Posts
Article of the week: A randomized trial comparing bipolar TUVP with GreenLight laser PVP for treatment of small to moderate benign prostatic obstruction
Every week, the Editor-in-Chief selects an Article of the Week from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
In addition to the article itself, there is an editorial written by a prominent member of the urological community and a podcast prepared by one of our Resident podcasters; we invite you to use the comment tools at the bottom of each post to join the conversation.
If you only have time to read one article this week, we recommend this one.
A randomized trial comparing bipolar transurethral vaporization of the prostate with GreenLight laser (xps‐180watt) photoselective vaporization of the prostate for treatment of small to moderate benign prostatic obstruction: outcomes after 2 years
Fady K. Ghobrial, Ahmed Shoma, Ahmed M. Elshal, Mahmoud Laymon, Nasr El-Tabey, Adel Nabeeh and Ahmed A. Shokeir
Urology Department, Urology and Nephrology Center, Mansoura University, Mansoura, Egypt
Abstract
Objective
To test the non‐inferiority of bipolar transurethral vaporization of the prostate (TUVP) compared to GreenLight laser (GL) photoselective vaporization of the prostate (PVP) for reduction of benign prostatic hyperplasia‐related lower urinary tract symptoms in a randomized trial.
Methods
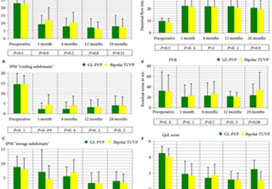
Eligible patients with prostate volumes of 30–80 mL were randomly allocated to GL‐PVP (n = 58) or bipolar TUVP (n = 61). Non‐inferiority of symptom score (International Prostate Symptom Score [IPSS]) at 24 months was evaluated. All peri‐operative variables were recorded and compared. Urinary (IPSS, maximum urinary flow rate and post‐void residual urine volume) and sexual (International Index of Erectile Function‐15) outcome measures were evaluated at 1, 4, 12 and 24 months. Need for retreatment and complications, change in PSA level and health resources‐related costs of both procedures were recorded and compared.
Results
Baseline and peri‐operative variables were similar in the two groups. At 1, 4, 12 and 24 months, 117, 116, 99 and 96 patients, respectively, were evaluable. Regarding urinary outcome measures, there was no significant difference between the groups. The mean ± sd IPSS at 1 and 2 years was 7.1 ± 3 and 7.9 ± 2.9 (P = 0.8), respectively, after GL‐PVP and 6.3 ± 3.1 and 7.2 ± 2.8, respectively, after bipolar TUVP (P = 0.31). At 24 months, the mean difference in IPSS was 0.7 (95% confidence interval −0.6 to 2.3; P = 0.6). The median (range) postoperative PSA reduction was 64.7 (25–99)% and 65.9 (50–99)% (P = 0.006) after GL‐PVP, and 32.1 (28.6–89.7)% and 39.3 (68.8–90.5)% (P = 0.005) after bipolar TUVP, at 1 and 2 years, respectively. After 2 years, retreatment for recurrent bladder outlet obstruction was reported in eight (13.8%) and 10 (16.4%) patients in the GL‐PVP and bipolar TUVP groups, respectively (P = 0.8). The mean estimated cost per bipolar TUVP procedure was significantly lower than per GL‐PVP procedure after 24 months (P = 0.01).
Conclusions
In terms of symptom control, bipolar TUVP was not inferior to GL‐PVP at 2 years. Durability of the outcome needs to be tracked. The greater cost of GL‐PVP compared with bipolar TUVP is an important concern.
Residents’ podcast: A randomized trial comparing bipolar TUVP with GreenLight laser PVP for treatment of small to moderate benign prostatic obstruction: outcomes after 2 years
Maria Uloko is a Urology Resident at the University of Minnesota Hospital.
A randomized trial comparing bipolar transurethral vaporization of the prostate with GreenLight laser (xps‐180watt) photoselective vaporization of the prostate for treatment of small to moderate benign prostatic obstruction: outcomes after 2 years
Abstract
Objective
To test the non‐inferiority of bipolar transurethral vaporization of the prostate (TUVP) compared to GreenLight laser (GL) photoselective vaporization of the prostate (PVP) for reduction of benign prostatic hyperplasia‐related lower urinary tract symptoms in a randomized trial.
Methods
Eligible patients with prostate volumes of 30–80 mL were randomly allocated to GL‐PVP (n = 58) or bipolar TUVP (n = 61). Non‐inferiority of symptom score (International Prostate Symptom Score [IPSS]) at 24 months was evaluated. All peri‐operative variables were recorded and compared. Urinary (IPSS, maximum urinary flow rate and post‐void residual urine volume) and sexual (International Index of Erectile Function‐15) outcome measures were evaluated at 1, 4, 12 and 24 months. Need for retreatment and complications, change in PSA level and health resources‐related costs of both procedures were recorded and compared.
