Article of the week: 68Ga‐PSMA PET/CT predicts complete biochemical response from RP and lymph node dissection in intermediate‐ and high‐risk PCa
Every week, the Editor-in-Chief selects an Article of the Week from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
In addition to the article itself, there is an editorial written by a prominent member of the urological community. These are intended to provoke comment and discussion and we invite you to use the comment tools at the bottom of each post to join the conversation.
If you only have time to read one article this month, it should be this one.
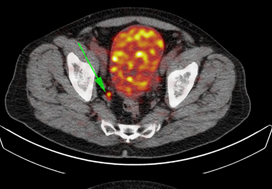
Gallium‐68‐prostate‐specific membrane antigen (68Ga‐PSMA) positron emission tomography (PET)/computed tomography (CT) predicts complete biochemical response from radical prostatectomy and lymph node dissection in intermediate‐ and high‐risk prostate cancer
Abstract
Objective
To determine the value of gallium‐68‐prostate‐specific membrane antigen (68Ga‐PSMA)‐11 positron emission tomography (PET) /computed tomography (CT) in men with newly diagnosed prostate cancer.
Patients and methods
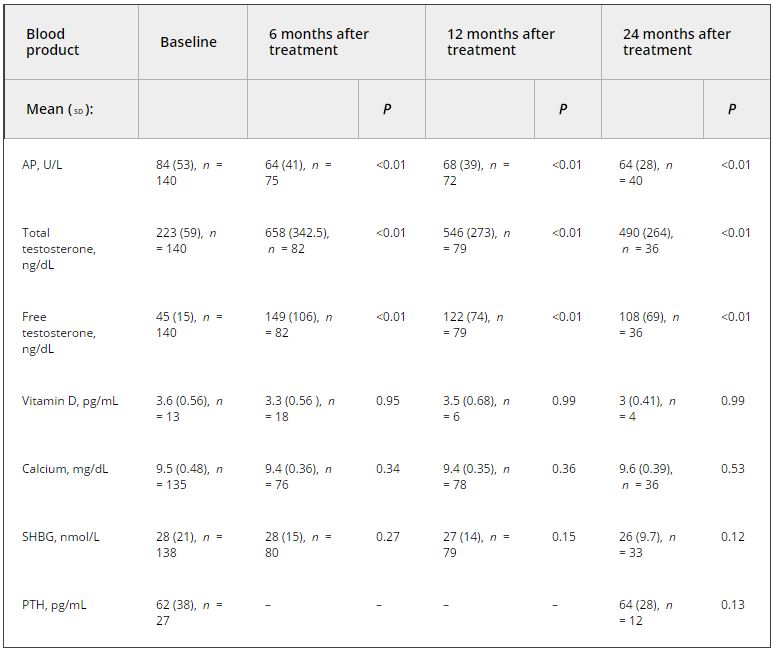
We analysed results of 140 men with intermediate‐ and high‐risk prostate cancer. All men underwent 68Ga‐PSMA‐11 PET/CT and multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging (mpMRI) before radical prostatectomy (RP) with extended pelvic lymph node (LN) dissection. For each patient, the clinical and pathological features were recorded. Prostate‐specific antigen (PSA) was documented at staging scan, and after RP, at a median (interquartile range) of 110 (49–132) days. A PSA level of ≥0.03 ng/mL was classified as biochemical persistence (BCP). Logistic regression was performed for association of clinical variables and BCP.
Results
In these 140 patients with intermediate‐ and high‐risk prostate cancer, 27.1% had PSMA PET/CT‐positive findings in the pelvic LNs. Sensitivity and specificity for detection of LN metastases were 53% and 88% (PSMA PET/CT) and 14% and 99% (mpMRI), respectively. The overall BCP rate was 25.7%. The BCP rate was 16.7% in men who were PSMA PET/CT LN‐negative compared to 50% in men who were PSMA PET/CT LN‐positive (P < 0.05). The presence of PSMA‐positive pelvic LNs was more predictive of BCP after RP than cT‐stage, PSA level, and the Gleason score, adjusted for surgical margins status.
Conclusions
68Ga‐PSMA‐11 PET/CT is highly predictive of BCP after RP, and should play an important role informing men with intermediate‐ or high‐risk prostate cancer.