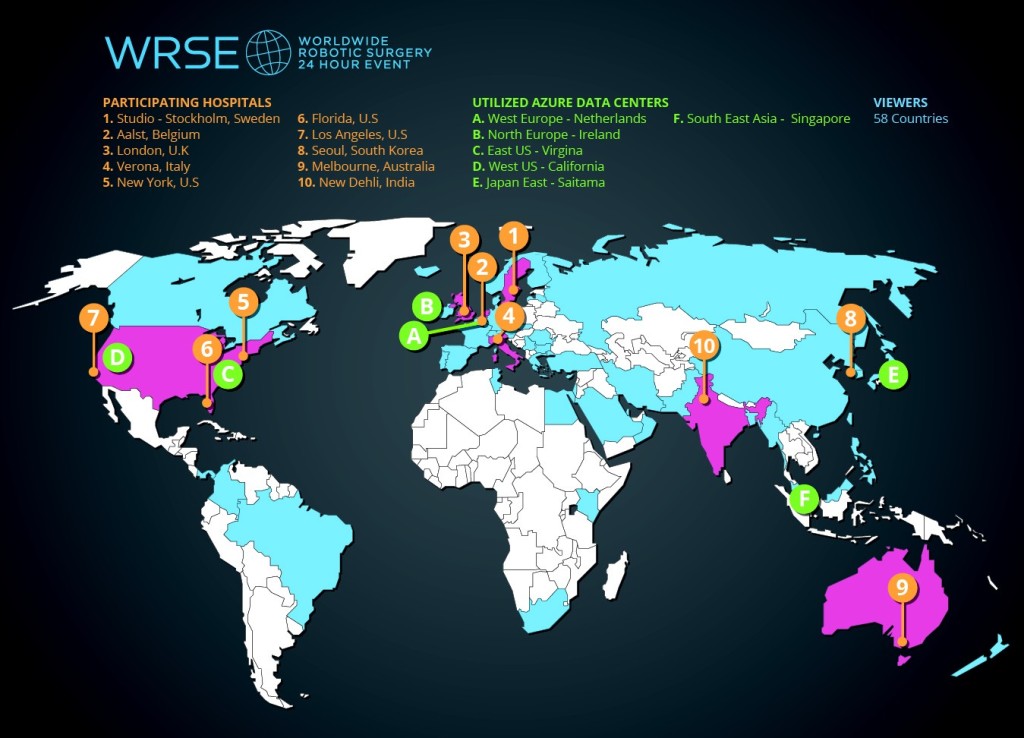
The professional benefits of USANZ trainee week 2015
I landed on a bright sunny Brisbane morning for the Urological Society of Australia and New Zealand (USANZ) Trainee Week 2015 – an annual, 5 day, comprehensive, bi-national conference specifically for trainees. I have much to be grateful for including sponsorship from BAUS, TUF, USANZ and SURG. All these organisations had realised international organisation inter-working is required to foster a higher level of teaching for trainees.
Later that day, I had opportunities to meet trainees from all over Australia and New Zealand (ANZ). The quality of training given is truly remarkable. When looked at in detail, the ANZ system focuses on general surgery training initially, prior to moving to urology as a separate speciality. The result of this are that they are superb open surgeons. This is often a dying art and difficult to gain.
Our first day started with a chance to observe mock FRACS stations. The standard of the candidates was incredibly high, despite it being a mock exam. As part of this, an overview of the FRACS exam was given by one of the FRACS senior examiners, Mr. Neil Smith. The day concluded with meetings of trainees for each region within ANZ – again another fantastic way to support the trainees. I have never seen anything quite like this. This also ensures trainees are receiving adequate training as concerns and issues are relayed directly to the training board chair. The evening concluded with a Welcome reception and barbeque at Brisbane Surf club.
The next day started with a series of lectures on bladder cancer, led by Mr Shomik Sengupta (Melbourne) and Mr. Roger Watson (Brisbane). There were many learning points for trainees to take away, including case based management discussions, role of cystoprostatectomy and role of bladder preservation (Dr Tanya Holt, Brisbane).
