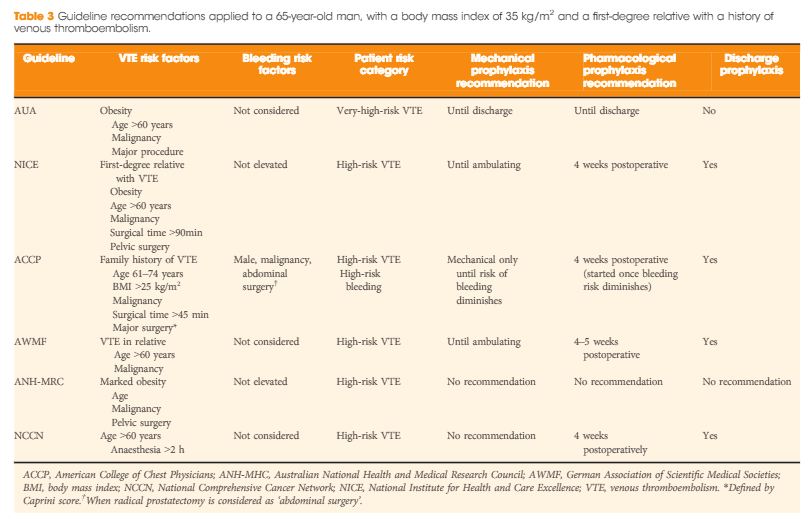
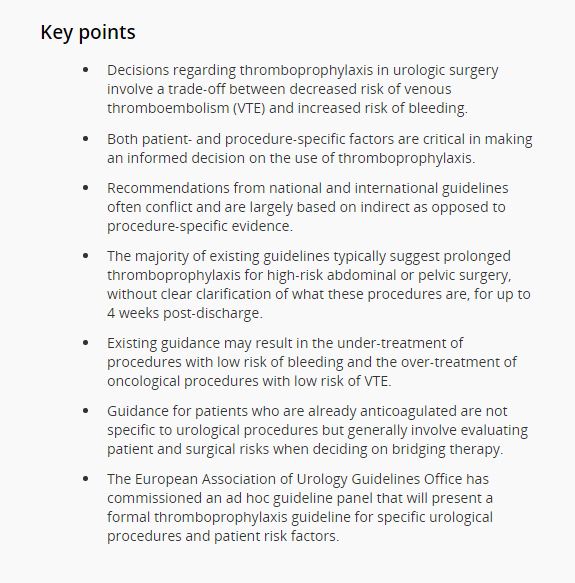
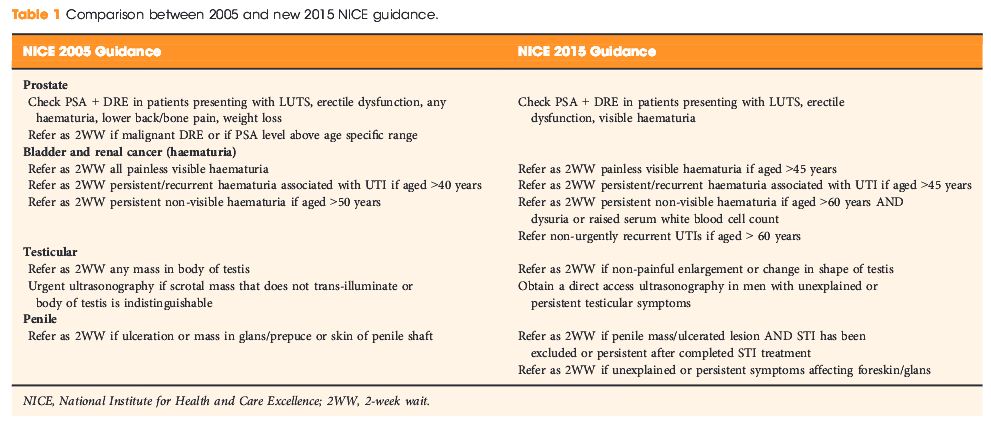
Editorial: Celebrating BAUS and NICE Guidance
On behalf of the BAUS Council, I am delighted to write this editorial looking forward to the 73rd annual meeting of the BAUS, which will be held in Glasgow from 26 to 28 June. In response to feedback we had from delegates following BAUS 2016 and the successful European Association of Urology meeting in London this March, we have changed the format and duration of the meeting, ensuring that it has a distinct feel, reflecting the best of British Urology.
