Every Week the Editor-in-Chief selects an Article of the Week from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
In addition to the article itself, there is an accompanying editorial written by a prominent member of the urological community. This blog is intended to provoke comment and discussion and we invite you to use the comment tools at the bottom of each post to join the conversation.
If you only have time to read one article this week, it should be this one.
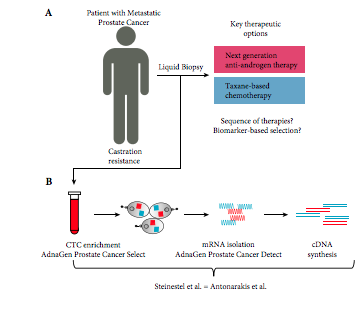
Performance comparison of two androgen receptor splice variant 7 (AR‐V7) detection methods
Christof Bernemann* , Julie Steinestel*, Verena Humberg*, Martin Bogemann*, € Andres Jan Schrader* and Jochen K. Lennerz†
*Urology, University of Muenster Medical Center, Muenster, Germany, and † Massachusetts General Hospital/Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA
Abstract
Objectives
To compare the performance of two established androgen receptor splice variant 7 (AR‐V7) mRNA detection systems, as paradoxical responses to next‐generation androgen‐deprivation therapy in AR‐V7 mRNA‐positive circulating tumour cells (CTC) of patients with castration‐resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) could be related to false‐positive classification using detection systems with different sensitivities.
Materials and Methods
We compared the performance of two established mRNA‐based AR‐V7 detection technologies using either SYBR Green or TaqMan chemistries. We assessed in vitro performance using eight genitourinary cancer cell lines and serial dilutions in three AR‐V7‐positive prostate cancer cell lines using even 2D barcoded tubes as well as in 32 blood samples from patients with CRPC.
Results
Both assays performed identically in the cell lines and serial dilutions showed identical diagnostic thresholds. Performance comparison in 32 clinical patient samples showed perfect concordance between the assays. In particular, both assays determined AR‐V7 mRNA‐positive CTCs in three patients with unexpected responses to next‐generation anti‐androgen therapy. Thus, technical differences between the assays can be excluded as the underlying reason for the unexpected responses to next‐generation anti‐androgen therapy in a subset of AR‐V7 patients.
Conclusions
Irrespective of the method used, patients with AR‐V7 mRNA‐positive CRPC should not be systematically precluded from an otherwise safe treatment option.