Video: Be Clear on Cancer – Blood in Pee
Assessing the impact of mass media public health campaigns. ‘Be Clear on Cancer: Blood in Pee’ a case in point
Objectives
To assess the impact on suspected cancer referral burden and new cancer diagnosis of Public Health England’s recent Be Clear on Cancer ‘blood in pee’ mass media campaign.
Methods
A retrospective cohort study design was used. For two distinct time periods, August 2012 to May 2013 and August 2013 to May 2014, all referrals of patients deemed to be at risk of urological cancer by the referring primary healthcare physician to Imperial College NHS Healthcare Trust were screened. Data were collected on age and sex and whether the referral was for visible haematuria, non-visible haematuria or other suspected urological cancer. In addition to referral data, hospital episode data for all new renal cell (RCC) and upper and lower tract transitional cell carcinoma (TCC), as well as testicular and prostate cancer diagnoses for the same time periods were obtained.
Results
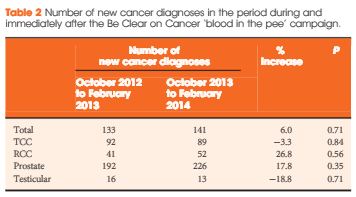
Over the campaign period and the subsequent 3 months, the number of haematuria referrals increased by 92% (P = 0.013) when compared with the same period a year earlier. This increase in referrals was not associated with a significant corresponding rise in cancer diagnosis; instead changes of 26.8% (P = 0.56) and −3.3% (P = 0.84) were seen in RCC and TCC, respectively.
Conclusions
This study has shown that the Be Clear on Cancer ‘blood in pee’ mass media campaign significantly increased the number of new suspected cancer referrals, but there was no significant change in the diagnosis of target cancers across a large catchment. Mass media campaigns are expensive, require significant planning and appropriate implementation and, while the findings of this study do not challenge their fundamental objective, more work needs to be done to understand why no significant change in target cancers was observed. Further consideration should also be given to the increased referral burden that results from these campaigns, such that pre-emptive strategies, including educational and process mapping, across primary and secondary care can be implemented.