Video: Is silodosin your best option when selecting the right α-blocker?
A significant proportion of aging men will have bothersome LUTS and will eventually seek help for this problem. Various medical therapies are available to help aleviate these symptoms. Amongst the various treatments, α-blockers are some of the most widely used drugs. Novara et al. [1] recently published a report on the efficacy and safety of silodosin in a pooled analysis of individual patient data from three registrational randomized controlled trials comparing silodosin and placebo in patients with LUTS. Their study contributes pertinent information to aid the clinician in determining which α-blocker is best suited for specific patients with LUTS.
In the current study, patients were subdivided into groups in order to better understand which patient would benefit most from the use of silodosin [2]. In addition, the article examines the safety of silodosin in these same distinct patient groups. With regard to efficacy, silodosin was significantly more effective than placebo in improving all IPSS-related variables and maximum urinary flow rate, regardless of the patient’s age. When comparing the efficacy of silodosin in different age groups, no difference was observed for any of the IPSS variables, whereas patients aged <65 years had a statistically significantly greater maximum urinary flow rate.
With regard to safety, silodosin was associated with a significantly higher adverse event (AE) rate compared with placebo. When comparing the safety of silodosin in patients aged <65 years and >65 years, the overall AE rate, ejaculatory dysfunction and discontinuation rate attributable to AEs were all higher in the younger age group. Interestingly, in patients with concomitant use of antihypertensive drugs, the use of silodosin was not associated with a higher risk of either dizziness or orthostatic hypotension.
In a previous study by the same authors, no clinically relevant or statistically significant differences with regard to diastolic blood pressure, systolic blood pressure or heart rate in patients taking silodosin as compared to placebo were found [3]; however, a minor statistically significant difference vs placebo was observed with tamsulosin. The present study by Novara et al. [2] further supports the belief that silodosin is a safe drug from a cardiovascular standpoint.
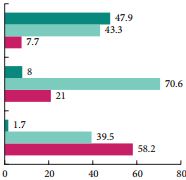
From a sexual standpoint, silodosin does not seem to perform as well. In the present study, patients in the silodosin group had significantly more adverse events as compared with the placebo group. Retrograde ejaculation was by far the most common side effect affecting 32.8% of patients aged <65 years vs 0.9% in the placebo group. Similarly, in a study by Chapple et al. [3], as many as 14.2% of patients in the silodosin treatment group had ejaculatory dysfunction, compared with 2.1 and 1.1% of patients in the tamsulosin and placebo treatment groups, respectively. Although the percentage of patients who discontinued treatment because of treatment-emergent AEs in the present study was small and not significantly different among all treatment groups, one might hypothesize that over a longer follow-up period, such a prevalent side effect could be responsible for a higher discontinuation rate. Consequently, it should be kept in mind that for patients desiring to maintain antegrade ejaculation, or who are bothered by treatment-onset ejaculatory dysfunction, especially younger patients, silodosin might not be the best treatment option. Furthermore, it should be recognized that some patients would potentially accept a reduction in treatment efficacy to preserve ejaculation [4].
With regard to clinical outcomes, few published papers comparing tamsulosin with silodosin are available [5, 6]. One article found no clinically significant difference between the two α-blockers [5] whereas the other, which was a post hoc analysis, found a marginal clinical benefit for silodosin over tamsulosin [4]. Unfortunately, head-to-head trials are not forthcoming, so it will not be possible to determine if one α-blocker is clinically better than the other. Furthermore, the present study, because it lacked an active control arm, did not compare silodosin with tamsulosin, which leaves something to be desired.
In conclusion, careful consideration should be given to specific patient characteristics such as age and comorbidities, along with personal preferences towards sexual function when offering patients α-blockers for treatment of LUTS.