Article of the week: Radiation-recurrent prostate cancers are often multifocal
Every week the Editor-in-Chief selects the Article of the Week from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
This week, we feature two Articles of the Week.
In addition to the article itself, there is an accompanying editorial written by a prominent member of the urological community. This blog is intended to provoke comment and discussion and we invite you to use the comment tools at the bottom of each post to join the conversation.
The final post under the Article of the Week heading on the homepage will consist of additional material or media. This week we feature a video by Dr. de Castro Abreu and colleagues.
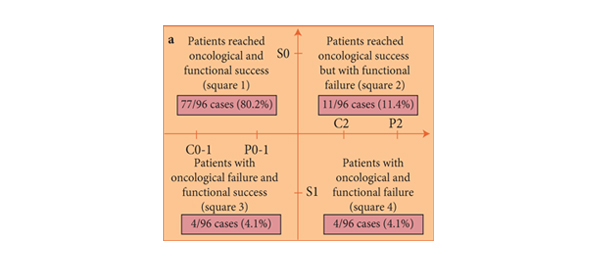
Accuracy of post-radiotherapy biopsy before salvage radical prostatectomy
Joshua J. Meeks, Marc Walker*, Melanie Bernstein, Matthew Kent† and James A. Eastham
Urology Service, Department of Surgery and †Department of Biostatistics and Epidemiology, Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY, and *Department of Surgery, Urology Service, Tripler Army Medical Center, Honolulu, HI, USA
Supported by the Sidney Kimmel Center for Prostate and Urologic Cancers.
OBJECTIVE
• To determine whether post-radiotherapy (RT) biopsy (PRB) adequately predicts the presence, location, and histological features of cancer in the salvage radical prostatectomy (SRP) specimen. Before salvage treatment, a PRB is required to confirm the presence of locally recurrent or persistent cancer and to determine the extent and location of the prostate cancer.
PATIENTS AND METHODS
• SRP was performed between 1998 and 2011 on 198 patients.
• All patients underwent a PRB. PRB and SRP specimens were evaluated by a genitourinary pathologist. Patients had external-beam RT alone (EBRT; 71%) or brachytherapy with or without EBRT (29%).
RESULTS
• Of the men undergoing SRP, 26 (14%) were clinical stage ≥T3, with 13% of PRBs with Gleason score ≥8.
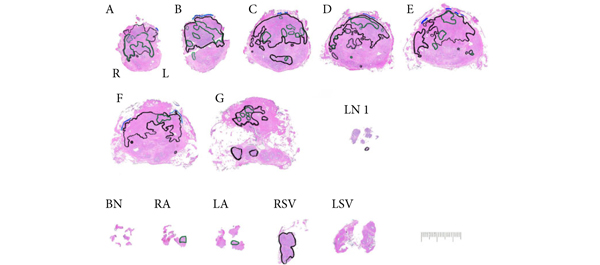
• Cancer was unilateral in 120 (61%) biopsies, with contralateral or bilateral prostate cancer at SRP in 49%. In the SRP specimen, cancer was multifocal in 57%.
• Cancer was upgraded at SRP in 58% of men, with 20% having an increase in primary Gleason grade.
• The accuracy of PRB varied by region from 62% to 76%, with undetected cancers ranging from 12% to 26% and most likely to occur at the mid-gland.
CONCLUSIONS
• Radiation-recurrent prostate cancers were often multifocal, and biopsy missed up to 20% of tumours.
• More than half of the cancers were upgraded at SRP, and many that were unilateral on PRB were bilateral at SRP.
Read Previous Articles of the Week