With Brexit looming and the precarious state of NHS finances, the continuing challenge for all of us working in the NHS is to deliver high-quality care within available resources, while embracing the latest evidence informing clinical practice. This month’s BJUI sees the first publication of National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) guidance on urological topics – ‘MTG29 GreenLight XPS for treating benign prostatic hyperplasia’ [1]. NICE has a fantastic track record in publishing highly regarded evidence-based syntheses across the breath of medicine and this guidance will stimulate the development and adoption of Greenlight laser for treating BPH as a day case procedure in the UK.
Assessing and critiquing new evidence are key elements of the annual BAUS meeting and this year is no exception. In all, 535 abstracts were submitted of which 157 will be presented. Whilst much of our clinical practice is of a high quality, analysis of the work done by the ‘Getting it right first time’ (GIRFT) team has shown a wide variation in practice for many common conditions in Urology. Simon Harrison, who leads the GIRFT team, will be giving an update on the progress of the work in a session looking at how standards can be applied in the real world at a session on Tuesday 27 June, entitled ‘Urology standards and the real world’.
On Monday 26 June, Academic Urology, Andrology and Genito-Urethral Surgery (AGUS), and Female, Neurological and Urodynamic Urology (FNUU) will be holding their annual meetings. State of the art lectures include Professor Trinity Bivalacqua speaking on ‘Molecular genetics and the prospect for future treatment strategies in Urology’. The AGUS section will focus on the genital emergencies consultation and the future of andrology in the UK, shedding light on specialist commissioning and training in the speciality. Highlights of the FNUU section meeting will include an update on meshes and tapes and the medicolegal consequences of adverse outcomes.
British urology has played a pivotal role in our understanding of the diagnosis and management of prostate cancer. Reflecting this, a point-counterpoint debate will take place on Tuesday 27 June, with Caroline Moore and Paul Cathcart debating the necessity for prostate biopsy in patients with Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System (PI-RADS) 1and 2 lesions seen on MRI, drawing on evidence from the recent PROstate MRI Imaging Study (PROMIS) trial. On Wednesday 28, Noel Clarke will report on the latest news from the Systemic Therapy in Advancing or Metastatic Prostate Cancer: Evaluation of Drug Efficacy (STAMPEDE) study, which to date has recruited >9000 patients. New evidence from the study is likely to herald a change in the care of our patients with metastatic prostate cancer.
In addition to state of the art papers, we are delighted to have a number of key opinion leaders attending the meeting. Reflecting the public’s high expectations and pressures on clinicians, Professor David Speigelhalter, Winton Professor for the Public Understanding of Risk at the University of Cambridge, will speak on the nature of risk and uncertainty in clinical practice. The BJUI Guest lecture will be delivered by David Prior (Parliamentary Under Secretary of State in the House of Lords). With the recent publication of The Long-term Sustainability of the NHS and Adult Social Care report [2], he is uniquely placed to give a perspective on the future direction of the NHS.
For the first time at our meeting there will be a session entitled ‘When things go wrong’. This session will focus on the impact of adverse events and burnout on Urologists, which promises to be insightful and thought provoking. With plenty of science, innovations in urological care and some politics, BAUS 2107 promises to be a fascinating meeting. I look forward to seeing you there.
How to Cite
O’Flynn, K. (2017), Celebrating BAUS and NICE Guidance. BJU International, 119: 815. doi: 10.1111/bju.13899
References