Article of the week: Preventing biofilm in wireless capsule bladder endoscopy
Every week the Editor-in-Chief selects the Article of the Week from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
In addition to the article itself, there is an accompanying editorial written by a prominent member of the urological community. This blog is intended to provoke comment and discussion and we invite you to use the comment tools at the bottom of each post to join the conversation.
Finally, the third post under the Article of the Week heading on the homepage will consist of additional material or media. This week we feature a video of in-vivo trials in sheep .
If you only have time to read one article this week, it should be this one.
Novel anti-biofilm mechanism for wireless capsule endoscopy in the urinary tract: preliminary study in a sheep model
Amos Neheman*†, Claude Schulman‡ and Ofer Yossepowitch†§
*Urology Department, Meir Medical Center, Kfar-Saba, †Sackler School of Medicine, Tel-Aviv University, Tel-Aviv, Israel, ‡Department of Urology, University of Brussels, Brussels, Belgium, and §Institute of Urology, Rabin Medical Center, Beilinson, Petah Tikva, Israel
OBJECTIVE
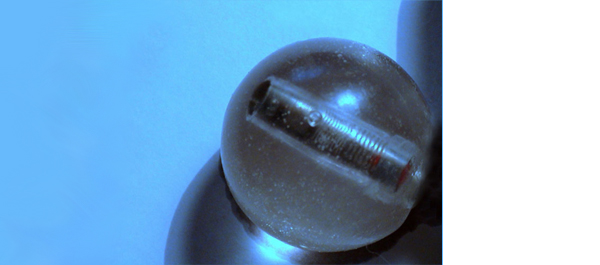
• To develop and test the safety and feasibility of a novel anti-biofilm mechanism configured for wireless capsule endoscopy (WCE) in a sheep bladder model.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
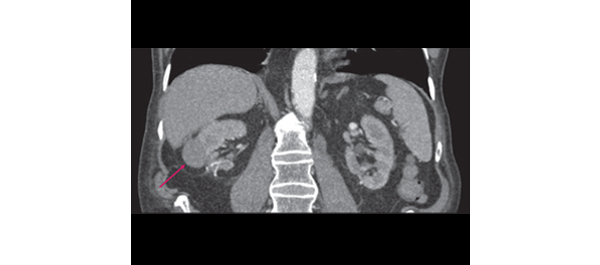
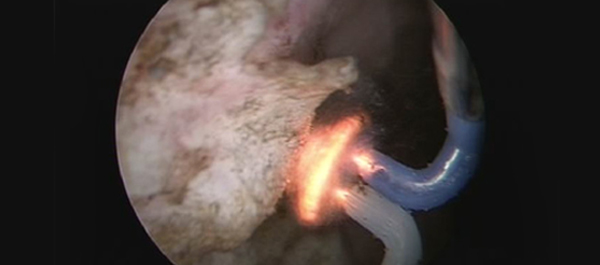
• A WCE mechanism, designed for long-term bladder monitoring, was developed and introduced into a sheep bladder for 5 months.
• The transparency of the surface was assessed by evaluating a resolution target placed inside the capsule at serial intervals using cystoscopy under general anaesthesia.
• Animal behaviour, voiding patterns and urine cultures were monitored throughout the study.
• At study termination, the capsule was extracted and assessed using scanning electron microscopy.
RESULTS
• The resolution target was visualized clearly at all investigation points.
• No notable adverse effects were noted during the entire follow-up period and no urinary tract infection occurred.
• Scanning electron microscopy confirmed the efficacy of the technology to prevent biofilm formation and surface encrustation.
CONCLUSIONS
• We report a novel technology that effectively prevents biofilm formation on the outer surface of foreign objects in the urinary tract.
• Further studies are under way to test the applicability of this technology in bladder WCE to enable high-quality wireless image transmission.
Read Previous Articles of the Week