
Editorial: Do all patients with renal cell carcinoma need a chest computed tomography?
While all patients with RCC need chest imaging for staging evaluation, the answer to the question in the title is ‘No’, and, in fact, many patients would be adequately staged with a chest X-ray, albeit with reduced accuracy. Evidence to support this assertion is provided by Larcher et al. [1] in this issue of BJUI, who retrospectively evaluated 1946 patients with a solitary and sporadic RCC mass. While excluding patients who did not have surgery and those with visceral metastases seen…
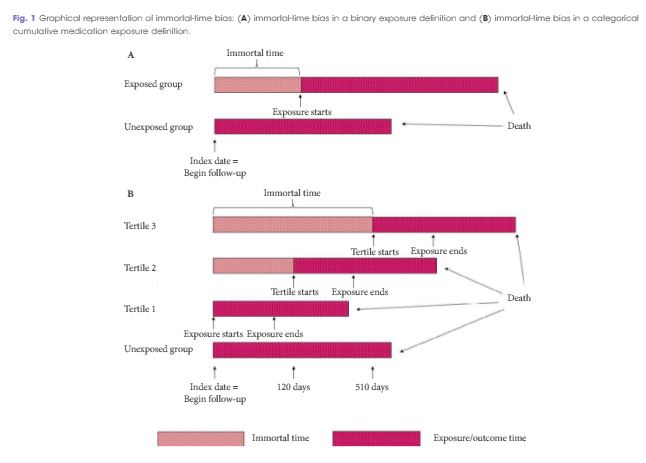
Article of the Month: Immortal-Time Bias in Urological Research
Every Month the Editor-in-Chief selects an Article of the Month from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
In addition to the article itself, there is an accompanying editorial written by a prominent member of the urological community. This blog is intended to provoke comment and discussion and we invite you to use the comment…

Editorial: Immortal-Time Bias – A Crucial Yet Overlooked Confounder in Urological Research
The measurement of treatment effect through observational studies has become commonplace in the medical literature. These cohort studies provide valuable data on outcomes that can be difficult to assess in randomized controlled trials, such as long-term mortality. Accurate interpretation of observational data, however, requires accounting for potential confounders of study design, including the immortal-time bias. In this issue of BJUI, Wallis et al. [1] show how accounting for this bias…

Video: Immortal-Time Bias in Urological Research
Estimating the effect of immortal-time bias in urological research: a case example of testosterone-replacement therapy
Abstract
Objective
To quantify the effect of immortal-time bias in an observational study examining the effect of cumulative testosterone exposure on mortality.
Patients and Methods
We used a population-based matched cohort study of men aged ≥66 years, newly treated with testosterone-replacement therapy (TRT), and matched-controls from…
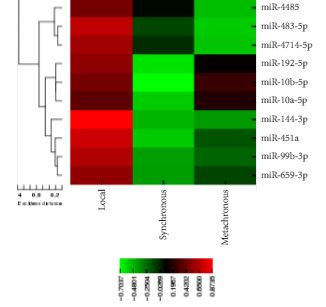
Article of the Week: Profiling microRNA from nephrectomy and biopsy specimens
Every Week the Editor-in-Chief selects an Article of the Week from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
In addition to the article itself, there is an accompanying editorial written by a prominent member of the urological community. This blog is intended to provoke comment and discussion and we invite you to use the comment…

Editorial: The utility of microRNAs as biomarkers in predicting progression and survival in patients with clear-cell renal cell carcinoma
RCC constitutes a diverse group of malignancies, yet the clear-cell subtype comprises ~80% of all diagnosed RCC cases [1]. The widespread use of abdominal imaging and subsequent stage migration has resulted in improved RCC 5-year cancer-specific survival. However, the overall mortality of RCC remains largely unchanged [2] and one-third of the patients have metastatic disease at the time of presentation [3]. Accordingly, the ability to precisely predict patient outcome has become an increasingly…
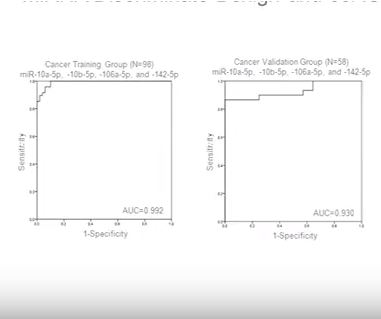
Video: Profiling microRNA from nephrectomy and biopsy specimens
Profiling microRNA from nephrectomy and biopsy specimens: predictors of progression and survival in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
Objective
To identify microRNA (miRNA) characteristic of metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) and those indicative of cancer-specific survival (CSS) in nephrectomy and biopsy specimens. We also sought to determine if a miRNA panel could differentiate benign from ccRCC tissue.
Materials and Methods
RNA…
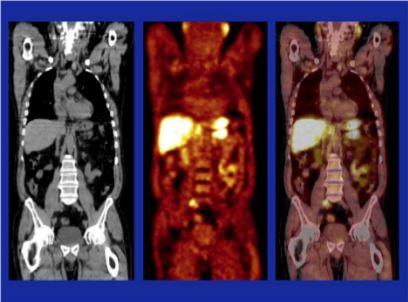
Article of the Week: 11C-acetate PET/CT imaging for detection of recurrent disease after RP or RT in patients with PCa
Every Week the Editor-in-Chief selects an Article of the Week from the current issue of BJUI. The abstract is reproduced below and you can click on the button to read the full article, which is freely available to all readers for at least 30 days from the time of this post.
In addition to the article itself, there is an accompanying editorial written by a prominent member of the urological community. This blog is intended to provoke comment and discussion and we invite you to use the comment…

Editorial: Is choline-based PET imaging still relevant in recurrent prostate cancer?
The search for the ideal imaging method to detect small metastatic deposits has largely remained elusive in the field of prostate cancer. However, functional positron emission tomography (PET)/CT is now guiding us in different directions. 11C-acetate PET/CT imaging was one of the first molecular imaging probes showing promise in clinical studies, along with 11C-choline, and more recently challenged by 68Ga-prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) PET/CT [1-3]. So against this background,…

Residents’ Podcast: sRPLND+PLND for ‘node-only’ recurrent PCa
1 Comment
/
Jesse Ory, Kyle Lehmann and Jeff Himmelman
Department of Urology, Dalhousie University
Halifax, NS, Canada
Abstract
Objectives
To describe the technique of robot-assisted high-extended salvage retroperitoneal and pelvic lymphadenectomy (sRPLND+PLND) for ‘node-only’ recurrent prostate cancer.
Patients and Methods
In all, 10 patients underwent robot-assisted sRPLND+PLND (09/2015–03/2016) for ‘node-only’ recurrent prostate cancer, as identified by 11C-acetate…
