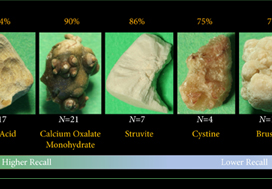
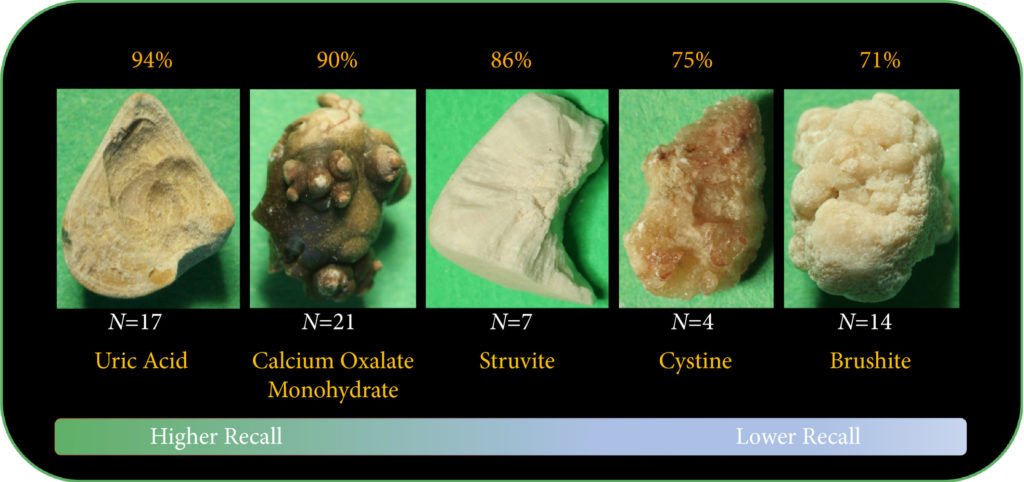
Article of the week: Single-port robot assisted radical prostatectomy (SP-RARP): a systematic review and pooled analysis of the preliminary experiences
This is the final Article of the Week selected by the outgoing Editor-in-Chief from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
If you only have time to read one article this week, we recommend this one.
Single‐port robot‐assisted radical prostatectomy: a systematic review and pooled analysis of the preliminary experiences
Enrico Checcucci*, Sabrina De Cillis*, Angela Pecoraro*, Dario Peretti*, Gabriele Volpi*, Daniele Amparore*, Federico Piramide*, Alberto Piana*, Matteo Manfredi*, Cristian Fiori*, Riccardo Autorino†, Prokar Dasgupta‡, Francesco Porpiglia* and on behalf of the Uro-technology and SoMe Working Group of the Young Academic Urologists Working Party of the European Association of Urology
*Department of Urology, San Luigi Gonzaga Hospital, University of Turin, Turin, Italy, †Division of Urology, VCU Health, Richmond, VA, USA, and ‡King’s College London, Guy’s Hospital, London, UK
Abstract
Objective
To summarize the clinical experiences with single‐port (SP) robot‐assisted radical prostatectomy (RARP) reported in the literature and to describe the peri‐operative and short‐term outcomes of this procedure.
Material and Methods
A systematic review of the literature was performed in December 2019 using Medline (via PubMed), Embase (via Ovid), Cochrane databases, Scopus and Web of Science (PROSPERO registry number 164129). All studies that reported intra‐ and peri‐operative data on SP‐RARP were included. Cadaveric series and perineal or partial prostatectomy series were excluded.

Results
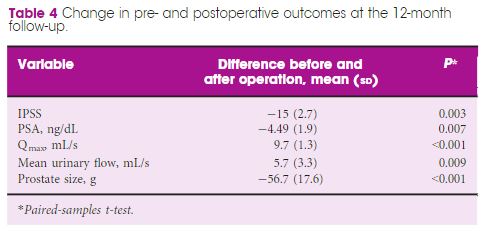
The pooled mean operating time, estimated blood loss, length of hospital stay and catheterization time were 190.55 min, 198.4 mL, 1.86 days and 8.21 days, respectively. The pooled mean number of lymph nodes removed was 8.33, and the pooled rate of positive surgical margins was 33%. The pooled minor complication rate was 15%. Only one urinary leakage and one major complication (transient ischaemic attack) were recorded. Regarding functional outcomes, pooled continence and potency rates at 12 weeks were 55% and 42%, respectively.
Conclusions
The present analysis confirms that SP‐RARP is safe and feasible. This novel robotic platform resulted in similar intra‐operative and peri‐operative outcomes to those obtained with the standard multiport da Vinci system. The advantages of single incision can be translated into a preservation of the patient’s body image and self‐esteem and cosmesis, which have a great impact on a patient’s quality of life.