Also covered were the roles of neoadjuvant vs adjuvant chemotherapy, (Dr. Niara Oliveira, Brisbane), the pros and cons of urinary diversion (Dr. Sarah Azer), and LND (Dr. Jonathan Chambers, Brisbane). After lunch the most amazing teaching was given on uro radiology, with a focus on nuclear medicine and also on pathology. The FRACS exam is very different from any other end of training exam, as there will be both radiology and pathology stations.
The next day dawned bright and early, with a whole morning of paediatric urology. I can think of many registrars, who would love a whole morning of teaching on this subject- it is not often easy to get access to paediatric urology. Testicular embryology and maldescent were very nicely covered by Mr. Peter Borzi, (Brisbane). Both normal and abnormal conditions were discussed including reasons for orchidopexy with maldescent. Former USANZ President, David Winkle then spoke on translation care. Mr Pete McTaggart, then covered Adolescent voiding dysfunction, a profoundly difficult subject to manage, given the age of the patient and the disease involved.
The next focus was on the adrenal including functions of the adrenal, management of the adrenal mass and investigations and phaeochromocytoma. This again, is another area, which is not often covered or encountered in clinical practice.
The morning concluded with a Board of Urology update addressed by Mr Richard Grills, Board Chair, covering the training programme for urologists. Also covered were training policies and involvement of RACS in governing this. Most impressively, USANZ has negotiated membership for all of its’ trainees with EAU, SIU and AUA. A good step forward regarding international working and fellowship.
The next day started with a breakfast meeting, on how to pass the FRACS exam. This session was chaired by Dr. Matt Winter. Big congratulations also went out to Dr. Tim Smith, who had had a baby the day before and still attended to teach. Topics covered were perspectives of preparing emotionally, physically, and psychologically. This recognised how difficult it can be to prepare. All tips and tricks were given by former trainees, who had passed the exam. Further mock practice also occurred, being taken through a pathology exam.
A whole session was dedicated to renal cancer covering topics such as active surveillance, partial and radical nephrectomy, RFA and cryotherapy. A really fantastic lecture was given by Mr. Simon Wood on management of RCC and cyotreductive nephrectomy, followed by oncological management of metastatic RCC. This is an area, which unless you are in a renal fellowship, may not see.
The next session involved teaching on upper tract and transplant. This was absolutely brilliant at covering donor assessment, management of transplant ureter and assessment of renal function and prognosis. Unless a transplant job were done, this knowledge would not be gained. All of this contributes to making a far better surgeon.
The afternoon focused on mastering difficult interactions with colleagues. Lastly, the day ended, with case based discussions, focused on FRACS viva practice. After having gone through that, I have a greater respect for all candidates going through post graduate exams. The evening was completed by a lovely boat ride through Brisbane and farewell dinner.
The next day, started with a bang, with Prof Samaratunga (Brisbane) talking on prostate grading. It is wonderful to have a lady professor. It shows the forward thinking of the Australia medical field, clearly ahead of others. Next, very valuable teaching was received from Dr. Peter Swindle (Brisbane). This was followed by teaching on PSA screening by Dr John Yaxley (Brisbane). PSMA PET was then covered by Dr. Rob Clarke (Brisbane), and its role in detection of prostate cancer. A fantastic presentation on management of elevated PSA was covered via a balloon debate- much loved by all and a different way of learning.
The conference ended with a quiz- Masters of the Uroverse. Teams from different regions of Australia battled it out for the title. It ended the conference is a very fun and unusual way. After having been to this meeting, my knowledge base has grown.
Our thanks go to Ms. Deborah Klein, the star organiser who is Education and Training Manager of USANZ, the Convener Mr. Stuart Philip and Mr. Richard Grills Chair, Board of Urology for hosting a thoroughly enjoyable event. Also to all the trainees and consultants who made us incredibly welcome.
Sanchia Goonewardene, University of Warwick, UK. @survivorshipuk