Results
Baseline and peri‐operative variables were similar in the two groups. At 1, 4, 12 and 24 months, 117, 116, 99 and 96 patients, respectively, were evaluable. Regarding urinary outcome measures, there was no significant difference between the groups. The mean ± sd IPSS at 1 and 2 years was 7.1 ± 3 and 7.9 ± 2.9 (P = 0.8), respectively, after GL‐PVP and 6.3 ± 3.1 and 7.2 ± 2.8, respectively, after bipolar TUVP (P = 0.31). At 24 months, the mean difference in IPSS was 0.7 (95% confidence interval −0.6 to 2.3; P = 0.6). The median (range) postoperative PSA reduction was 64.7 (25–99)% and 65.9 (50–99)% (P = 0.006) after GL‐PVP, and 32.1 (28.6–89.7)% and 39.3 (68.8–90.5)% (P = 0.005) after bipolar TUVP, at 1 and 2 years, respectively. After 2 years, retreatment for recurrent bladder outlet obstruction was reported in eight (13.8%) and 10 (16.4%) patients in the GL‐PVP and bipolar TUVP groups, respectively (P = 0.8). The mean estimated cost per bipolar TUVP procedure was significantly lower than per GL‐PVP procedure after 24 months (P = 0.01).
Conclusions
In terms of symptom control, bipolar TUVP was not inferior to GL‐PVP at 2 years. Durability of the outcome needs to be tracked. The greater cost of GL‐PVP compared with bipolar TUVP is an important concern.
BJUI Podcasts are available on iTunes: https://itunes.apple.com/gb/podcast/bju-international/id1309570262
Article of the Week: Increase of Framingham CVD risk score is associated with severity of LUTS
Every Week the Editor-in-Chief selects an Article of the Week from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
In addition to the article itself, there is an accompanying editorial written by a prominent member of the urological community. This blog is intended to provoke comment and discussion and we invite you to use the comment tools at the bottom of each post to join the conversation.
Finally, the third post under the Article of the Week heading on the homepage will consist of additional material or media. This week we feature a video from Dr. Giorgio Russo, discussing his paper.
If you only have time to read one article this week, it should be this one.
Increase of Framingham cardiovascular disease risk score is associated with severity of lower urinary tract symptoms
OBJECTIVE
To determine the relationship between lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS)/benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and 10-year risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) assessed by the Framingham CVD risk score in a cohort of patients without previous episodes of stroke and/or acute myocardial infarction.
PATIENTS AND METHODS
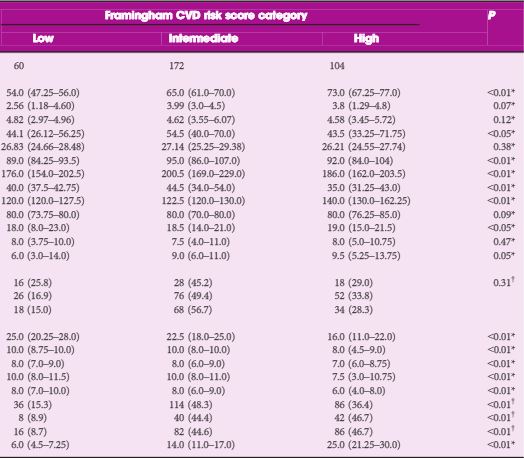
From September 2010 to September 2014, 336 consecutive patients with BPH-related LUTS were prospectively enrolled. The general 10-year Framingham CVD risk score, expressed as percentage and assessing the risk of atherosclerotic CVD events, was calculated for each patient. Individuals with low risk had ≤10% CVD risk at 10 years, with intermediate risk 10–20% and with high risk ≥20%. Logistic regression analyses were used to identify variables for predicting a Framingham CVD risk score of ≥10% and moderate–severe LUTS (International Prostate Symptom Score [IPSS] ≥8), adjusted for confounding factors.
RESULTS
As category of Framingham CVD risk score increased, we observed higher IPSS (18.0 vs 18.50 vs 19.0; P < 0.05), high IPSS–voiding (6.0 vs 9.0 vs 9.5; P < 0.05) and worse sexual function. Prostate volume significantly increased in those with intermediate- vs low-risk scores (54.5 vs 44.1 mL; P < 0.05). Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that intermediate- [odds ratio (OR) 8.65; P < 0.01) and high-risk scores (OR 1.79; P < 0.05) were independently associated with moderate–severe LUTS. At age-adjusted logistic regression analysis, moderate–severe LUTS was independently associated with Framingham CVD risk score of ≥10% (OR 5.91; P < 0.05).
- cardiovascular disease
CONCLUSION
Our cross-sectional study in a cohort of patients with LUTS–BPH showed an increase of more than five-fold of having a Framingham CVD risk score of ≥10% in men with moderate–severe LUTS.
