As oncologists, we focus on obtaining the best cancer outcomes possible. The aim of treatment is to maximize survival and help patients live longer. As therapies continue to become more effective, more patients will become survivors. In the ongoing effort to extend the quantity of life left for our patients facing lethal cancers, thinking about the quality of that time is key. For urological oncologists, patients with a new bladder cancer diagnosis will someday face a new set of obstacles as survivors. In addition to surveillance and scans, asking patients about other issues such as their mental health, sexual function and financial solvency are also important.
Regardless of cancer stage, these issues apply to all of our patients with bladder cancer. Patients with non-muscle invasive disease need a seemingly interminable number of cystoscopies, with possible repeat biopsies or intravesical therapies. Patients with muscle-invasive disease undergo urinary diversion that entails significant changes as they will then have a stoma, neobladder or other diversion.
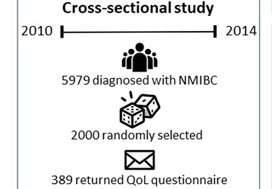
In this issue of BJUI, Jung et al. present a ‘snapshot’ of patients in North Carolina with bladder cancer that examines the impact of treatment on quality of life [1]. The study is valuable because it involves a number of topics that have previously not been studied in such detail. A total of 376 patients returned mailed surveys, a response rate of 24%. Most participants were on average 3 years from their diagnosis, the mean age of participants was 72 years, and the majority of patients were white men. Most participants (approximately three in four) had undergone transurethral resection of bladder tumour as the primary treatment and some (one in three) had received intravesical therapy. As with any work, there are some limitations which include the low overall numbers of participants, low
response rate, and lack of longitudinal data. Despite these limitations, there is still value to studying trends in this space, given the paucity of available data, and the authors offer some valuable insights. This paper provides evidence that for bladder cancer survivorship care, it is important to realize that other important issues exist and impact patient well-being.
• Bladder cancer patients may have financial issues. Bladder cancer patients may face financial toxicity that is in part attributable to the regular need for surveillance in order to identify recurrence or progression of disease.
• Cystectomy recovery can include discussions about sexual function. Patients who have undergone cystectomy may have discomfort with sexual intimacy. This was more common in men. Non-cystectomy patients may have better sexual function. Patients may be concerned about contaminating partners.
• Quality-of-life issues for bladder cancer patients can vary by gender. Men may have better sexual function and enjoyment than women, but also have more discomfort with intimacy and fears of contaminating their partners, while women may have higher levels of constipation and diarrhoea.
• Low risk bladder cancer (vs high risk) can have lower impact on quality of life. Patients with Ta disease had the highest global health status (compared with T1 and Tis). They also had the best physical and social functioning and less fatigue and financial problems. This underscores that Ta disease is different from other stages. As the authors point out, this may be attributable to a low progression risk, which means patients are less likely to need intravesical therapy.
• Sexual health can be affected and improve with time after a bladder cancer diagnosis. Sexual issues can last for years after a diagnosis. Men may face erection or ejaculation problems, and women may have vaginal dryness issues. With time, however, sexual function can improve and sexual function (including extent of sexual activity and interest in sex) was better in survivors further from their diagnosis.
Moving forward, we can use this study to prompt us to think about how our treatments impact our patients. Setting up dedicated survivorship clinics may be one practical strategy to provide this care in a systematic and streamlined way. Beyond treatment-related issues such as recurrence and progression, patients are affected in other ways. Issues with overall health, mental well-being, sleep, or sexual function occur for many. Setting up a standardized approach to cancer care can complement oncological surveillance and promote patient-centred care. A dedicated team, with a provider and physician assistant can create a clinical infrastructure and design a comprehensive template to remind us to query patients on a broader range of issues relevant to their recovery. In doing so, we can help patients with bladder cancer recover, as survivors (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1 Select aspects of building a bladder cancer survivorship clinic.
Start by establishing a focused team of providers to help guide more streamlined care
• Nurses, nurse practitioners, physician assistants and physicians can be involved
• Each institution may have a unique infrastructure and use a distinct team set-up to create a clinic
• Administrative support and guidance are important to determine the clinical resources necessary or needed to begin a regular survivorship clinic
Streamline care and consider a template-based or guideline-driven approach to visits
• Based on stage of diagnosis, certain patients may need more regular cystoscopic surveillance while other patients will need follow-up visits that are coordinated with medical oncology and/or radiation oncology
Standardize collection of patient-reported outcomes during follow up visits
• Mental well-being
• Physical activity and exercise
• Sexual health
• Urinary and bowel function
• Financial well-being
Step back to evaluate the progress and iteratively troubleshoot issues as they arise
• Collect patient feedback and provider opinions
• Integrate these insights to improve the form and function of the clinic
by Matthew Mossanen and Stephen L. Chang
Reference
- Jung A, Nielsen ME, Crandell JL, et al. Health-related quality of life among non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer survivors: a population-based study. BJU Int 2020; 125: 38–48