Article of the Month: PROMs in the ProtecT trial of PCa treatments
Every Month the Editor-in-Chief selects an Article of the Month from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
In addition to the article itself, there is an accompanying editorial written by a prominent member of the urological community. This blog is intended to provoke comment and discussion and we invite you to use the comment tools at the bottom of each post to join the conversation.
Finally, the third post under the Article of the Week heading on the homepage will consist of additional material or media. This week we feature a video discussing the paper.
If you only have time to read one article this week, it should be this one.
Patient-reported outcomes in the ProtecT randomized trial of clinically localized prostate cancer treatments: study design, and baseline urinary, bowel and sexual function and quality of life
Objectives
To present the baseline patient-reported outcome measures (PROMs) in the Prostate Testing for Cancer and Treatment (ProtecT) randomized trial comparing active monitoring, radical prostatectomy and external-beam conformal radiotherapy for localized prostate cancer and to compare results with other populations.
Materials and Methods
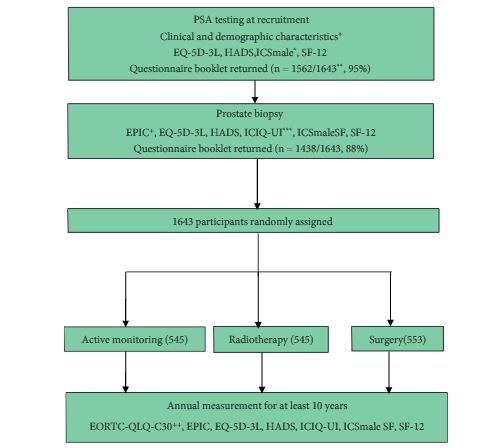
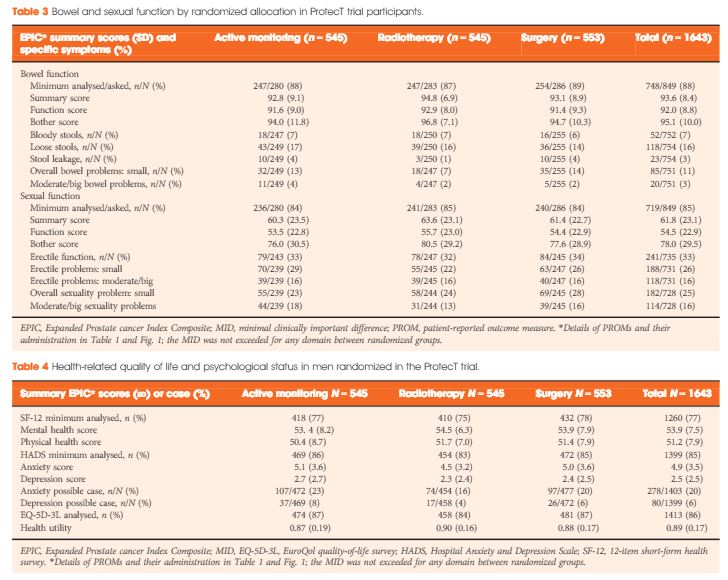
A total of 1643 randomized men, aged 50–69 years and diagnosed with clinically localized disease identified by prostate-specific antigen (PSA) testing, in nine UK cities in the period 1999–2009 were included. Validated PROMs for disease-specific (urinary, bowel and sexual function) and condition-specific impact on quality of life (Expanded Prostate Index Composite [EPIC], 2005 onwards; International Consultation on Incontinence Questionnaire-Urinary Incontinence [ICIQ-UI], 2001 onwards; the International Continence Society short-form male survey [ICSmaleSF]; anxiety and depression (Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale [HADS]), generic mental and physical health (12-item short-form health survey [SF-12]; EuroQol quality-of-life survey, the EQ-5D-3L) were assessed at prostate biopsy clinics before randomization. Descriptive statistics are presented by treatment allocation and by men’s age at biopsy and PSA testing time points for selected measures.
Results
A total of 1438 participants completed biopsy questionnaires (88%) and 77–88% of these were analysed for individual PROMs. Fewer than 1% of participants were using pads daily (5/754). Storage lower urinary tract symptoms were frequent (e.g. nocturia 22%, 312/1423). Bowel symptoms were rare, except for loose stools (16%, 118/754). One third of participants reported erectile dysfunction (241/735) and for 16% (118/731) this was a moderate or large problem. Depression was infrequent (80/1399, 6%) but 20% of participants (278/1403) reported anxiety. Sexual function and bother were markedly worse in older men (65–70 years), whilst urinary bother and physical health were somewhat worse than in younger men (49–54 years, all P < 0.001). Bowel health, urinary function and depression were unaltered by age, whilst mental health and anxiety were better in older men (P < 0.001). Only minor differences existed in mental or physical health, anxiety and depression between PSA testing and biopsy assessments.
Conclusion
The ProtecT trial baseline PROMs response rates were high. Symptom frequencies and generic quality of life were similar to those observed in populations screened for prostate cancer and control subjects without cancer.