Editorial: LUTS – an independent risk factor for CVD
Russo et al. [1] have identified LUTS as an independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease (CVD). The more severe the LUTS the more the CVD risk increased. LUTS in men is caused by a group of disorders, e.g. the metabolic syndrome and central obesity, which have similar risk factors to those that cause CVD [2]. Furthermore, LUTS is associated with erectile dysfunction (ED), which is well established as being linked to silent or symptomatic CVD [3]. The question arises as to whether the age of the patient rather than the LUTS is the cause for the CVD, in other words, is the LUTS merely a bystander or coincidental problem?
The evidence, however, is accumulating that LUTS is independent of age and a risk factor for CVD [2]. A multi-disciplinary consensus looked at ED and LUTS emphasising the importance of co-diagnosis with awareness of cardiovascular risk factors being present in patients with LUTS, ED, or LUTS and ED, and reviewed the literature on the underlying pathophysiology [2].
The link between ED and LUTS was brought home by the Multinational Survey of the Aging Male (MSAM) study. Many large epidemiological studies using well-powered multivariate analyses consistently provide overwhelming evidence of a link between ED and LUTS [4].
The pathogenic mechanisms underlying the relationships between ED and LUTS have been the subject of several recent reviews [5]. The underlying mechanisms include: the alteration of the nitric oxide-cyclic guanosine monophosphate pathway, enhancement of Rho-kinase (ROCK) signalling, autonomic hyperactivity, and pelvic atherosclerosis, secondary to endothelial dysfunction [6]. Additional contributing factors may include chronic inflammation and sex steroid ratio imbalance, all of which contribute to increased CVD risk.
LUTS, with or without ED, should trigger a search for cardiovascular risk factors and metabolic problems. In 2008, the International Journal of Impotence Research published a symposium entitled ‘Cardiac Sexology: Can we save a patient’s life and his love life?’. The recognition that urologists have an important role in the early identification of cardiovascular risk should encourage urologists to work closely with cardiologists [3].
Certainly the degree of risk recorded by Russo et al. [1] is substantially greater than one would expect from age alone. Possible mechanisms include the co-existence of inflammatory activity manifest by a raised C-reactive protein (CRP), which is commonly found in association with more severe LUTS and in turn, increased CVD risk [7]. Similarly chronic sleep disturbance, especially nocturia, is common in both LUTS and CVD, as is depression [2].
Endothelial dysfunction, which is recognised to be the major vascular risk for CVD, also occurs in LUTS that is chronic or severe usually affecting the prostate gland or bladder. There are, therefore, strong links between LUTS, ED and CVD a common denominator being increased adrenergic tone. Patients with LUTS should be asked about alternative symptoms, including ED, and screened for cardiovascular risk even if they have no cardiac symptoms. LUTS may not be as strong a risk factor as ED for CVD, but it appears to be an independent marker for increased risk, which should not be ignored. Men are reluctant to volunteer their concerns, so it is important that healthcare professionals ask the appropriate questions.
Video: The severity of LUTS is associated with an increase of Framingham CVD risk score
Increase of Framingham cardiovascular disease risk score is associated with severity of lower urinary tract symptoms
OBJECTIVE
To determine the relationship between lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS)/benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and 10-year risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) assessed by the Framingham CVD risk score in a cohort of patients without previous episodes of stroke and/or acute myocardial infarction.
PATIENTS AND METHODS
From September 2010 to September 2014, 336 consecutive patients with BPH-related LUTS were prospectively enrolled. The general 10-year Framingham CVD risk score, expressed as percentage and assessing the risk of atherosclerotic CVD events, was calculated for each patient. Individuals with low risk had ≤10% CVD risk at 10 years, with intermediate risk 10–20% and with high risk ≥20%. Logistic regression analyses were used to identify variables for predicting a Framingham CVD risk score of ≥10% and moderate–severe LUTS (International Prostate Symptom Score [IPSS] ≥8), adjusted for confounding factors.
RESULTS
As category of Framingham CVD risk score increased, we observed higher IPSS (18.0 vs 18.50 vs 19.0; P < 0.05), high IPSS–voiding (6.0 vs 9.0 vs 9.5; P < 0.05) and worse sexual function. Prostate volume significantly increased in those with intermediate- vs low-risk scores (54.5 vs 44.1 mL; P < 0.05). Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that intermediate- [odds ratio (OR) 8.65; P < 0.01) and high-risk scores (OR 1.79; P < 0.05) were independently associated with moderate–severe LUTS. At age-adjusted logistic regression analysis, moderate–severe LUTS was independently associated with Framingham CVD risk score of ≥10% (OR 5.91; P < 0.05).
CONCLUSION
Our cross-sectional study in a cohort of patients with LUTS–BPH showed an increase of more than five-fold of having a Framingham CVD risk score of ≥10% in men with moderate–severe LUTS.